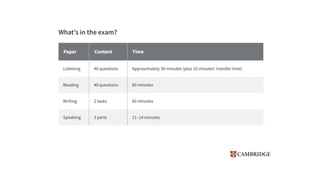
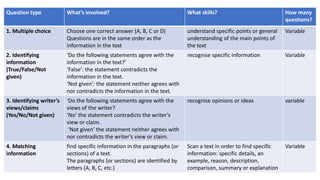
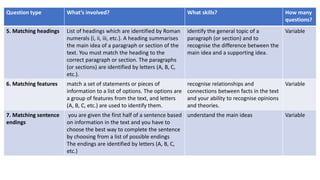
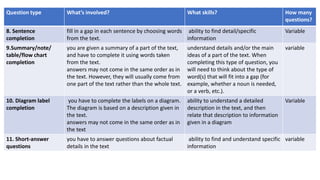
The document provides information about the IELTS Reading Test, including its purpose, format, question types, and skills assessed. The test contains three sections of increasing difficulty and covers everyday topics, work-related topics, and longer general interest texts. It assesses understanding of main ideas and specific details through multiple choice, true/false, matching, and short answer questions. Test takers must transfer their answers during the allotted time and spelling and grammar affect scoring.