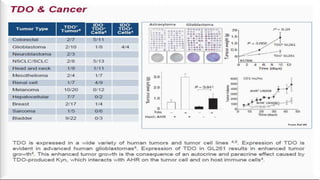
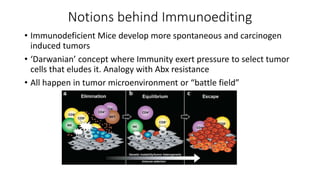
This document outlines the history and mechanisms of the indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) pathway and its role in cancer immunotherapy. It discusses key findings such as:
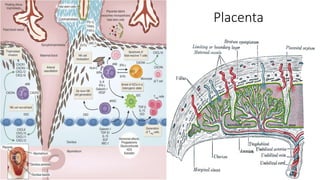
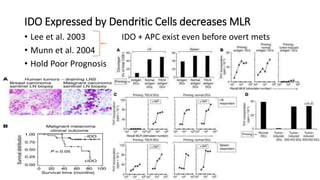
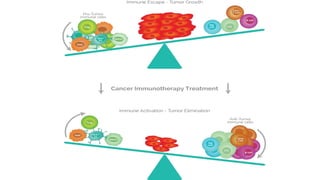
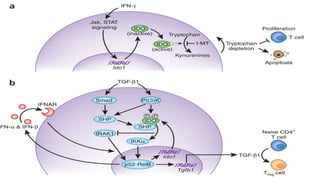
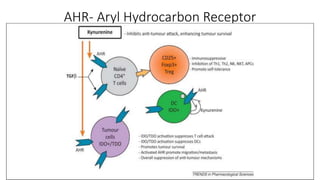
1) Munn's 1999 discovery that IDO suppresses T-cell mediated rejection of tumors and fetal allografts by depleting tryptophan.
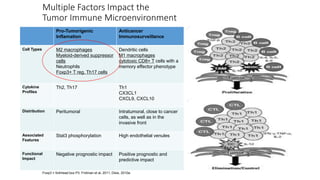
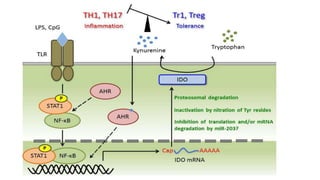
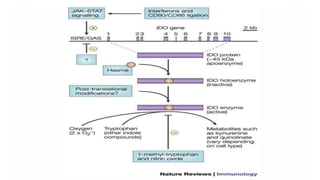
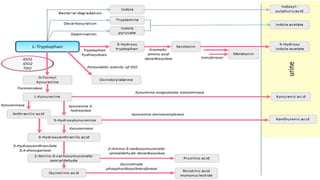
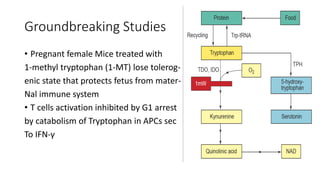
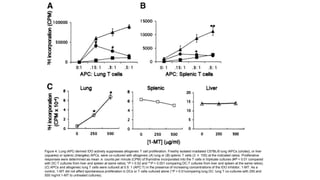
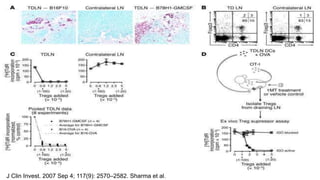
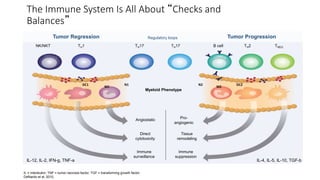
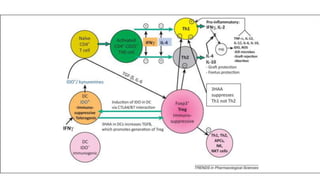
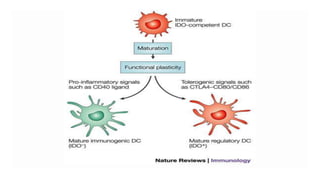
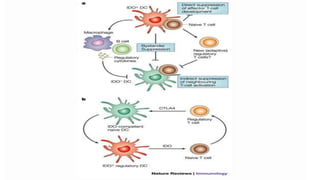
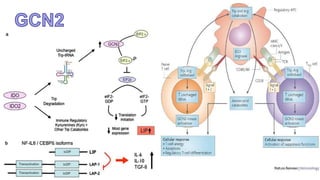
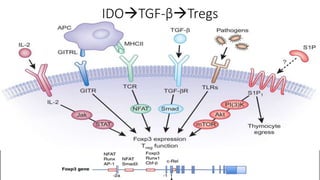
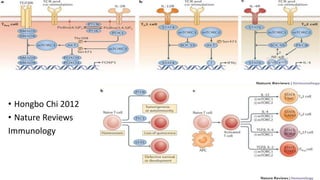
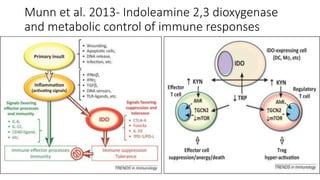
2) Mechanistic studies showing IDO induces T-cell arrest and inhibits proliferation through tryptophan depletion and kynurenine production, leading to Treg differentiation and CTL inhibition.
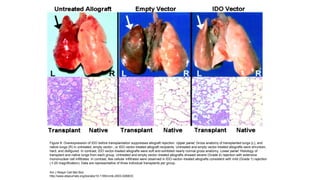
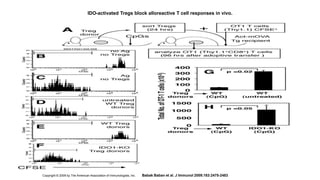
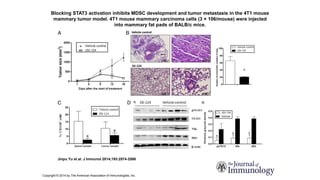
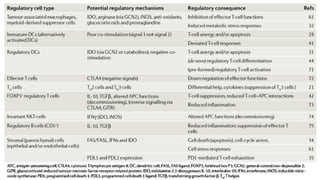
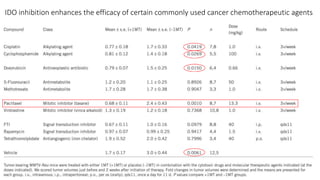
3) Preclinical studies combining IDO inhibitors with chemotherapy or vaccines, showing enhanced anti-tumor effects.
4) Ongoing clinical




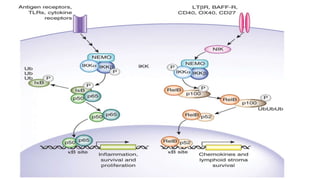
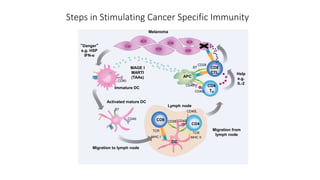
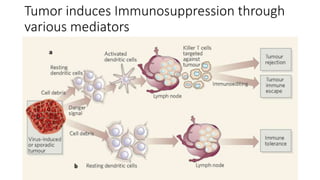
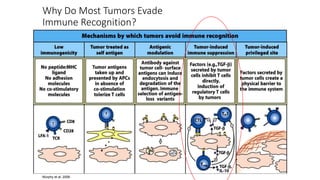











![IDO Inhibitors
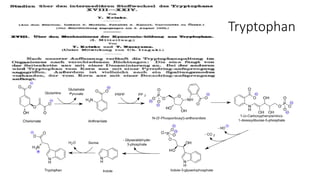
• 1-methyl-dl-tryptophan, β-(3-benzofuranyl)-dl-alanine and β-[3-
benzo(b)thienyl]-dl-alanine are competitive inhibitors for indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase. By S Cady et al. 1991
• Newlinks : 1MT or Indoximod , and GDC-0919 and many
others(IDO/TDO inhibitors)
• Incyte Corp. : Epacadostat
• Bristol-Myers Squibb: F001287
• Curadev Pharma: IDO/TDO-I: PCT/US14/24920
• IOmet Pharma: IDO/TDO-I:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idograndround-161009032839/85/IDO-pathway-from-bench-to-clinic-46-320.jpg)



![Vaccine Therapy and 1-MT in Treating Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer
Participants receive adenovirus-p53 transduced dendritic cell
(Ad.p53-DC) vaccine ID in weeks 1, 3, 5, and 10, and then every
3 weeks for 6 total doses. Participants also receive
1-methyl-d-tryptophan (indoximod) orally (PO) daily (QD)
on days 1-21. Treatment with 1-methyl-d-tryptophan repeats
every 28 days (patients with stable disease) for up to 12 courses
in the absence of disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Treatment (Vaccine Therapy,
1-methyl-d-tryptophan)
Number of Participants
[units: participants] 44
Age
[units: participants]
<=18 years 0
Between 18 and 65 years 36
>=65 years 8
Age
[units: years]
Mean (Full Range)
52.68 (27 to 73)
Gender
[units: participants]
Female 40
Male 4
Region of Enrollment
[units: participants]
United States 44
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier:
NCT01042535
First received: January 4, 2010
Last updated: September 21, 2015
Last verified: September 2015](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idograndround-161009032839/85/IDO-pathway-from-bench-to-clinic-51-320.jpg)

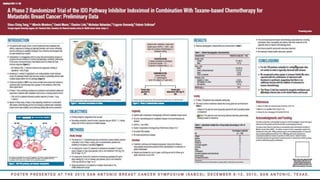
![[TITLE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idograndround-161009032839/85/IDO-pathway-from-bench-to-clinic-53-320.jpg)

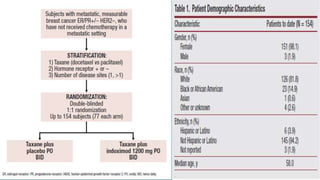
![[TITLE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idograndround-161009032839/85/IDO-pathway-from-bench-to-clinic-55-320.jpg)