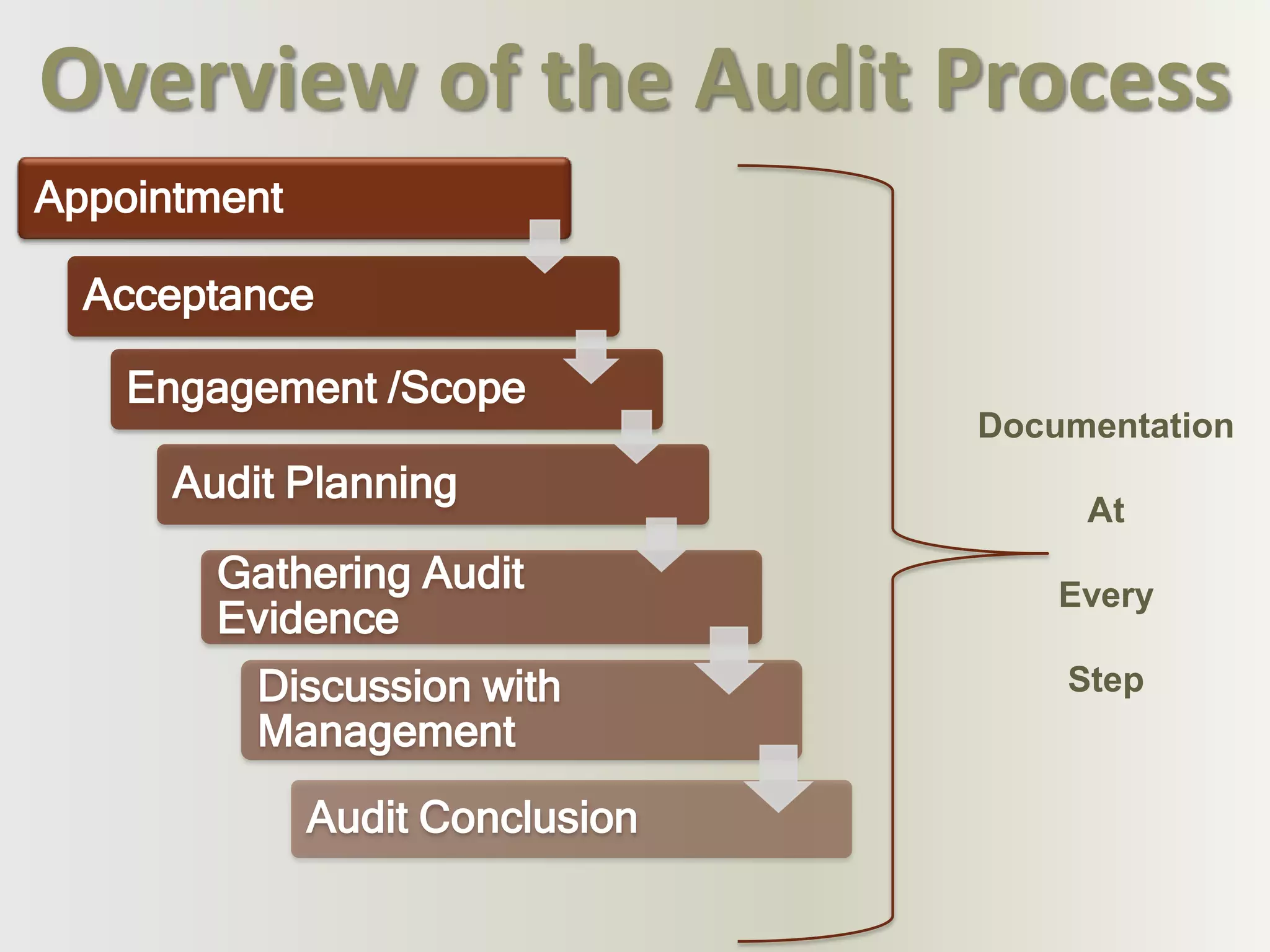
Maintaining audit documentation is important to demonstrate the work performed was sufficient and in accordance with auditing standards. The audit documentation should provide a clear understanding of the work done, evidence obtained, and conclusions reached.