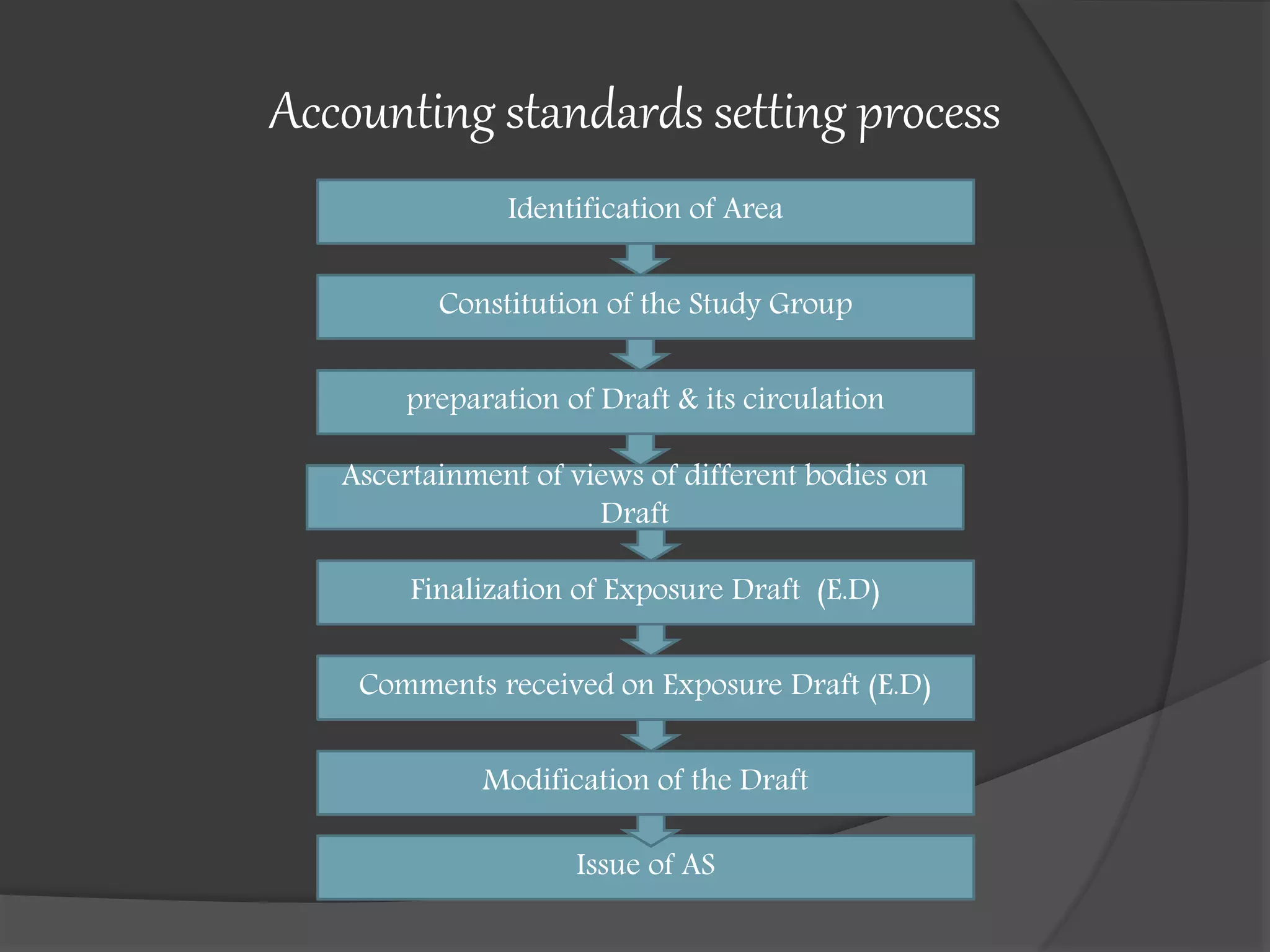
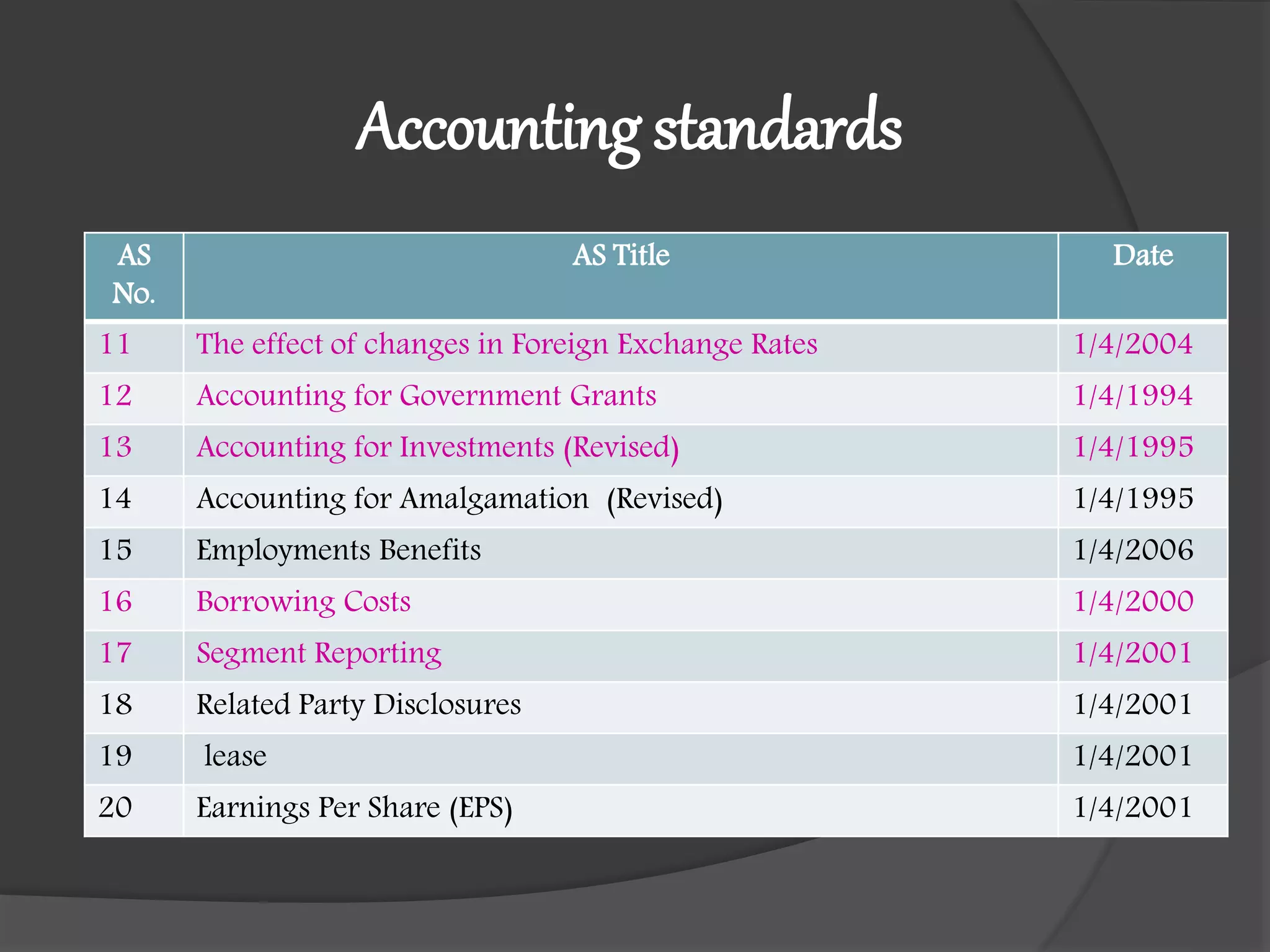
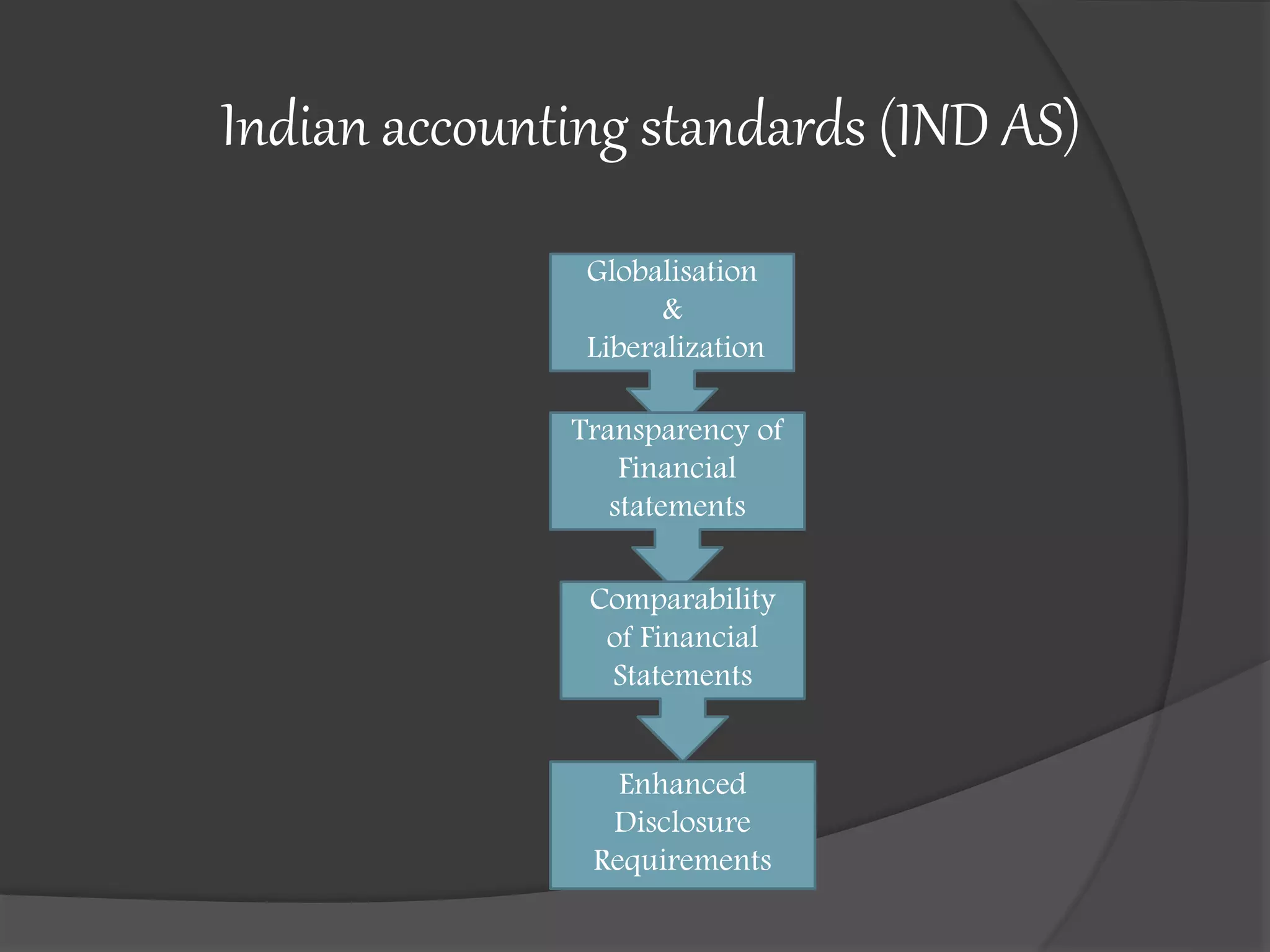
This document outlines the syllabus for an accounting course covering Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS). The syllabus is divided into 3 modules. Module 1 covers an introduction to accounting standards, frameworks for financial statements, and an overview of accounting standards. It provides details on regulatory bodies that issue standards in India and benefits of standards. Module 2 covers various topics related to financial statements of companies. Module 3 covers additional accounting topics including investments, insurance claims, departmental accounts, and partnership accounts. The document also provides details on the convergence of Indian standards with IFRS and differences between the two frameworks.