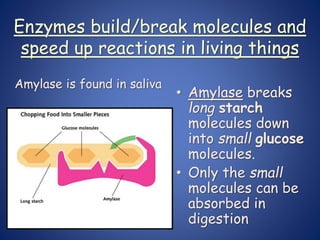
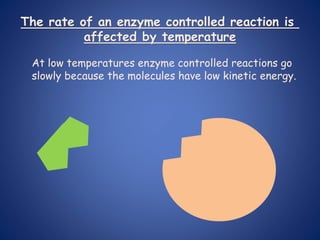
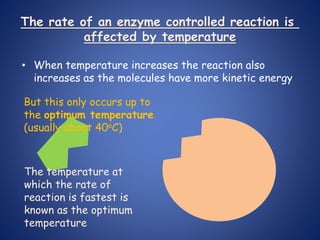
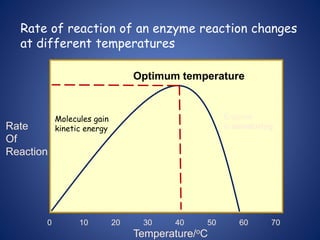
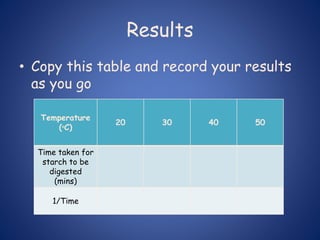
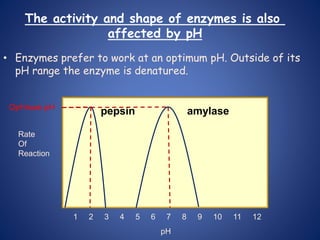
This document discusses the structure of biological molecules and enzymes. It provides information on the following:
- The main elements that make up carbohydrates, proteins and lipids are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and sometimes nitrogen.
- Carbohydrates are long chains of simple sugars joined by glycosidic bonds. Proteins are long chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Lipids include triglycerides made of glycerol and three fatty acids joined by ester bonds.
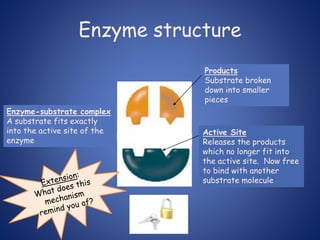
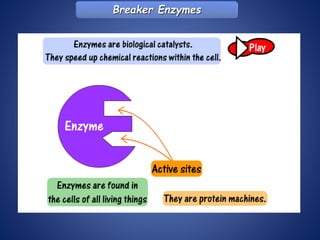
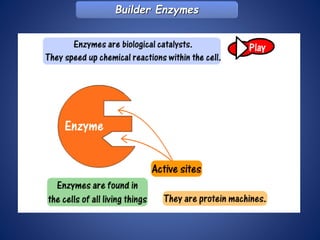
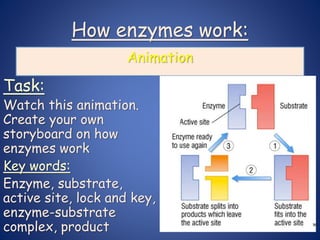
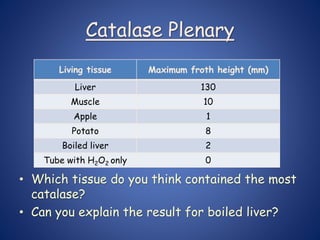
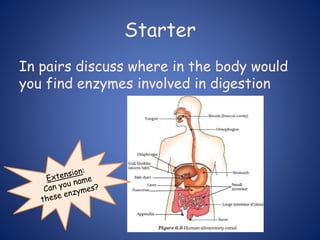
- Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up metabolic reactions. They work by binding to substrate molecules in a "lock and key" fashion and converting them to products. The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions