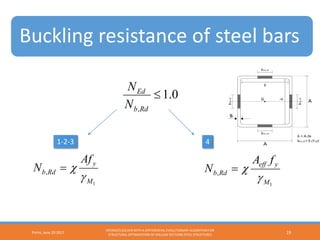
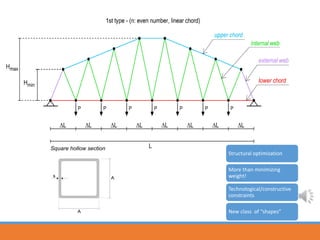
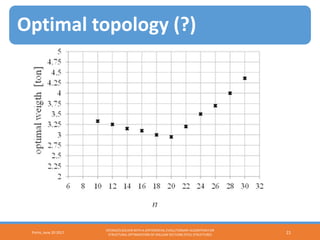
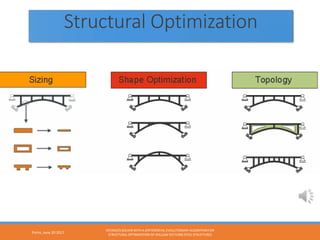
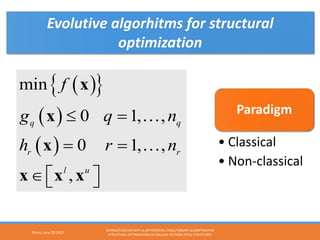
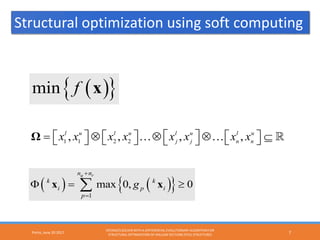
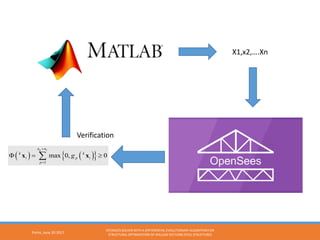
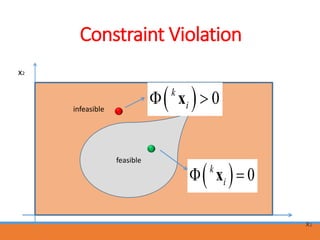
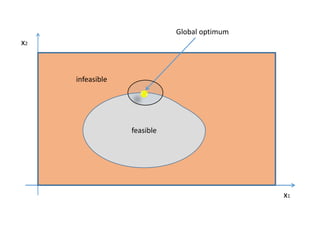
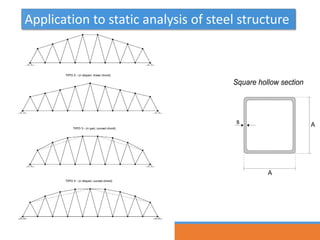
The document describes using a differential evolutionary algorithm to optimize the structural design of hollow steel structures using OpenSees. It develops a connection between Matlab and OpenSees to perform structural analysis and optimization. The algorithm handles constraints and is applied to a simple steel structure example. The goal is to optimize structural properties like weight while meeting requirements like stress limits.


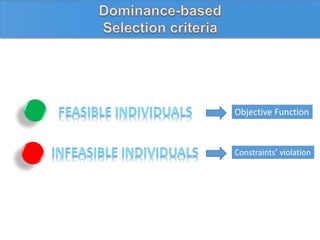
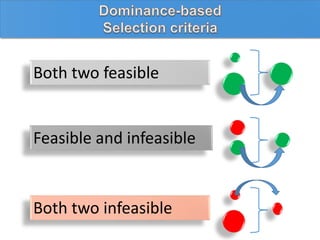
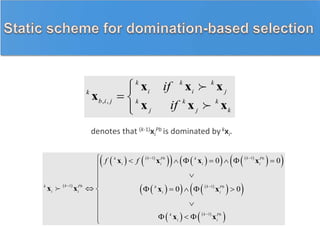
![0k k Pb
µΦ= ≥Φ
( ) ( ) ( ){ }1
k Pb k Pb k Pb k Pb
i N=Φ Φ ΦΦ x x x
( )
( ) ( )
( )( ) ( )( ) ( )
( )( )
( )( ) ( )
( )( )
( )( ) ( )
( )( ) ( ) ( )
( )( )
1 1
1 1
1 1
k kk Pb k k k Pb k k
i i i i
k kk Pb k k k Pb k k
i i i i
k kk k k Pb k k k Pb
i i i i
f f µ µ
µ µ
µ µ
− −
Φ Φ
− −
Φ Φ
− −
Φ Φ
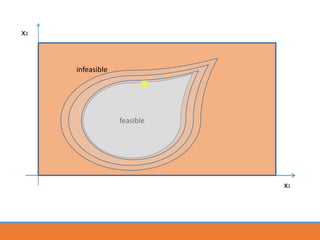
< ∧ Φ ≤ Ψ ∧ Φ ≤ Ψ
∨
⇔ Φ ≤ Ψ ∧ Φ > Ψ
∨
Φ > Ψ ∧ Φ > Ψ ∧ Φ < Φ
x x x x
x x x x
x x x x
( )
[ ] ( )01 0,1 0, , ;k k
k L
L
η
η +
Ψ= − ∈ = ∈
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationmaranodemartinogrecobriseghellafiore-170704232645/85/OpenSees-solver-with-a-differential-evolutionary-algorithm-for-structural-optimization-of-hollow-sections-steel-structures-15-320.jpg)
![Porto, June 20 2017
OPENSEES SOLVER WITH A DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHM FOR
STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION OF HOLLOW SECTIONS STEEL STRUCTURES 18
3
33
A s
s
ε
−
≤
] ]
3
33,38
A s
s
ε
−
∈
] ]
3
38,42
A s
s
ε
−
∈
3
42
A s
s
ε
−
>
Section Class
•1
•2
•3
•4
235
yf
ε =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationmaranodemartinogrecobriseghellafiore-170704232645/85/OpenSees-solver-with-a-differential-evolutionary-algorithm-for-structural-optimization-of-hollow-sections-steel-structures-18-320.jpg)