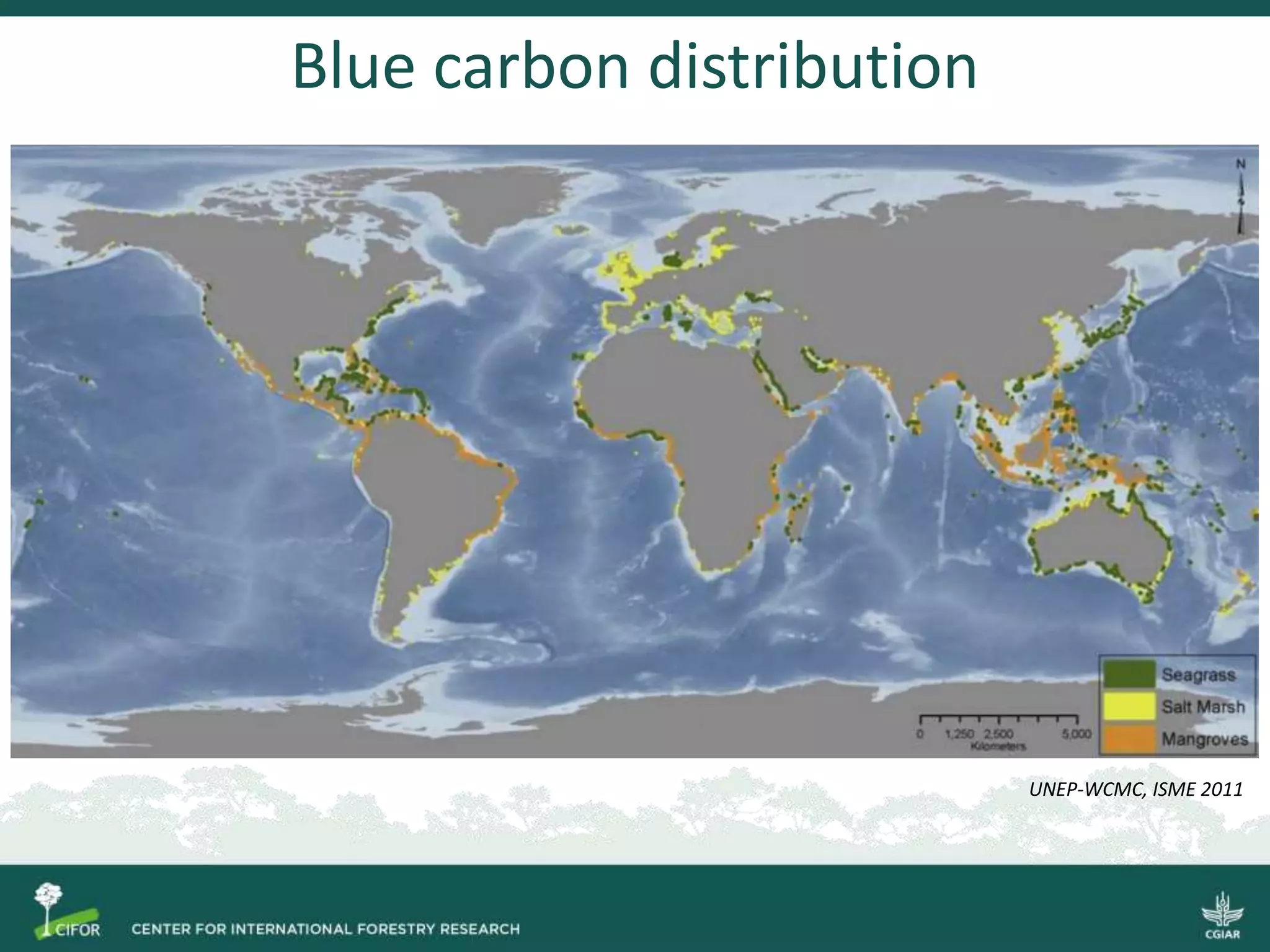
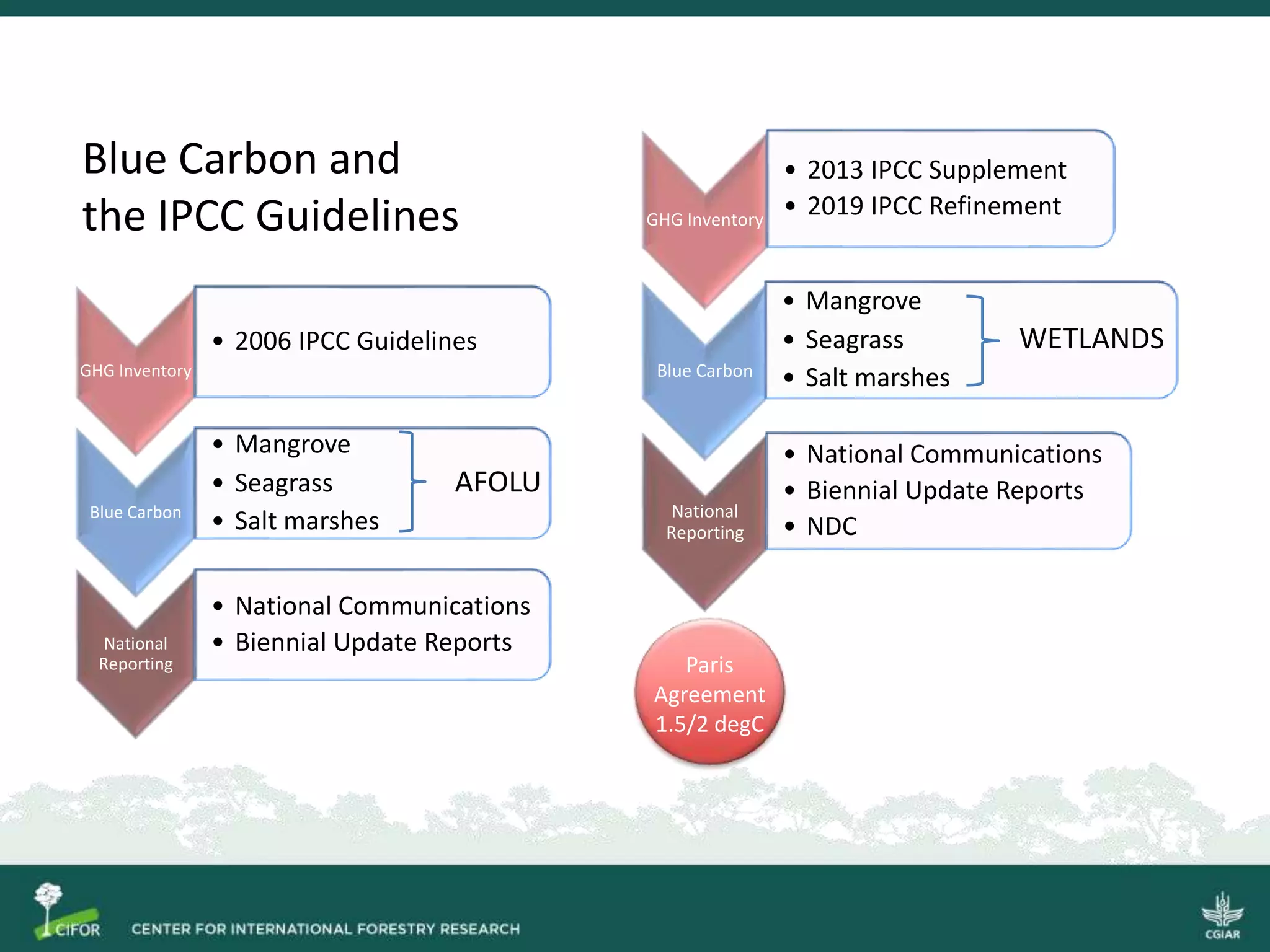
Blue carbon refers to carbon stored in coastal and ocean carbon pools, including mangroves, seagrass, and tidal wetlands. In Indonesia, significant carbon stocks exist but are threatened by deforestation, emitting considerable greenhouse gases. Enhancing regulations and conservation efforts, through mechanisms like REDD+, presents an opportunity to improve blue carbon management and contribute to climate change mitigation.