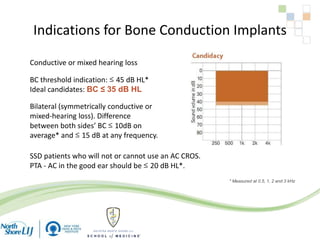
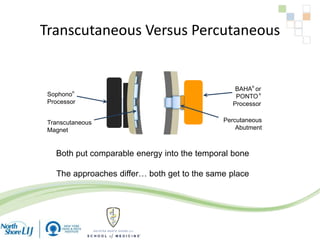
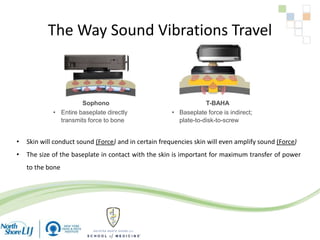
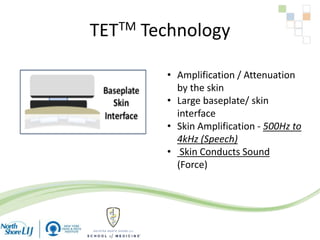
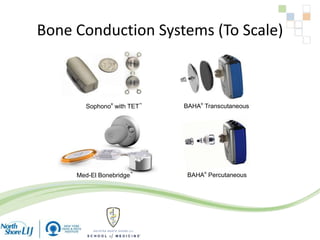
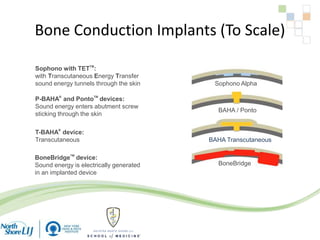
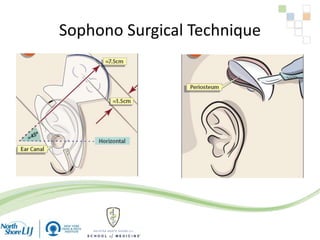
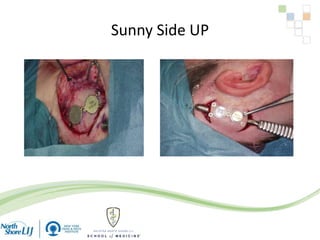
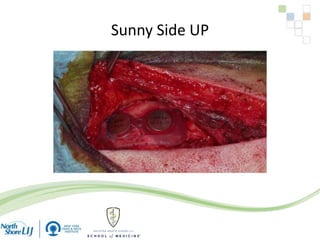
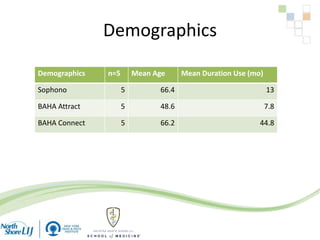
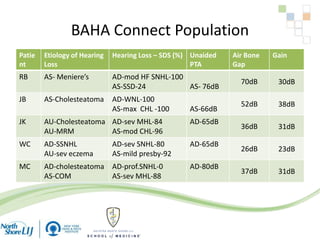
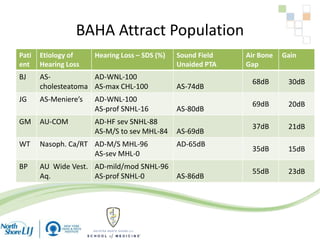
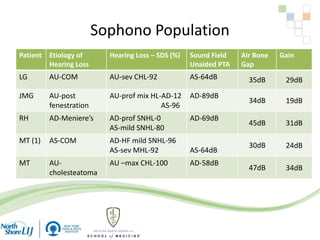
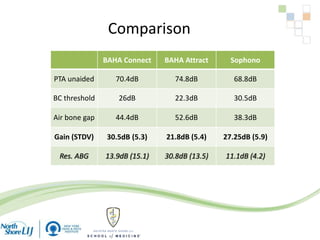
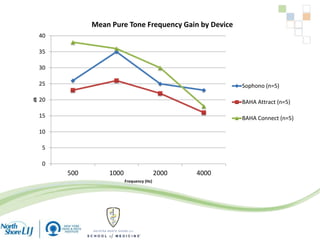
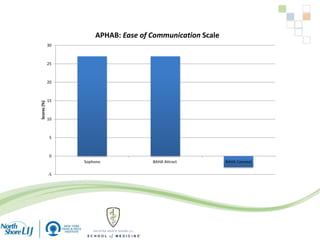
The document discusses implantable auditory devices (IADs) for hearing loss, including bone conduction implants. It provides details on indications for different IAD options and compares the Sophono device to percutaneous and transcutaneous BAHA systems. A preliminary prospective study showed that while all IADs provided benefit, the Sophono device resulted in better high frequency gain and smaller residual air-bone gaps than the BAHA Attract, though the BAHA Connect provided the highest overall gain. The Sophono was also found to have fewer late complications than the BAHA Connect.