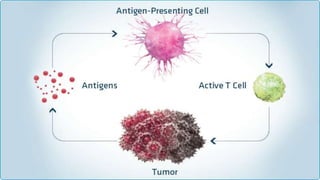
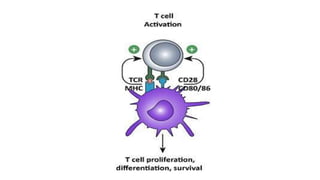
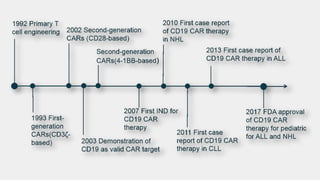
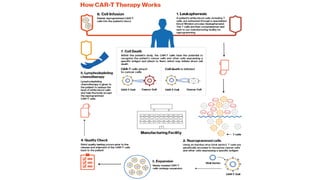
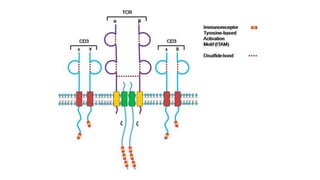
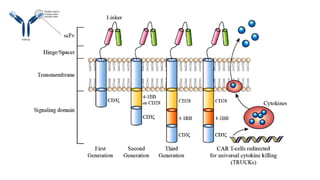
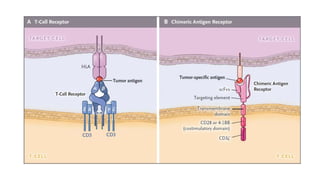
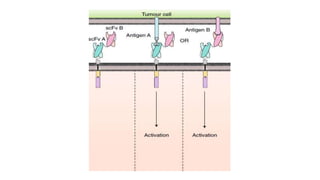
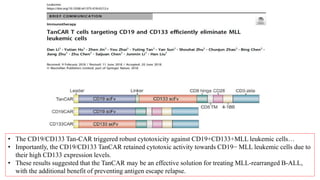
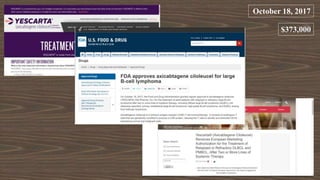
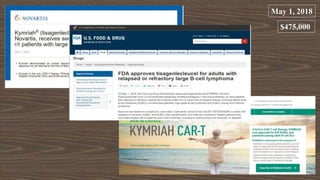
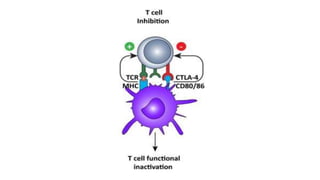
The document provides an overview of immune cell therapy, focusing on Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) therapy and its various forms, including newly developed CAR technologies like TAnCAR and universal CAR-T cells. It discusses the challenges presented by solid tumors, FDA-approved CAR therapies, and the impact of immune checkpoints and cytokine release syndrome related to CAR-T therapies. The future of CAR technology is highlighted as moving towards sophisticated T-cell mechanisms capable of targeting multiple antigens and utilizing gene editing for enhanced efficacy.