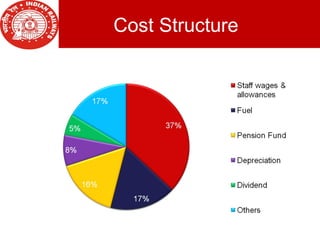
Indian Railways was introduced in 1853 and nationalized in 1951, becoming one of the largest rail networks in the world. It transports over 9 billion passengers annually across 27 states and 3 union territories. In addition to passenger services, Indian Railways provides freight transport and operates metro rail systems in major cities. While it faces weaknesses like outdated infrastructure and delays, opportunities exist to expand services through privatization and technological advancements. Indian Railways remains an important mode of transportation in India due to its affordability and connectivity.