The document discusses intellectual property rights (IPR) in Bangladesh. It provides background on IPR, noting its origins in the 19th century. Problems with protecting IPR in Bangladesh include piracy, internet challenges, immorality, profit motives, and lack of strong IPR laws. IPR can also create issues like monopoly and hindering development. The report aims to analyze IPR in Bangladesh, effectiveness of laws, and impacts of IPR. Limitations include the complexity of IPR, time constraints, and reliance on secondary data due to political conditions.








![Impact of Intellectual Property
Rights
Chapter- 1
Introduction
Intellectual property (IP) is a legal concept which refers to creations of the mind
for which exclusive rights are recognized.[1] Under intellectual property law,
owners are granted certain exclusive rights to a variety of intangible assets, such
as musical, literary, and artistic works; discoveries and inventions; and words,
phrases, symbols, and designs. Common types of intellectual property rights
include copyright, trademarks, patents, industrial design rights, trade dress, and
in some jurisdictions trade secrets.
In the era of globalization and digitalization the Intellectual Property Rights
1.1: Origin of the Report:
becomes a burning question. Electronic media like internet make easy to copy
one’s intellectual property by another. The imitation of intellectual property
makes concern the author of the new innovation. For protecting the rights of
intellectual property copyright, trademarks, patents, industrial design rights,
trade dress, and in some jurisdictions trade secrets are established.
My report is prepared for analysis how the intellectual properties are
exposed and copying, how the laws for protecting intellectual property are
implemented and can be made more effective, and the impacts of intellectual
property rights. This report on “Impact of Intellectual Property Rights” has
been prepared as a partial requirement for the completion of the course titled
“Fundamentals of MIS” for the BBA program of the Leading University, Sylhet.
The preparation of this report was supervised by Mr. Md. Rahimullah Miah,
Lecturer in MIS, Leading University, Sylhet, Bangladesh.
Although many of the legal principles governing intellectual property rights
1.2: History of IPR:
have evolved over centuries, it was not until the 19th century that the term](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-9-320.jpg)
![Impact of Intellectual Property Rights | 2
intellectual property began to be used, and not until the late 20th century
that it became commonplace in the majority of the world.[2] The British
Statute of Anne 1710 and the Statute of Monopolies 1623 are now seen as the
origins of copyright and patent law respectively.[3]
Modern usage of the term intellectual property goes back at least as far as
1867 with the founding of the North German Confederation whose
constitution granted legislative power over the protection of intellectual
property (Schutz des geistigen Eigentums) to the confederation. [4] When the
administrative secretariats established by the Paris Convention (1883) and
the Berne Convention (1886) merged in 1893, they located in Berne, and also
adopted the term intellectual property in their new combined title, the United
International Bureaux for the Protection of Intellectual Property. The
organization subsequently relocated to Geneva in 1960, and was succeeded
in 1967 with the establishment of the World Intellectual Property
Organization (WIPO) by treaty as an agency of the United Nations. According
to Lemley, it was only at this point that the term really began to be used in
the United States (which had not been a party to the Berne Convention), [2]
and it did not enter popular usage until passage of the Bayh-Dole Act in
1980.[5]
"The history of patents does not begin with inventions, but rather with royal
grants by Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603) for monopoly privileges.
Approximately 200 years after the end of Elizabeth's reign, however, a patent
represents a legal [right] obtained by an inventor providing for exclusive
control over the production and sale of his mechanical or scientific
invention...[demonstrating] the evolution of patents from royal prerogative to
common law doctrine.”[6]
In an 1818 collection of his writings, the French liberal theorist, Benjamin
Constant, argued against the recently introduced idea of "property which has
been called intellectual."[7] The term intellectual property can be found used
in an October 1845 Massachusetts Circuit Court ruling in the patent
case Davoll et al. v. Brown., in which Justice Charles L. Woodbury wrote that
"only in this way can we protect intellectual property, the labors of the mind,
productions and interests are as much a man's own as the wheat he](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-10-320.jpg)
![Impact of Intellectual Property Rights | 3
cultivates, or the flocks he rears."[8] The statement that "discoveries are
property" goes back earlier. Section 1 of the French law of 1791 stated, "All
new discoveries are the property of the author; to assure the inventor the
property and temporary enjoyment of his discovery, there shall be delivered
to him a patent for five, ten or fifteen years." [9] In Europe, French author A.
Nion mentioned propriete intellectuelle in his Droits civils des auteurs, artistes
et inventeurs, published in 1846.
Until recently, the purpose of intellectual property law was to give as little
protection possible in order to encourage innovation. Historically, therefore,
they were granted only when they were necessary to encourage invention,
limited in time and scope.[10]
The concept's origins can potentially be traced back further. Jewish
law includes several considerations whose effects are similar to those of
modern intellectual property laws, though the notion of intellectual creations
as property does not seem to exist – notably the principle of Hasagat Ge'vul
(unfair encroachment) was used to justify limited-term publisher (but not
author) copyright in the 16th century.[11] In 500 BCE, the government of the
Greek state of Sybaris offered one year's patent "to all who should discover
any new refinement in luxury." [12]
It is assumed that there is a positive correlation between both the IPR system
1.3: Relevant Problems Identified:
and innovation, and between innovation and economic growth. In addition, it
is assumed that the IPR system has a positive effect on, or at least doesn‘t
inhibit economic growth, and so overall has a positive influence on the
societal economic growth. However, the transition from industrial to
knowledge society has led to a series of significant changes in innovation
patterns and market conditions which in turn has led to new criteria within
the IPR system. There is a risk that the ongoing adjustments of the IPR
system could fall behind the rapid development of technology, making the
system become characterized by inertia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-11-320.jpg)



![Impact of Intellectual Property Rights | 7
Chapter- 2
General Context of the Study
The previous research works on Intellectual Property Rights are very few in
2.1: Previous Research work:
the context of Bangladesh. One of these research works is provided by Md.
Milan Hossain, a Senior Lecturer of Law Department in Northern University
Bangladesh. His research has provided the following information about IPR.
The cultural, industrial, and economical development of a country depends
on the progress of intellectual properties. Intellectual property is the things
that are created by the human thought; it is the result of intellectual activities.
Simply it refers copyright, trademark, patent design, trade secrets and
geographical indications etc. Very broadly, it means the legal rights which
result from intellectual activity in the industrial, scientific, literary and
artistic fields. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
Convention provides that “intellectual property shall include rights relating
to:
1. Literary, artistic and scientific works,
2. Performances of performing artists, phonograms and broadcasts,
3. Inventions in all fields of human endeavor,
4. Scientific discoveries,
5. Industrial designs,
6. Trademarks, service marks and commercial names and designations,
7. Protection against unfair competition, and
8. All other rights resulting from intellectual activity in the industrial,
scientific, literary or artistic fields.”[13]
Mr. Md. Milan Hossain’s Findings and Recommendation through his research
work are mention now.
Intellectual properties laws in Bangladesh are not very rich. Some
of them are not compatible with international treaties and conventions. Some
of them are not maintainable with the digital based society. We have no laws
on trade secrets, unfair competition, and geographical indication and lay out](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-15-320.jpg)



![Impact of Intellectual Property Rights | 11
The unauthorized usage of trademarks by producing and trading counterfeit
consumer goods is known as brand piracy.
The owner of a trademark may pursue legal action against trademark
infringement. Most countries require formal registration of a trademark as a
precondition for pursuing this type of action. In Bangladesh trademark is
registered by DPDT (Department of Patents, Designs and Trademarks).
A trademark may be designated by the following symbols:
TM (the "trademark symbol", which is the letters "TM", for an unregistered
trademark, a mark used to promote or brand goods)
SM(which is the letters "SM" in superscript, for an unregistered service
mark, a mark used to promote or brand services)
® (the letter "R" surrounded by a circle, for a registered trademark).
A trademark is typically a name, word, phrase, logo, symbol, design, image, or
a combination of these elements. There is also a range of non-conventional
trademarks comprising marks which do not fall into these standard
categories, such as those based on color, smell, or sound (like jingles).
The term trademark is also used informally to refer to any distinguishing
attribute by which an individual is readily identified, such as the well-known
characteristics of celebrities. When a trademark is used in relation to services
rather than products, it may sometimes be called a service mark.
Trade Dress: Trade dress is a legal term of art that generally refers to
characteristics of the visual appearance of a product or its packaging (or even
the design of a building) that signify the source of the product to consumers.
Trade dress may be registered with the United States Patent and Trademark
Office (PTO) in either the Principal Register or the Supplemental Register.[15]
Although registration is not required for legal protection, registration offers
several advantages. In the Principal Register, a registrant gains nationwide
constructive use and constructive notice, which prevent others from using or](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-19-320.jpg)
![Impact of Intellectual Property Rights | 12
registering that registrant’s trade dress (without contesting the
registration).[16] Further, a registrant in the Principal Register gains
incontestable status after five years, which eliminates many of the ways for
another party to challenge the registration. [17] Registration under the
Supplemental Register allows the registrant to protect its trade dress in
foreign countries, although the protections are much more limited than
protections under the Principal Register in the U.S. [18]
Trade Secrets: A trade secret is a formula, practice, process, design,
instrument, pattern, or compilation of information which is not generally
known or reasonably ascertainable, by which a business can obtain an
economic advantage over competitors or customers. In some jurisdictions,
such secrets are referred to as "confidential information", but should not be
referred to as "classified information", due to the nature of the word
"classified" in the USA. [19]
Above are the common types of Intellectual Property Rights. Patents, copyright,
industrial design rights and trademarks are now using in Bangladesh. All of the
four rights are registered by DPDT (Department of Patents, Designs and
Trademarks.) in Bangladesh.
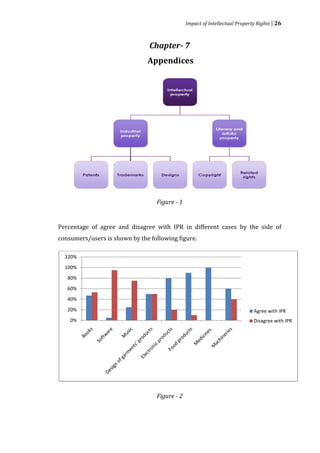
Impacts of Intellectual Property Rights
For why IP rights or laws are established? The stated answer will be that the most
intellectual property laws are established for promoting progress in innovation
and competition. That accelerates the industrial wheel and economy. The
impacts of intellectual property rights are as follows.
Motivating the individuals for new creations: Intellectual property rights
encourage individuals for new inventions. IPR ensures that the exclusive
inventions of an individual will not be copied without permission.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-20-320.jpg)
![Impact of Intellectual Property Rights | 13
Providing due recognition to the creators and inventors: IPR provides
the total control over a new innovation to its creator and permits to use
inventor’s name on the invention.
Ensuring material reward for intellectual property: IPR has rewarded the
intellectual property of an individual. IPR provides the facility to the inventor
to do monopoly business of his exclusive innovation or creation.
Ensuring the availability of the genuine and original products: IP rights
are facilitating the user or consumers to get / buy the genuine and original
products.
Maintaining differentiation: Trademark, logo, simple etc. common elements
of IPR are ensuring to differentiate an individual’s or organization’s products
from the competitors’ products. Customers can easily identify the preferred
source’s products.
Financial incentive: The exclusive rights allow owners of intellectual
property to enjoy benefits from the property they have created and providing
a financial incentive for the creation of an investment in intellectual property.
Economic growth: The WIPO treaty and several related international
agreements are premised on the notion that the protections of intellectual
property rights are essential to maintaining economic growth.[20] IPR
influences the individuals to new invention that ensure the society to get new
products, services, ideas, theories which will increase the economic growth.
To stop copying: IP rights restrict copying other’s design, idea, product and
conducts business by copying other’s intellectual property. That diverse one
to new creations.
Though IPR has many advantages, it has criticized from some angle. IPRs ensure
Criticisms of IPR:
a person to conduct monopoly business which may be a cause of high price of a
particular product or service or any other intellectual things. That may affect the
economy of a country. IPR makes the inventions personalized and that serves to
a certain region for that most of the people deprived from its benefits.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-21-320.jpg)


![Impact of Intellectual Property Rights | 16
Chapter- 3
Methodology of the Study
A methodology is usually a guideline system for solving a problem, with specific
components such as phases, tasks, methods, techniques and tools. It can be
defined also as follows:
1. "the analysis of the principles of methods, rules, and postulates employed
by a discipline";[21]
2. "the systematic study of methods that are, can be, or have been applied
within a discipline";[21]
3. "the study or description of methods".[21]
My research’s background area is Bangladesh which is a least developed
3.1: Background of Study Area:
country. Here I try to focus the Intellectual Property Rights of Bangladesh
comparing with the international intellectual property rights.
My initial survey was conducted over internet, library, some CD shops and
3.2: Reconnaissance Survey:
university going students.
Research design is a logical and systematic planning in directing a research.
3.3: Research Design:
There are three types of research design. These are...
i) Exploratory research design
ii) Descriptive research design
iii) Experimental research design
I follow the descriptive research design in my research work. Descriptive
research design is a scientific method which involves observing and describing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-24-320.jpg)







![Impact of Intellectual Property Rights | 24
Chapter- 6
References
Reference:
1. Intellectual Property Licensing: Forms and Analysis, by Richard
Raysman, Edward A. Pisacreta and Kenneth A. Adler. Law Journal Press,
1998–2008. ISBN 973-58852-086-9[verification needed]
2. "property as a common descriptor of the field probably traces to the
foundation of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) by
the United Nations." in Mark A. Lemley, Property, Intellectual Property,
and Free Riding, Texas Law Review, 2005, Vol. 83:1031, page 1033,
footnote 4.
3. Brad, Sherman; Lionel Bently (1999). The making of modern intellectual
property law: the British experience, 1760–1911. Cambridge University
Press. pp. 207. ISBN 9780521563635.
4. Article 4 No. 6 of the Constitution of 1867 (German)' Hastings Law
Journal, Vol. 52, p. 1255, 2001
5. Mark A. Lemley, "Property, Intellectual Property, and Free
Riding"(Abstract); see Table 1: 4–5.
6. Mossoff, A. 'Rethinking the Development of Patents: An Intellectual
History, 1550–1800,' Hastings Law Journal, Vol. 52, p. 1255, 2001
7. (French) Benjamin de Constant de Rebecque, Collection complète des
ouvrages publiés sur le gouvernement représentatif et la constitution
constitutionnelle, P. Plancher, 1818, p. 296.
actuelle de la France: formant une espèce de cours de politique
8. 1 Woodb. & M. 53, 3 West.L.J. 151, 7 F.Cas. 197, No. 3662, 2 Robb.Pat.Cas.
9. A Brief History of the Patent Law of the United States
303, Merw.Pat.Inv. 414
10. "Property, Intellectual Property, and Free Riding", Mark A.
Lemley, Texas Law Review 2007
11. Jewish Law and Copyright](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-32-320.jpg)





![d) How much you obey the IP laws in different situations?
Ans:
e] Do you think IP laws are properly implemented in Bangladesh?
lYeas ENo ffonsiderable
0 In what situations you think IP rights are inferior?
Ans:
g) What is your suggestion for making IP rights more applicable and more
enforceable?
Ans:
ba- c-oh3L:d?g1
1p ,,--ra<-)e.-el /-a-ws .
hJ What steps government should take for protecting intellectual property, you
think?
Ans:
q:?4t4Tu-t4: 9b.--*4-'.,.*n*rl}-.-'......f.5-*".....1.P.n*l*lf.*X..........](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impactofipr-130412040111-phpapp02/85/Impact-of-IPR-40-320.jpg)
