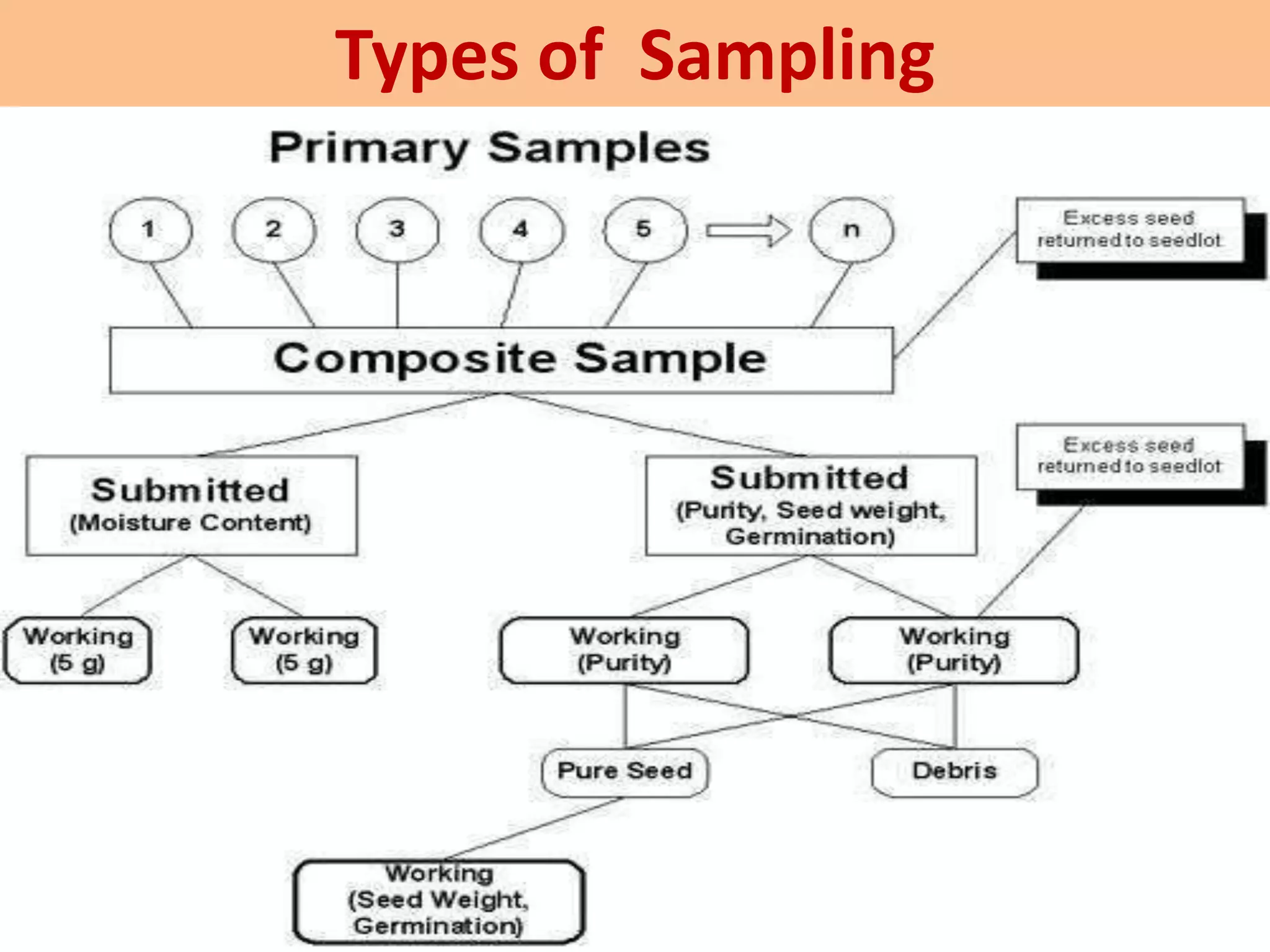
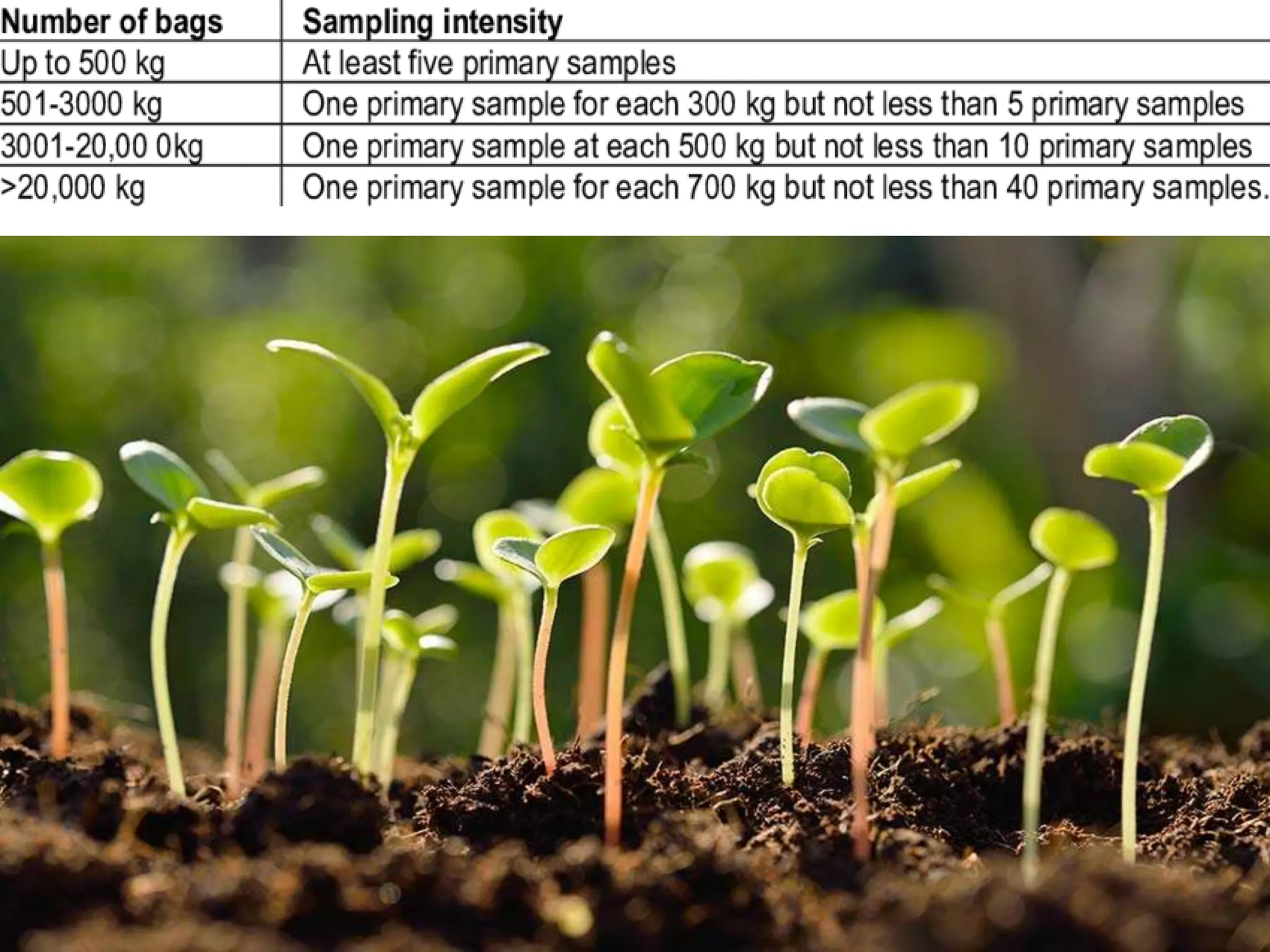
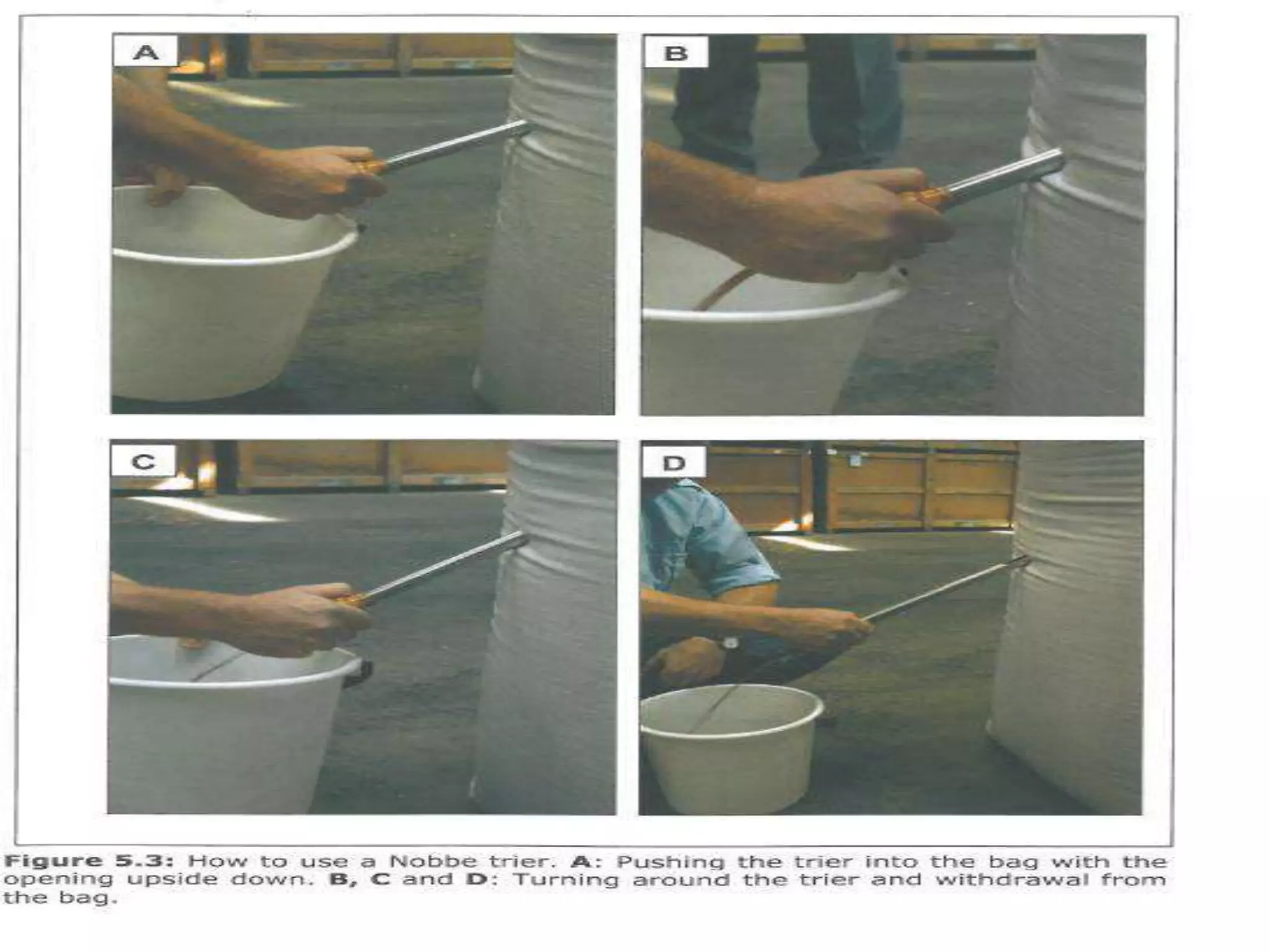
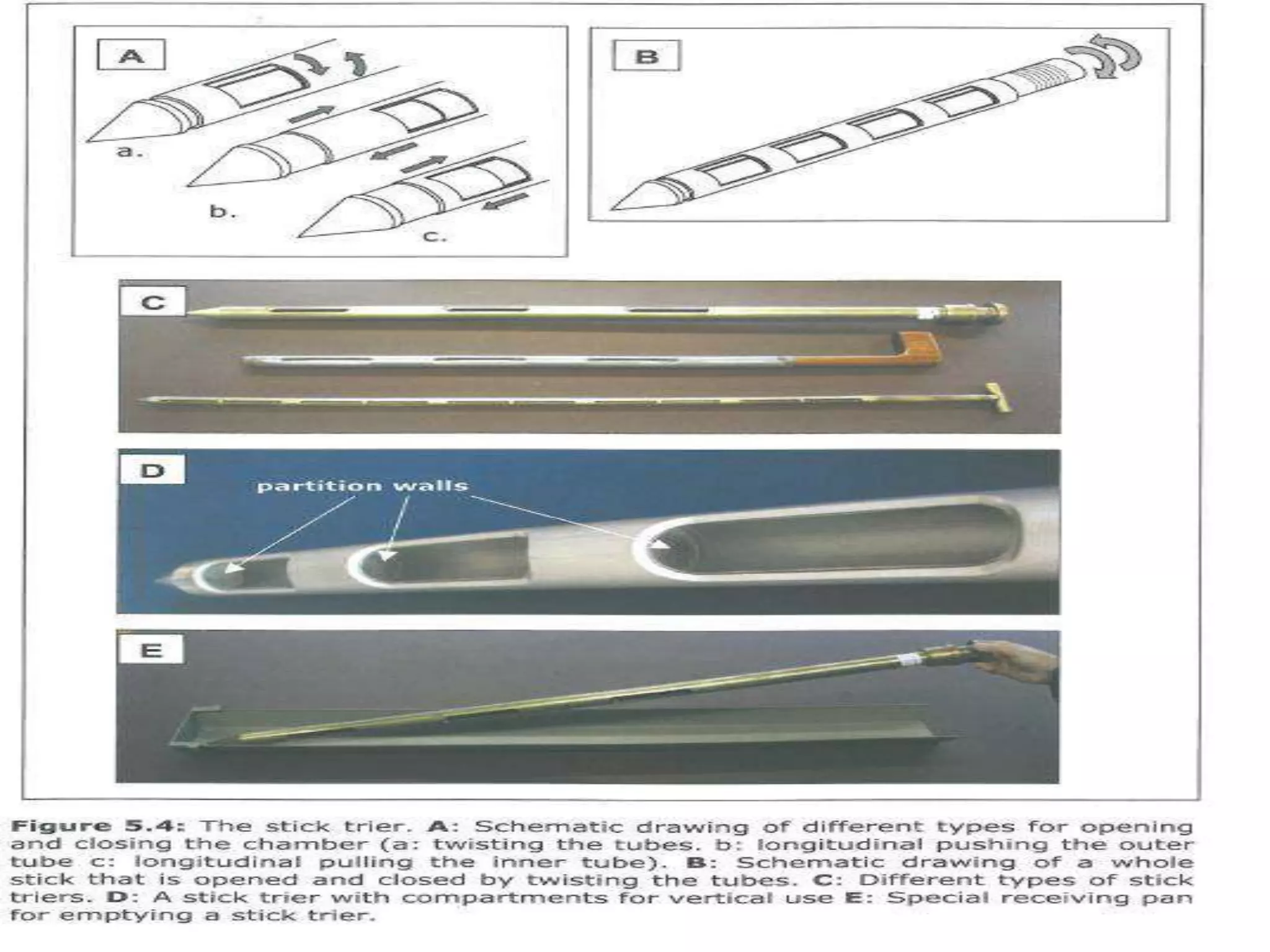
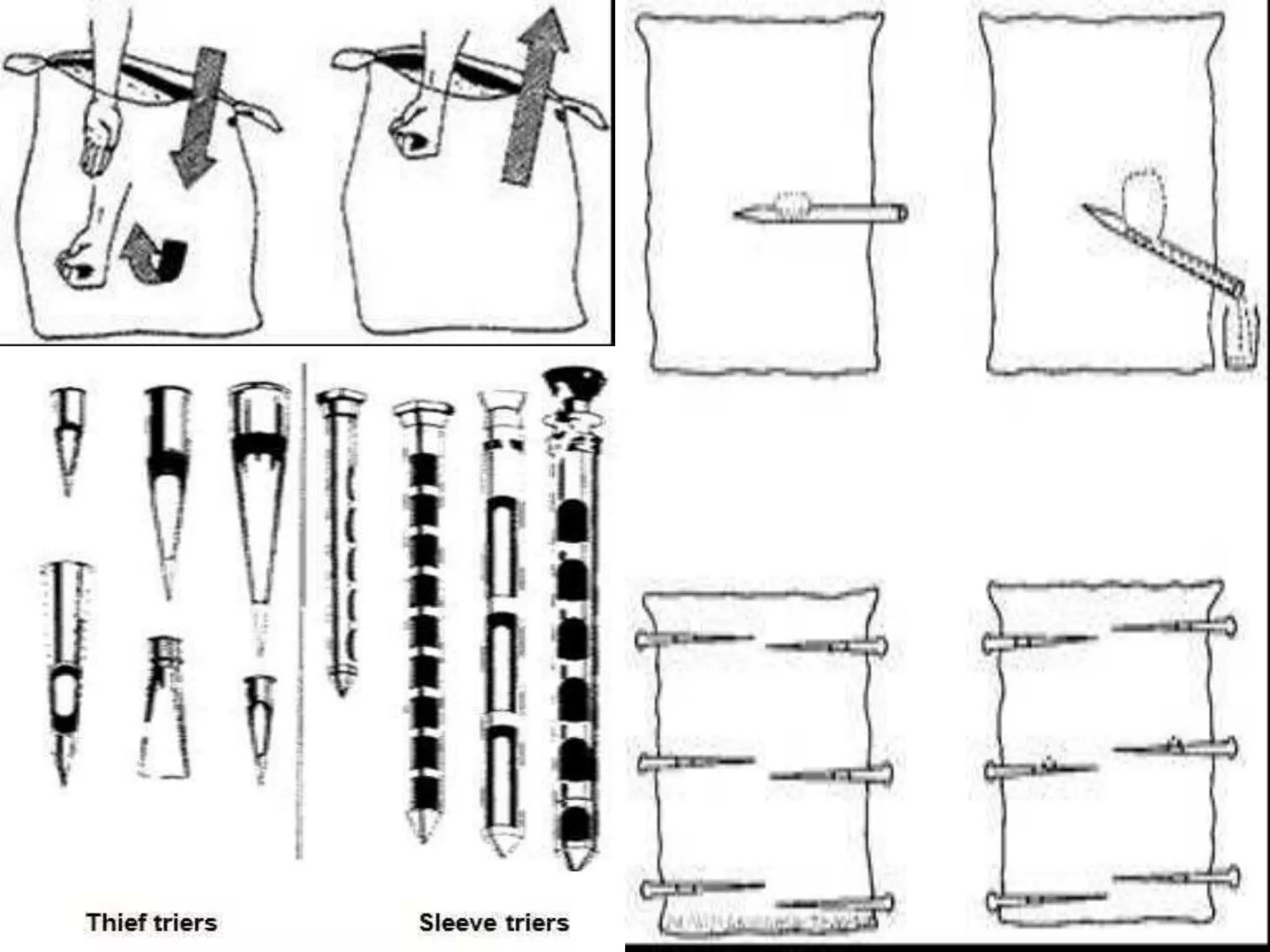
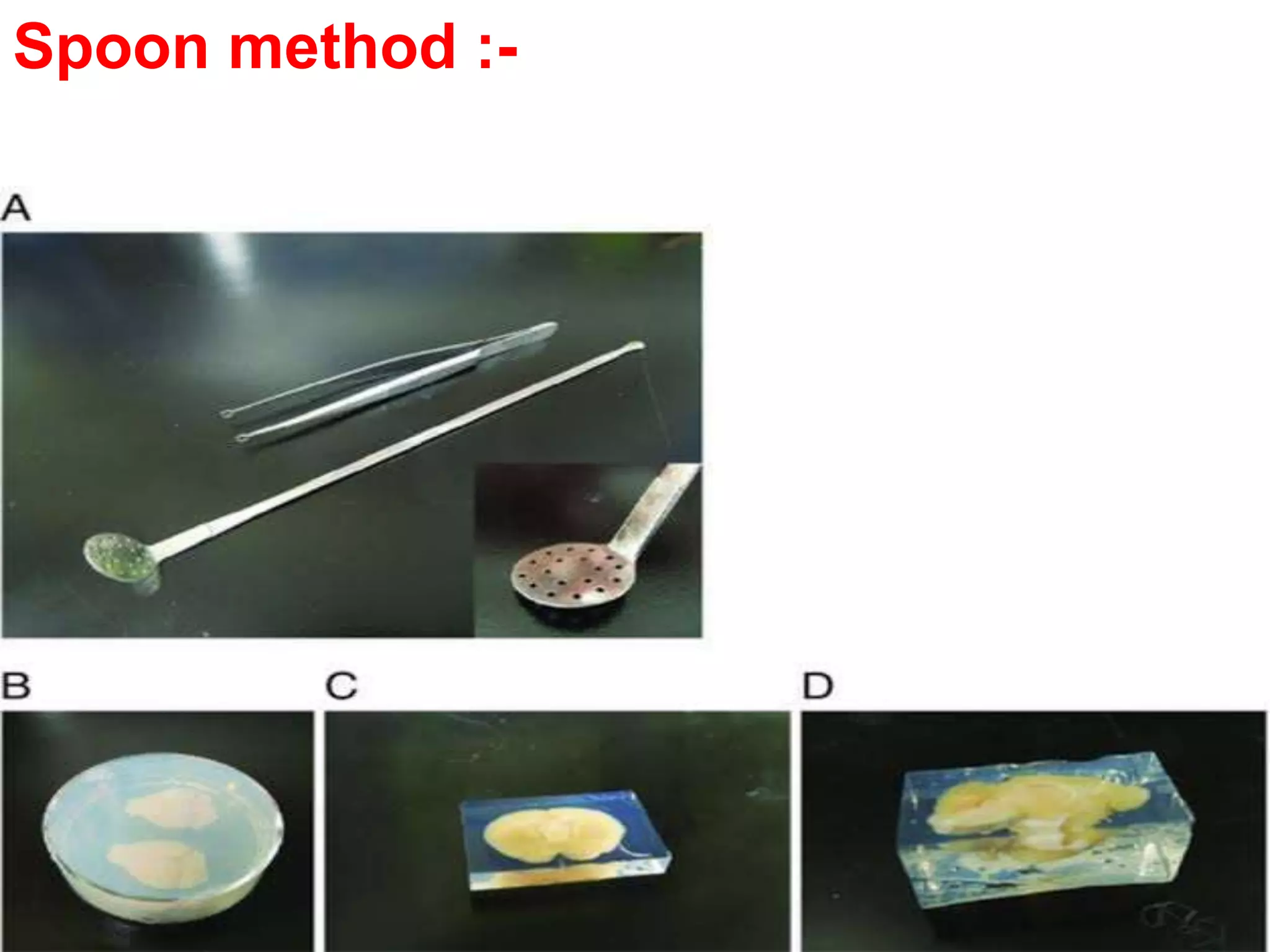
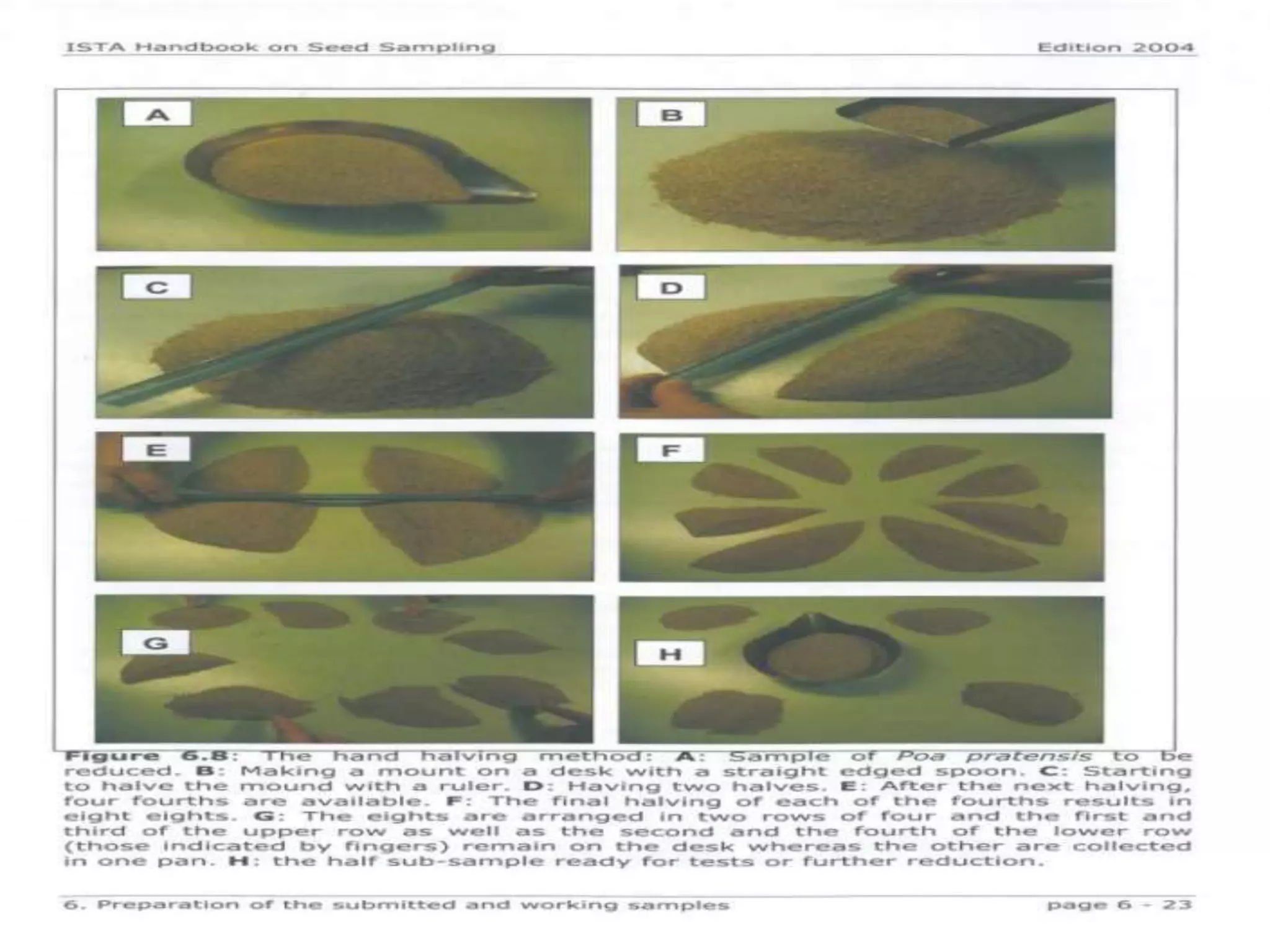
This document discusses seed sampling procedures. It defines key terms like seed lot, sample, and sampling. There are different types of sampling including primary, composite, submitted, and working samples. Sampling methods can be mechanical using equipment like triers, or done by hand. The objectives are to obtain a representative sample of a seed lot. Proper sampling intensity and equipment selection is important, as is following precautions to ensure an unbiased sample.