1. Foreign exchange exposure is the risk associated with activities involving currencies other than a firm's home currency. It is the risk that foreign currency movements negatively impact the firm.
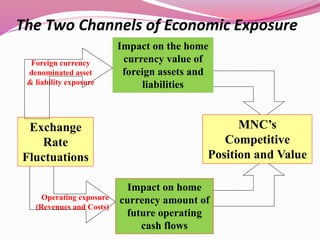
2. There are two types of foreign exchange exposure - translation exposure and economic exposure. Translation exposure affects financial statements but not cash flows, while economic exposure impacts future cash flows.
3. Economic exposure includes transaction exposure, relating to existing foreign currency contracts, and operating exposure, concerning future cash flows' sensitivity to exchange rate changes. Fluctuations in exchange rates can lead to profits or losses for firms involved in international transactions.