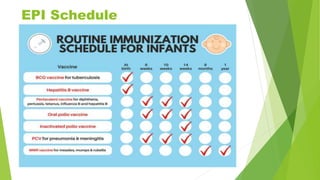
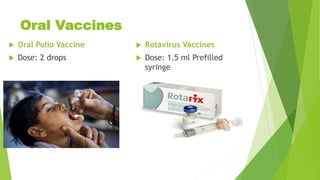
This document discusses immunization and vaccination. It defines immunization as rendering the subject immune by inoculating with a specific antigen to induce an immune response. It describes two types of immunity: active immunity produced by vaccines/toxoids that is long-lasting, and passive immunity produced by immunoglobulins that only provides temporary protection. It also discusses herd immunity and how a critical level of community immunity through vaccination protects even non-vaccinated individuals. The document outlines the expanded program on immunization in India and the vaccination schedule, describing various live attenuated, killed, and genetically engineered vaccine types for bacterial and viral diseases. It notes contraindications and potential adverse effects.