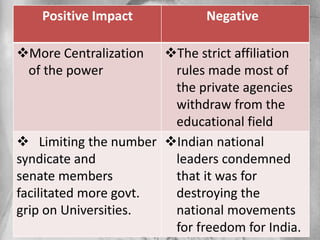
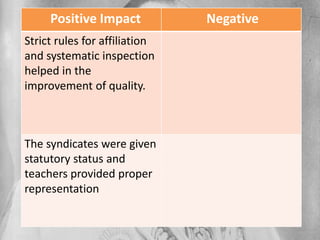
The Indian University Commission was appointed in 1902 by Lord Curzon to investigate and make recommendations about the future of universities in India. The commission recommended establishing new universities and reorganizing existing ones. It suggested reforms to university governance structures, affiliations with colleges, curriculum, examinations, facilities, and scholarships. As a result, the Indian University Act of 1904 was passed, which centralized some university administration but was also criticized for increasing government control over institutions of higher education.