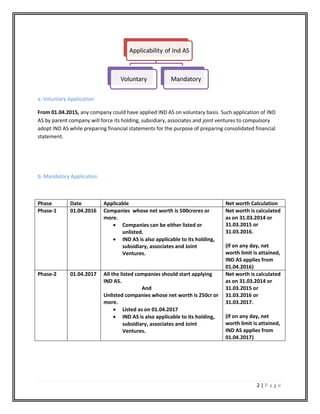
The document outlines the transition from Indian GAAP to Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS), emphasizing its adoption to enhance financial reporting and comparability with international standards. Ind AS was notified by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) in 2015 and applies in phases, with key deadlines set for companies based on net worth. Additionally, specific provisions for banking, non-banking financial institutions, and insurance companies highlight the timeline for mandatory compliance while noting that existing accounting standards remain in effect for other companies.