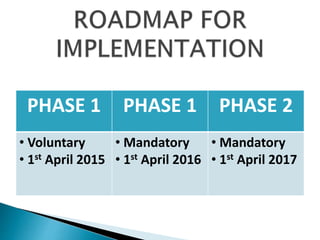
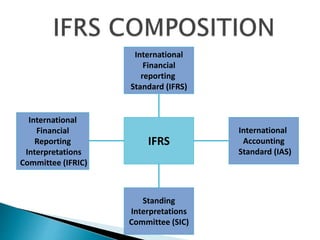
The document outlines Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) and their phased implementation timetable, with Phase 1 beginning April 1, 2015, for voluntary adoption and mandatory compliance following in 2016 and 2017 for certain companies. It highlights the benefits of adopting Ind AS, including improved transparency, reduced diversity in accounting practices, and a framework aligned with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). The standards apply to various companies, emphasizing that management and users must understand their implications for financial reporting.