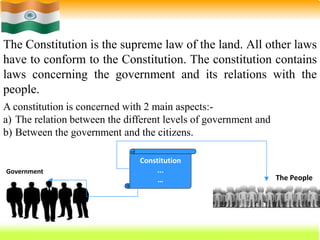
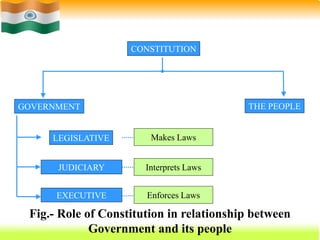
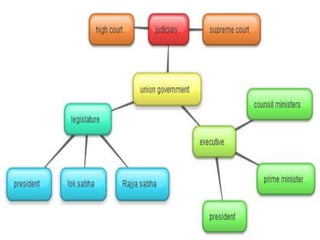
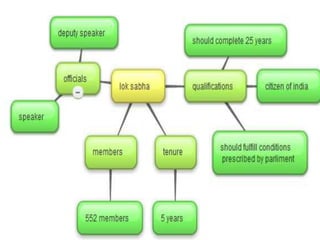
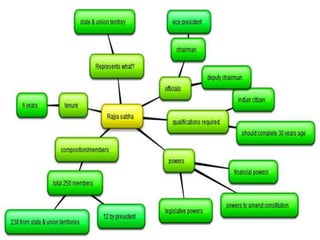
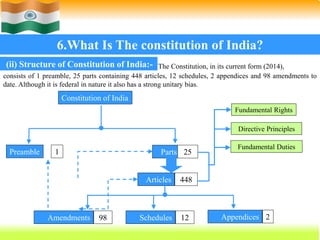
The Constitution of India, adopted on November 26, 1949, and effective January 26, 1950, is the supreme law that outlines the framework for governance, fundamental rights, and duties of citizens. It is the world's longest written constitution, consisting of 448 articles, and establishes the structure and functions of the government while ensuring the protection of various rights, particularly for minorities. Historical developments leading to its formation include the edicts of Ashoka, the British colonial period, and various legislative acts that shaped India's constitutional evolution.