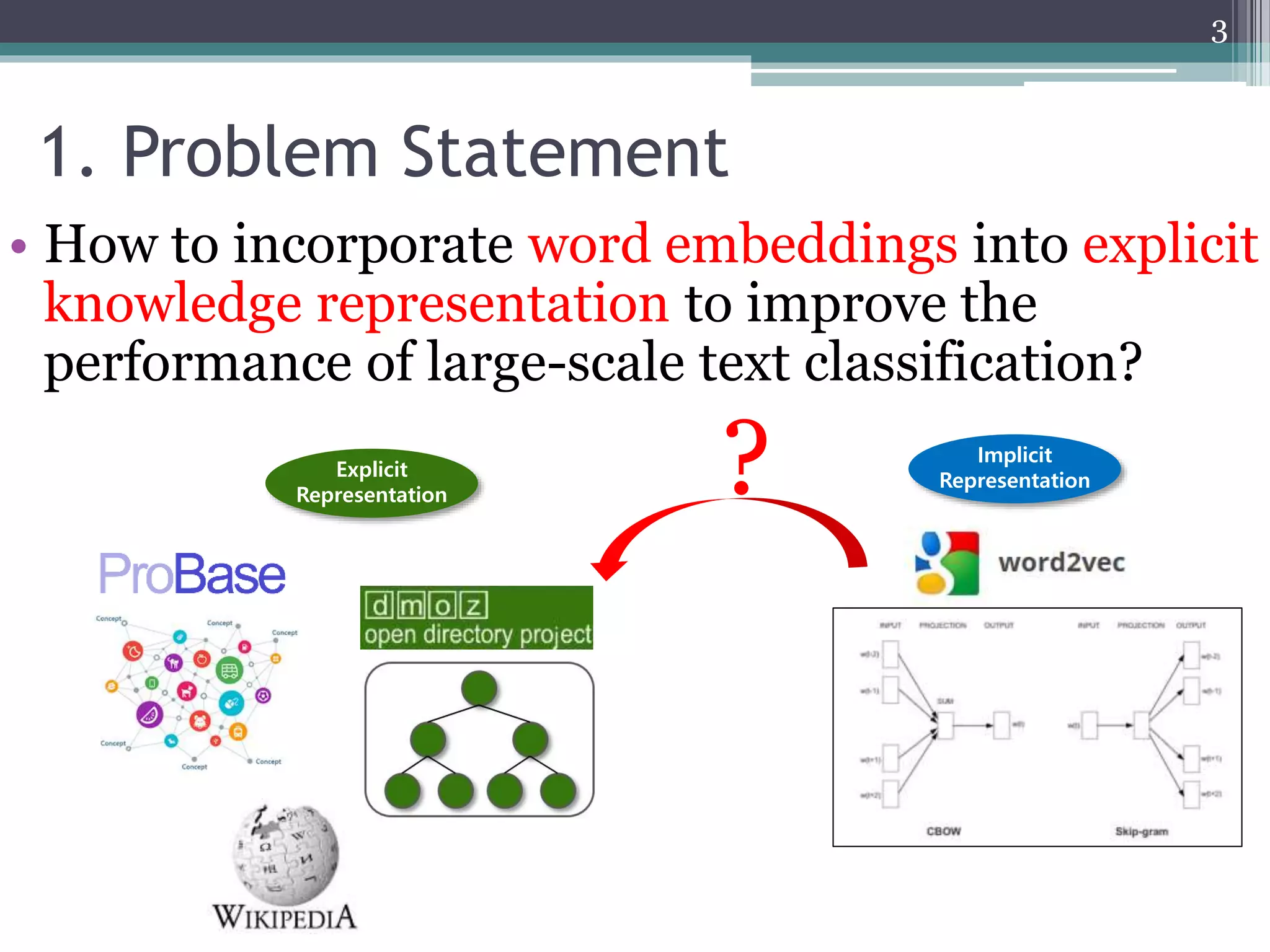
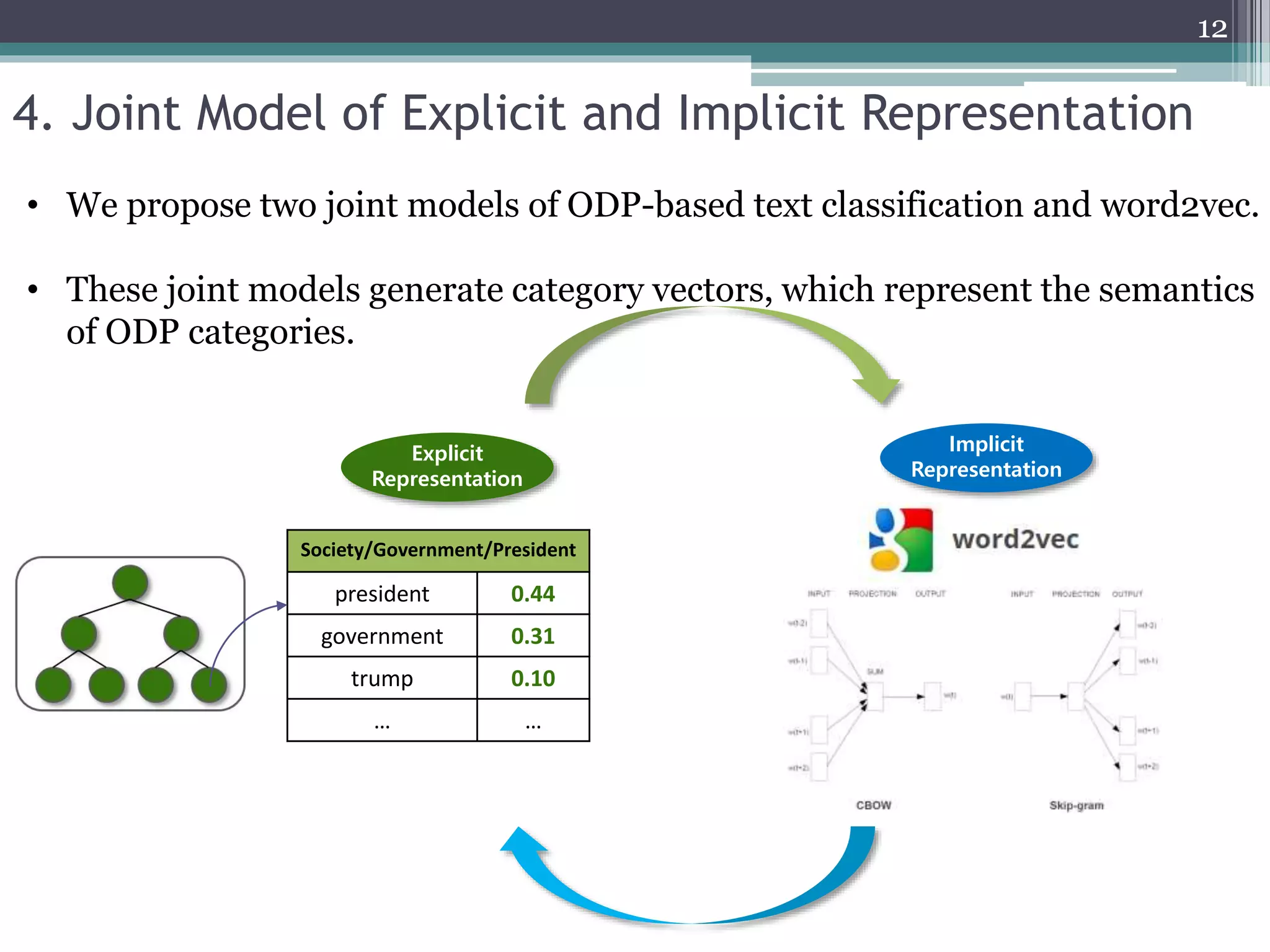
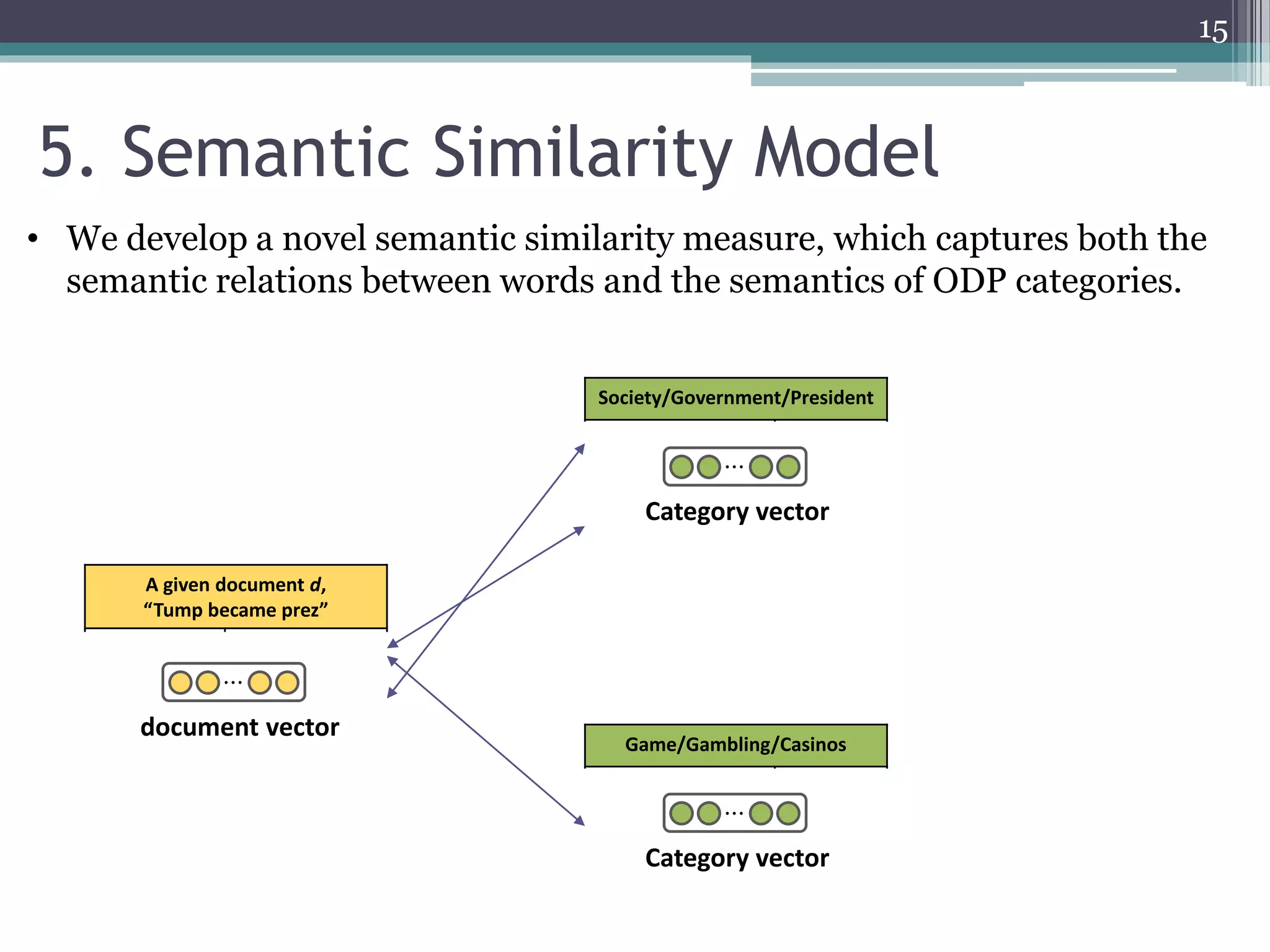
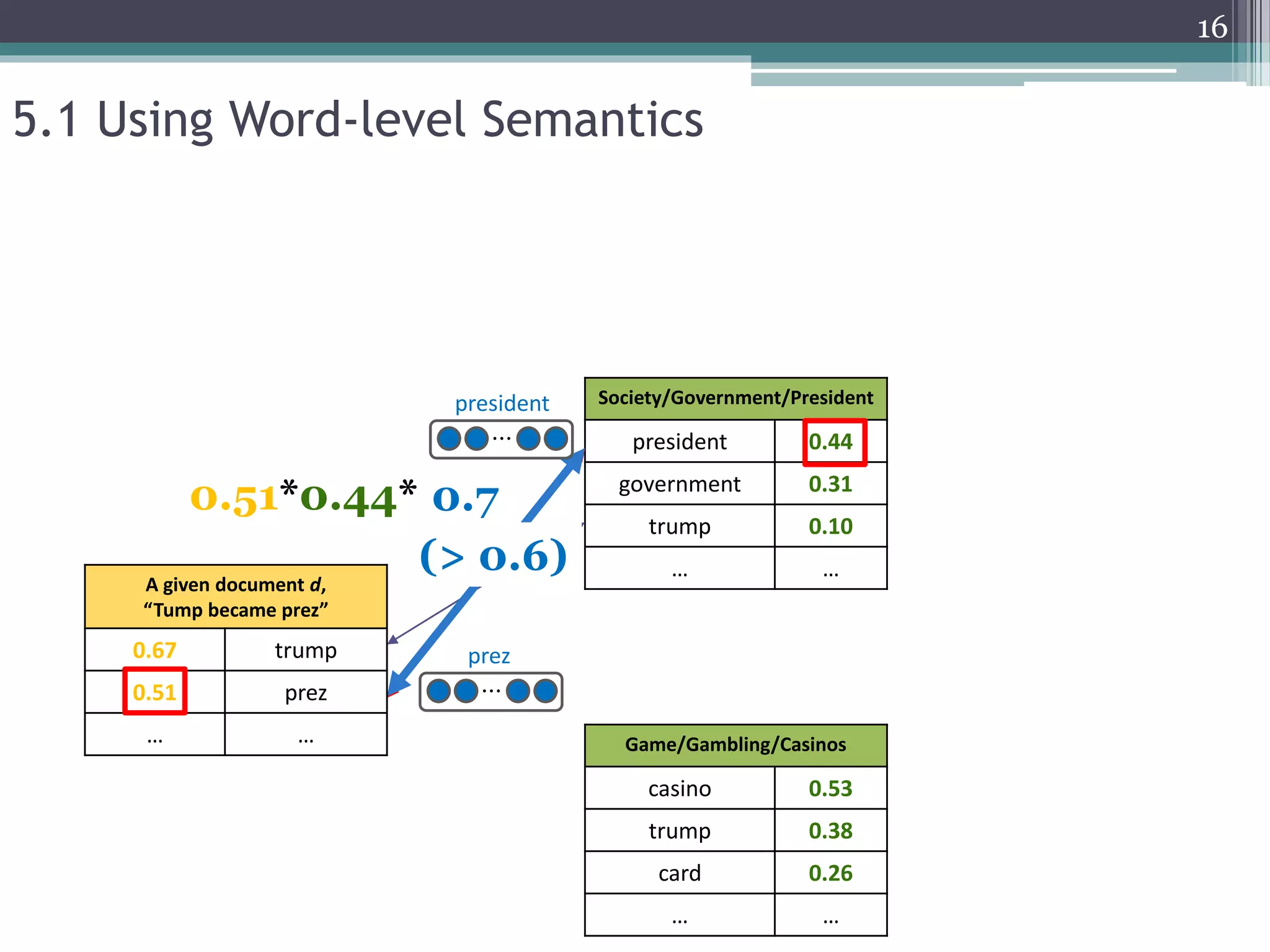
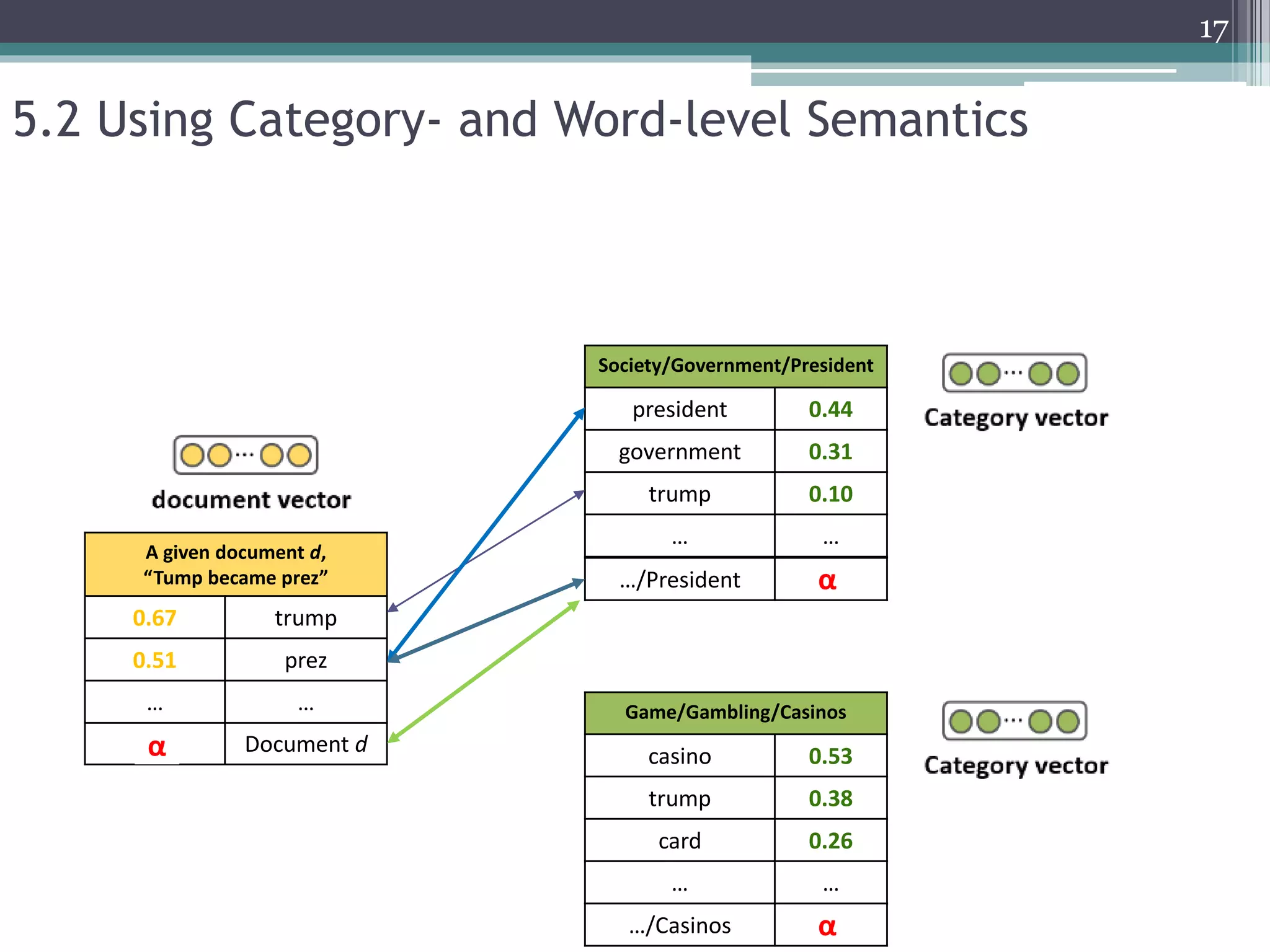
1. The document proposes two novel joint models that incorporate word embeddings into an Open Directory Project (ODP)-based classification framework to improve large-scale text classification.
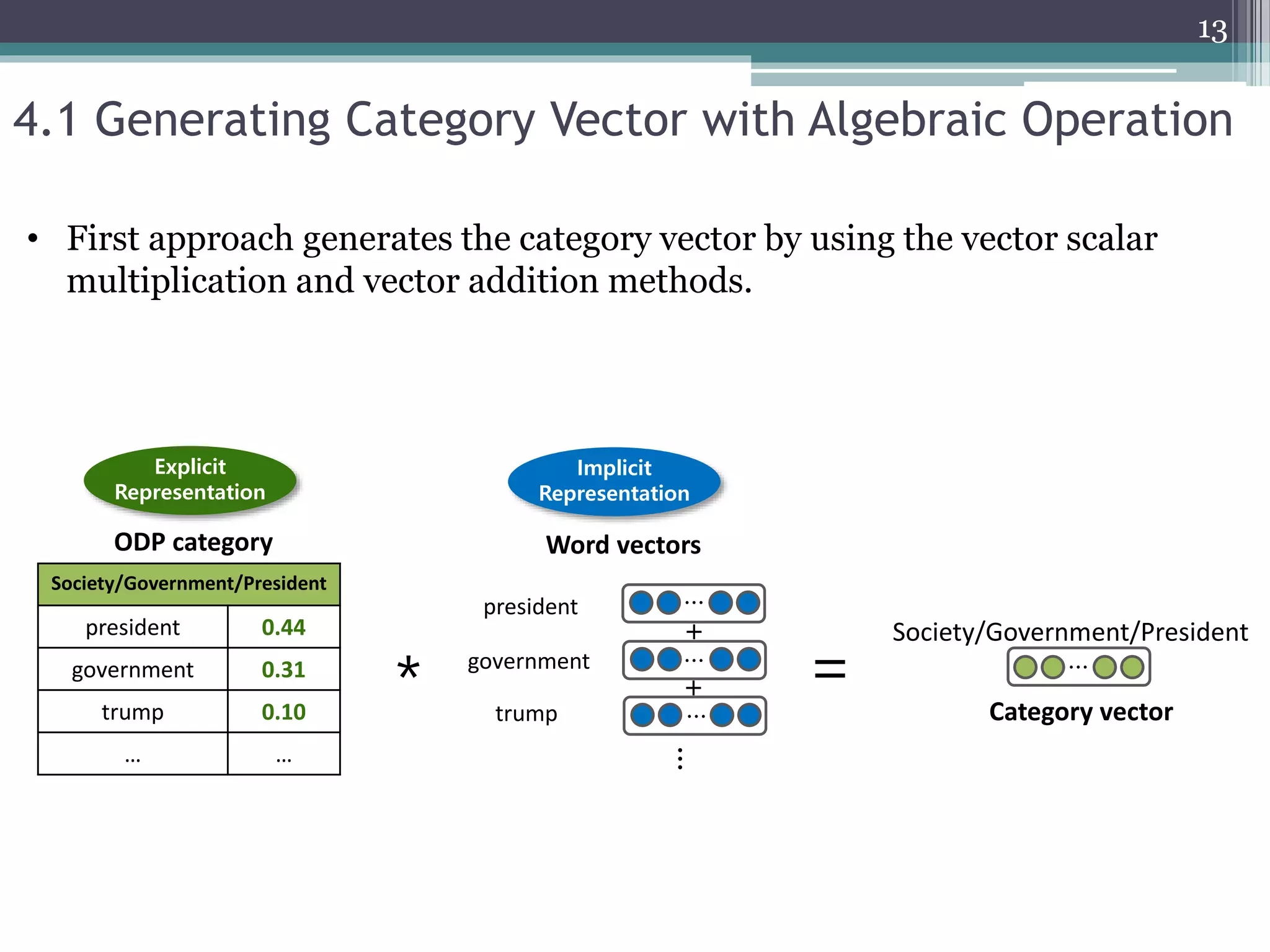
2. The models generate category vectors that represent the semantics of ODP categories using both the explicit ODP taxonomy and implicit word2vec representations.
3. Experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the models outperform state-of-the-art baselines, validating the efficacy of jointly leveraging explicit and implicit representations for large-scale text classification.



![• Text classification using NN [1][2]
Requires a lot of training data per class
Limited to small-
or moderate-scale
* Previous Works
[1] Kim, Y. , “Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification”, EMNLP 2014, 1746-1751.
[2] Le, Q.V., Mikolov, T., “Distributed representation of sentences and documents”, ICML 2014, 1188-1196
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pakdd2018kim20180605-200917224244/75/Incorporating-Word-Embeddings-into-Open-Directory-Project-Based-Large-Scale-Classification-5-2048.jpg)
![* Previous Works
• Text classification using knowledge base [1][2]
[1] Lee, J.H., Ha, J., Jung, J.Y., Lee, S. , “Semantic contextual advertising based on the open directory project”, ACM Trans. On the
Web 7(4) 2013, 24:1-24:22
[2] Shin, H., Lee, G., Rye, W.J., Lee, S., “Utilizing Wikipedia knowledge in open directory project based text classification”, SAC 2017,
309-314
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pakdd2018kim20180605-200917224244/75/Incorporating-Word-Embeddings-into-Open-Directory-Project-Based-Large-Scale-Classification-6-2048.jpg)

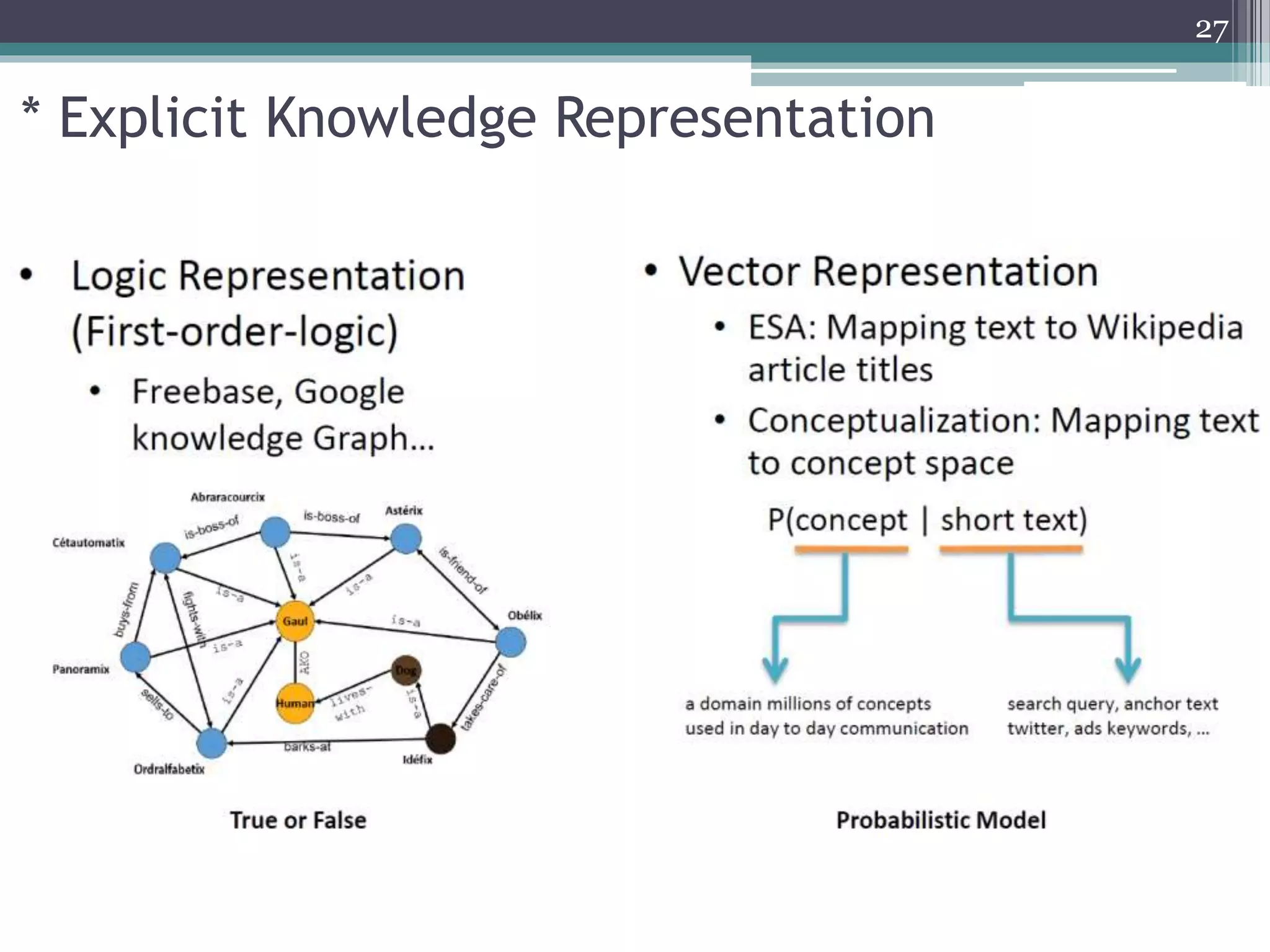
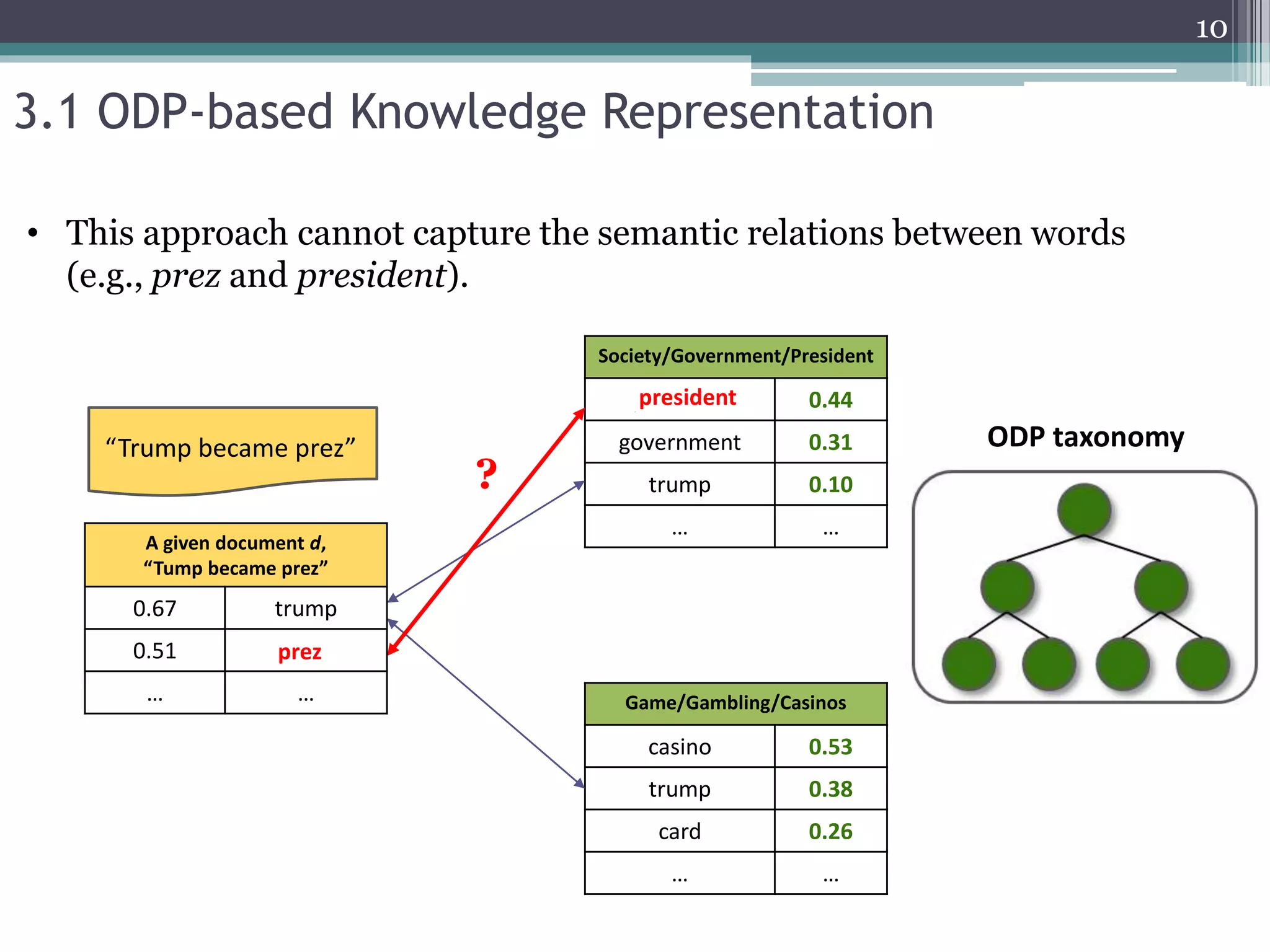
![3.1 ODP-based Knowledge Representation [1]
Top
Game Society
Online Gambling GovernmentCrime
.
.
.
.
.
.
List of government
officials and their title,
updated weekly…
ODP documents
…
3. Preliminary
Bag-of-words
word frequency
government 1
officials 1
updated 1
weekly 1
... ...
[1] Lee, J.H., Ha, J., Jung, J.Y., Lee, S. , “Semantic contextual advertising based on the open directory project”, ACM Trans. On the
Web 7(4) 2013, 24:1-24:22
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pakdd2018kim20180605-200917224244/75/Incorporating-Word-Embeddings-into-Open-Directory-Project-Based-Large-Scale-Classification-8-2048.jpg)
![Society/Government
government 0.47
election 0.29
… …
Averaged term vector
(TF-IDF scheme)
president 0.10
… …
3.1 ODP-based Knowledge Representation [1]
0.51
0.31
Top
Game Society
Online Gambling GovernmentCrime
.
.
.
.
.
.
…
9
[1] Lee, J.H., Ha, J., Jung, J.Y., Lee, S. , “Semantic contextual advertising based on the open directory project”, ACM Trans. On the
Web 7(4) 2013, 24:1-24:22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pakdd2018kim20180605-200917224244/75/Incorporating-Word-Embeddings-into-Open-Directory-Project-Based-Large-Scale-Classification-9-2048.jpg)
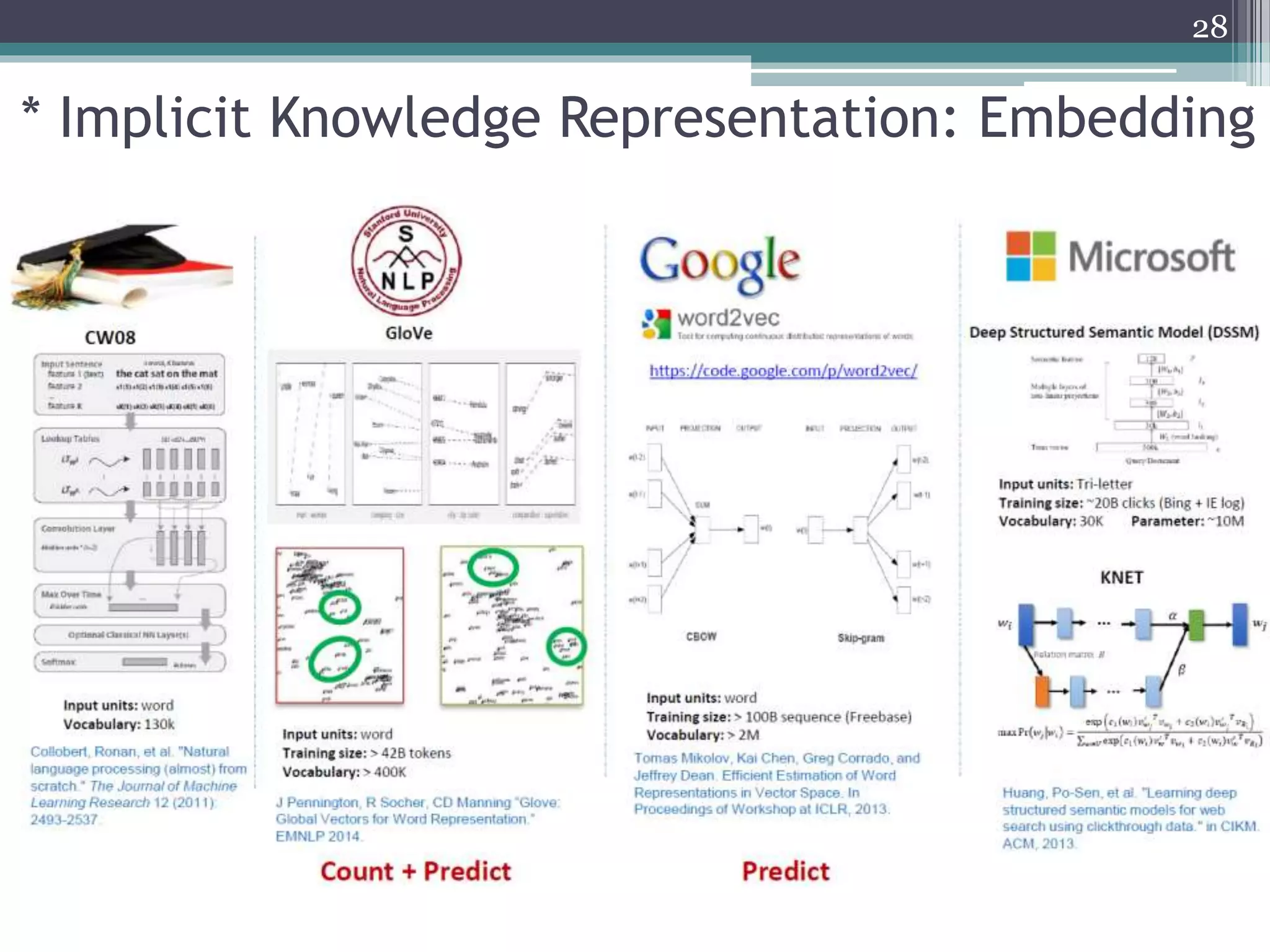
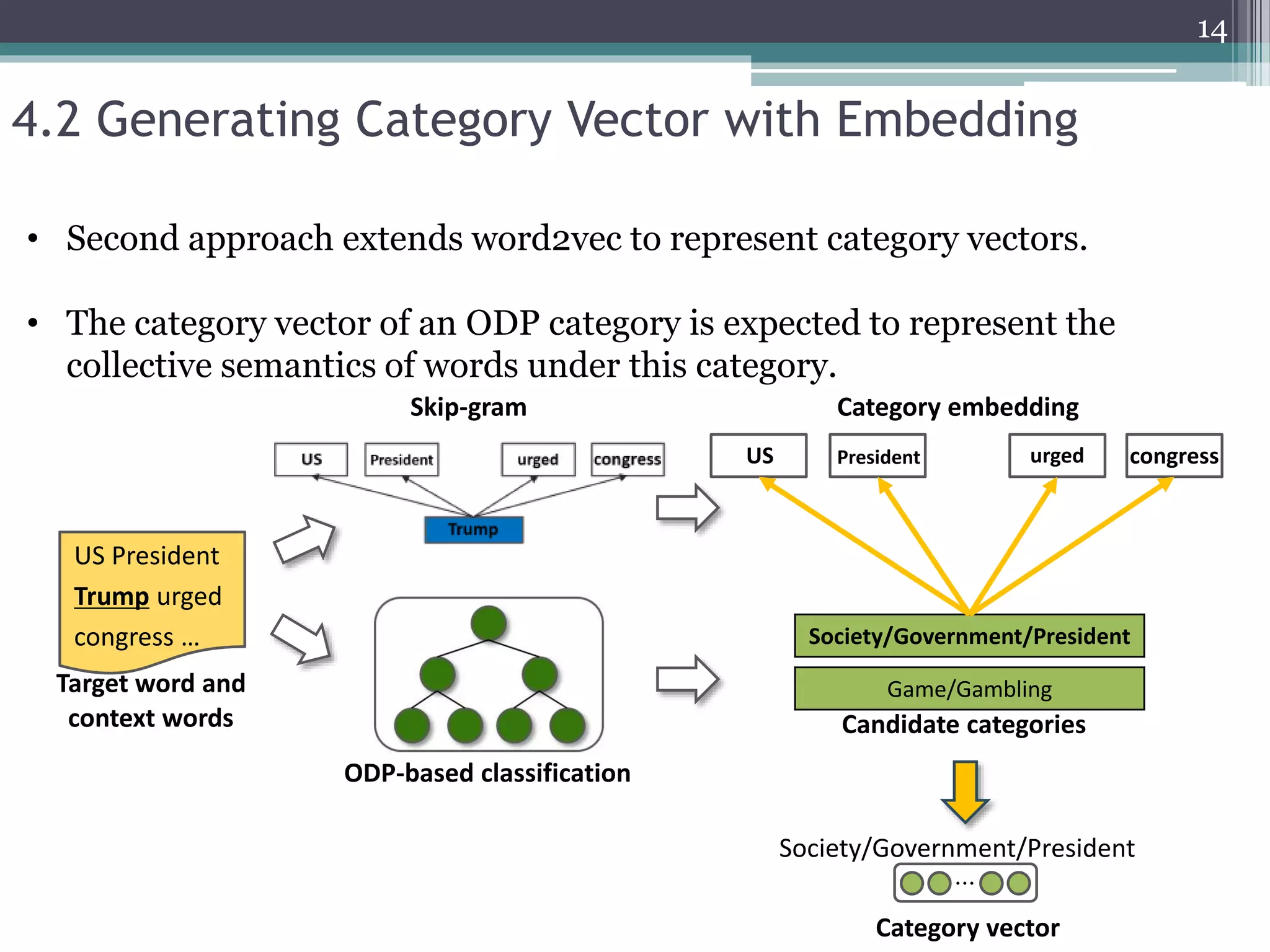
![• The word2vec projects words in a shallow layer structure and directly learns
the representation of words using context words.
• Trained word vectors with similar semantic meanings would be located at
high proximity within the vector space.
3.2 implicit representation model - Word2Vec[1][2]
prez
election
president
casino
gambling
[1] Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., Dean, J., “Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space”, ICLR (Workshop) 2013
[2] Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G., Dean, J., “Distributed representations of words and phrases and their
compositionality”, NIPS 2013, 3111-3119
11
“Additive compositionality”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pakdd2018kim20180605-200917224244/75/Incorporating-Word-Embeddings-into-Open-Directory-Project-Based-Large-Scale-Classification-11-2048.jpg)
![• Baselines
▫ 𝑂𝐷𝑃 [1]
▫ 𝑃𝑉 [2]
▫ 𝐶𝑁𝑁 [3]
• Proposed models
▫ 𝑂𝐷𝑃𝐶𝑉
▫ 𝑂𝐷𝑃 𝑊𝑉
▫ 𝑂𝐷𝑃𝐶𝑉+𝑊𝑉
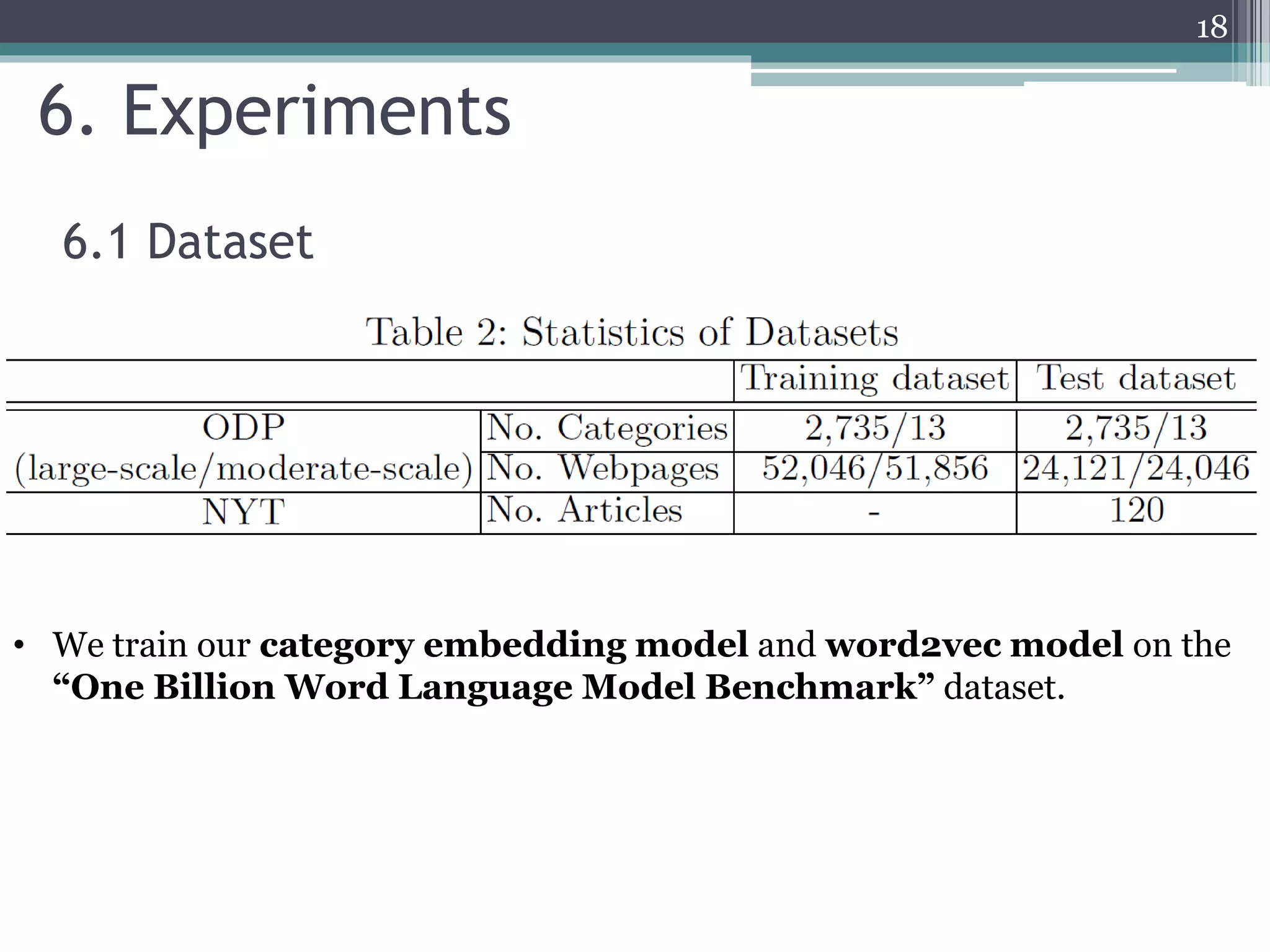
6.2 Experimental Setup
𝑂𝐷𝑃𝐶𝑉
𝑂𝐷𝑃 𝑊𝑉
𝑂𝐷𝑃𝐶𝑉+𝑊𝑉
19
[1] Lee, J.H., Ha, J., Jung, J.Y., Lee, S. , “Semantic contextual advertising based on the open directory project”, ACM Trans. On the
Web 7(4) 2013, 24:1-24:22
[2] Le, Q.V., Mikolov, T., “Distributed representation of sentences and documents”, ICML 2014, 1188-1196
[3] Kim, Y. , “Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification”, EMNLP 2014, 1746-1751
(category-level semantics)
(word-level semantics)
(category- and word-level semantics)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pakdd2018kim20180605-200917224244/75/Incorporating-Word-Embeddings-into-Open-Directory-Project-Based-Large-Scale-Classification-19-2048.jpg)
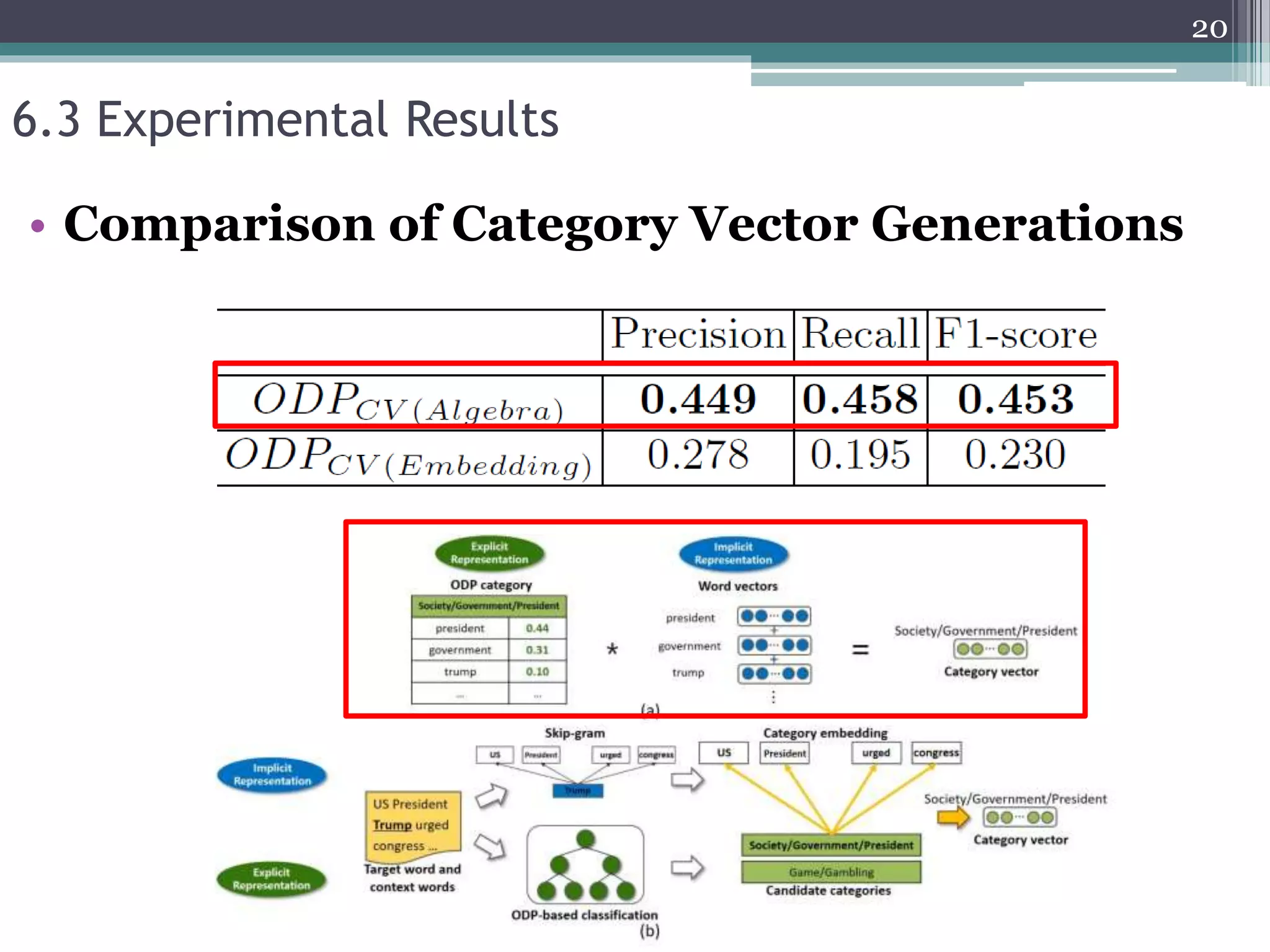
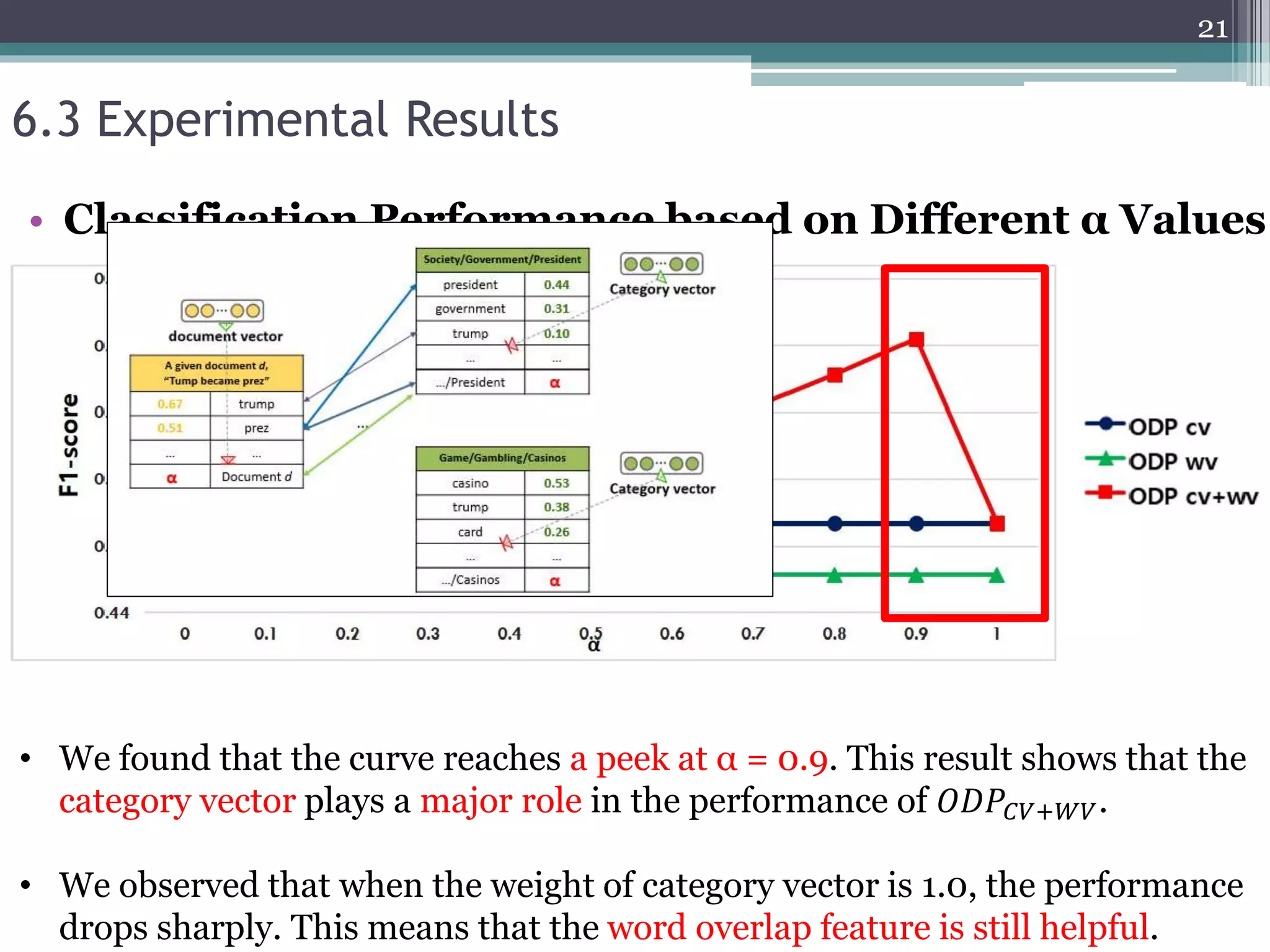
![6.3 Experimental Results
• 𝑂𝐷𝑃𝐶𝑉+𝑊𝑉 performs better than 𝑂𝐷𝑃 over 9%, 12%, and 10% on average in
terms of precision, recall, and F1-score, respectively.
• We observe that 𝐶𝑁𝑁 exhibits a better performance than 𝑂𝐷𝑃 in the
moderate-scale text classification.
22
• Classification Performance on the ODP Dataset
[1] Lee, J.H., Ha, J., Jung, J.Y., Lee, S. , “Semantic contextual advertising based on the open directory project”, ACM Trans. On the
Web 7(4) 2013, 24:1-24:22
[2] Le, Q.V., Mikolov, T., “Distributed representation of sentences and documents”, ICML 2014, 1188-1196
[3] Kim, Y. , “Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification”, EMNLP 2014, 1746-1751
[1]
[2]
[3]
[1]
[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pakdd2018kim20180605-200917224244/75/Incorporating-Word-Embeddings-into-Open-Directory-Project-Based-Large-Scale-Classification-22-2048.jpg)
![6.3 Experimental Results
23
• Classification Performance on the NYT Dataset
(2,735 categories)
• The performance of 𝑂𝐷𝑃𝐶𝑉+𝑊𝑉 outperforms all the methods.
• We also observe that both 𝑂𝐷𝑃𝐶𝑉 and 𝑂𝐷𝑃 𝑊𝑉 outperform ODP. These
results clearly demonstrate that both category and word vectors are effective
at text classification.
[1]
[2]
[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pakdd2018kim20180605-200917224244/75/Incorporating-Word-Embeddings-into-Open-Directory-Project-Based-Large-Scale-Classification-23-2048.jpg)