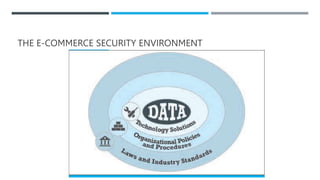
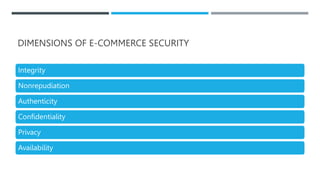
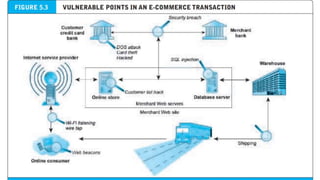
This document discusses e-commerce security and payment systems. It outlines key learning objectives about understanding e-commerce crime and security threats. It describes dimensions of e-commerce security like integrity, nonrepudiation, authenticity, confidentiality, and privacy. It then identifies common security threats in the e-commerce environment such as malware, phishing, hacking, data breaches, and denial of service attacks. It also describes major payment systems and issues involving credit card fraud.