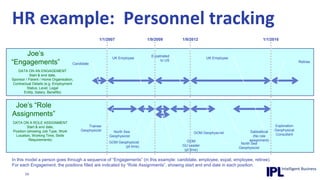
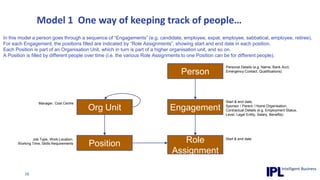
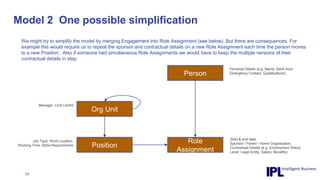
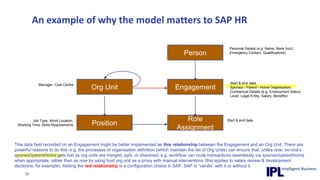
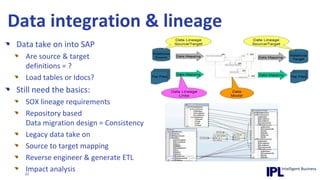
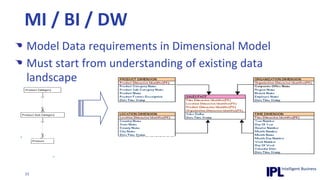
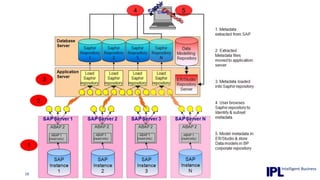
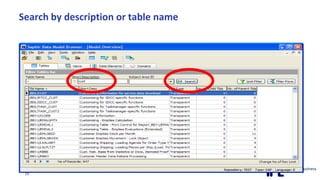
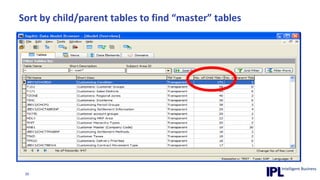
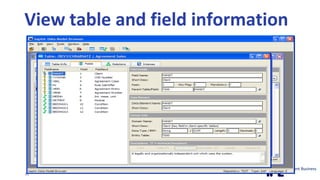
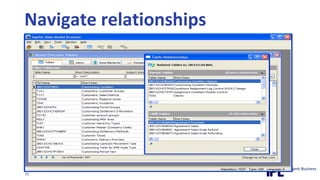
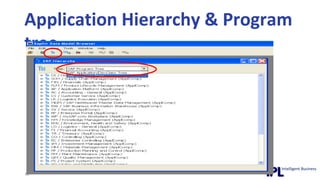
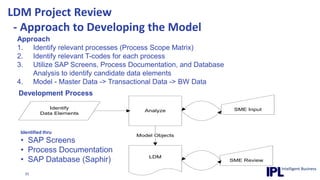
The document discusses the importance of integrating ERP metadata into information architecture, highlighting challenges in obtaining useful metadata and advocating for the use of data modeling to fulfill business needs. It outlines the benefits of data modeling in various contexts, such as data integration, requirements gathering, and compliance, while emphasizing the significance of maintaining effective information management amidst increasing data volumes. The text also shares insights from Chris Bradley's extensive experience in data governance, master data management, and enterprise information management.