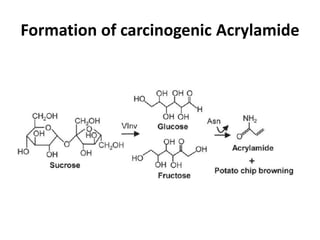
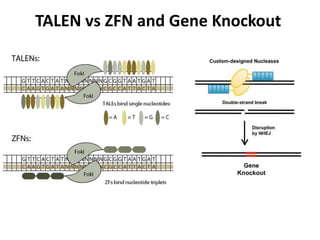
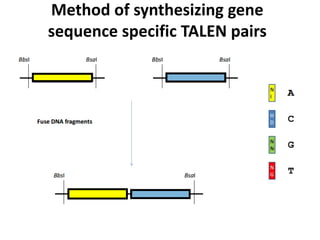
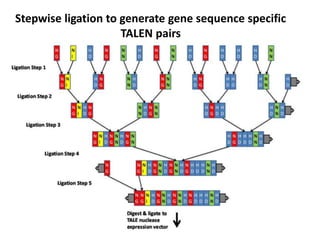
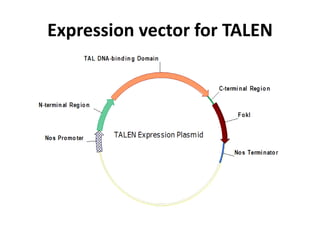
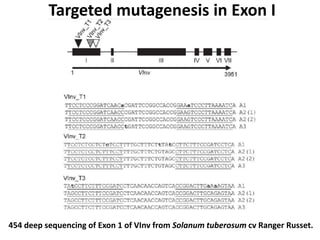
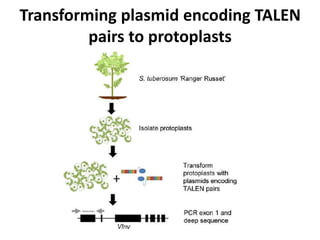
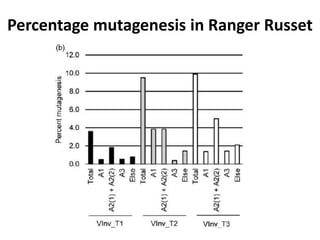
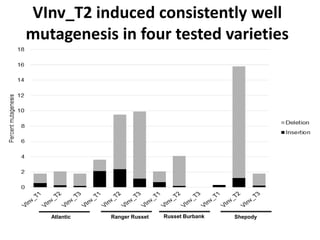
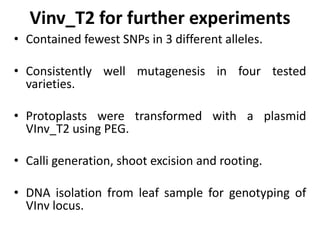
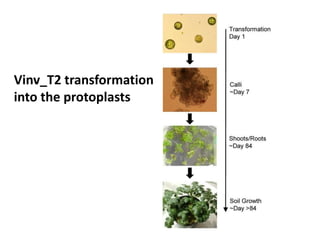
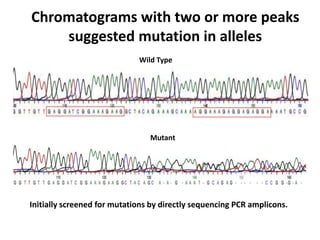
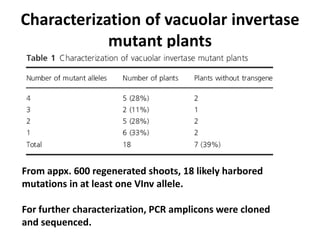
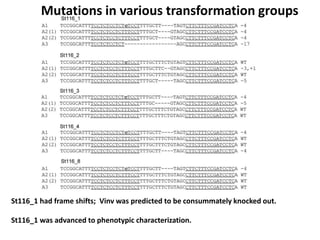
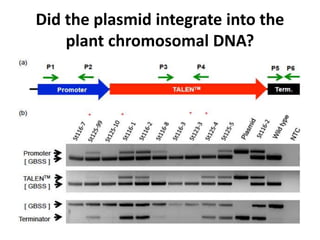
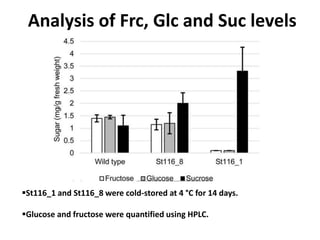
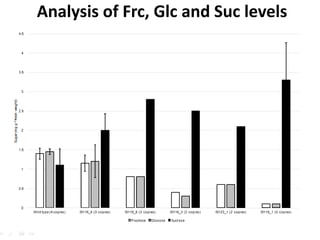
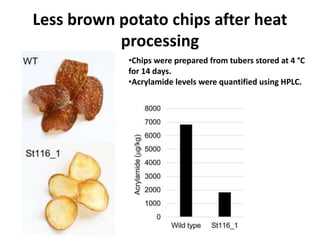
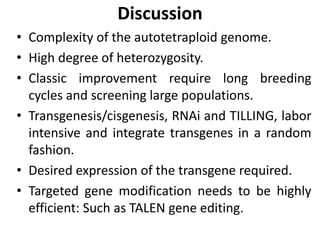
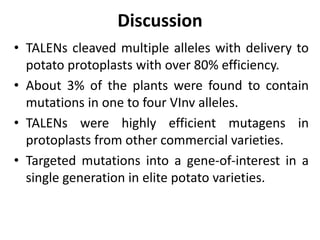
This document summarizes a research article that used targeted gene knockout to improve cold storage and processing traits in potato. The researchers used TALENs to generate mutations in the vacuolar invertase (VInv) gene in potato, which is responsible for accumulating reducing sugars during cold storage. This leads to cold-induced sweetening and the formation of carcinogenic acrylamide during processing. By knocking out the VInv gene in potato varieties Ranger Russet and others, the researchers found reduced reducing sugar levels and less browning and acrylamide formation during processing after cold storage. The targeted gene editing approach was more efficient than previous methods and could help improve potato varieties for storage and processing without introducing foreign DNA.