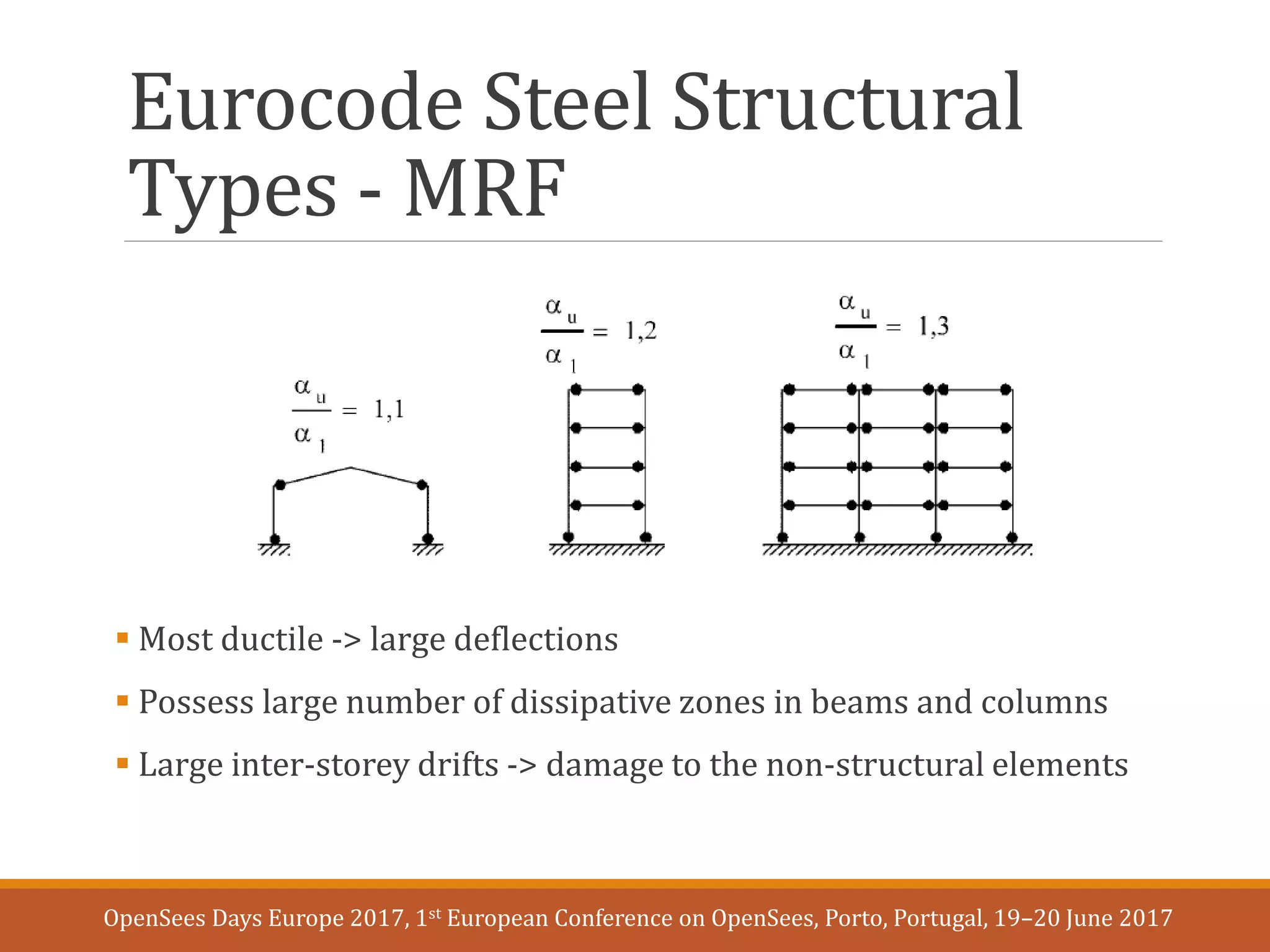
This document presents an improved approach for assessing drift in steel moment frames under realistic earthquake loading using the OpenSees modeling framework. Two modeling approaches - distributed plasticity and lumped plasticity - are compared based on their predicted floor drift demands and residual drifts under medium and high hazard earthquake scenarios. The lumped plasticity model is found to experience greater drift, particularly at drift levels over 3%, while the distributed plasticity model more closely matches previous research. The improved modeling approach captures key influences on drift from structural and loading characteristics.