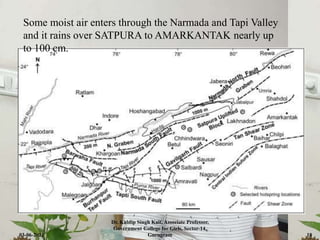
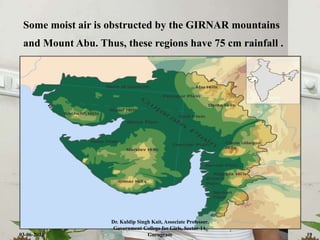
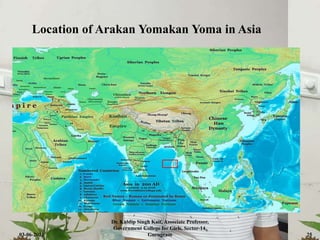
The document discusses the Indian monsoon system, defining monsoon as a seasonal reversal of winds influenced by thermodynamic modifications in trade winds. It highlights two primary types of monsoons in India: the south-west monsoon and the north-east monsoon, detailing their origins, characteristics, and impact on rainfall distribution across the region. The text emphasizes the importance of monsoon rainfall for India's agriculture.