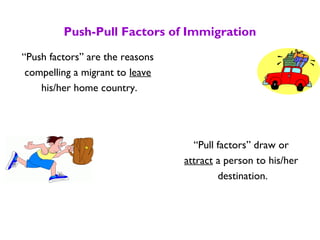
The document provides an overview of immigration to the United States, covering the process of becoming a citizen, categories of immigrants, and the factors driving immigration. It highlights the distinction between lawful permanent residents, refugees, and asylees, and discusses pathways to obtain a green card including family reunification, employment, and the diversity visa lottery. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of creating welcoming environments for immigrants and remaining informed about immigration issues.