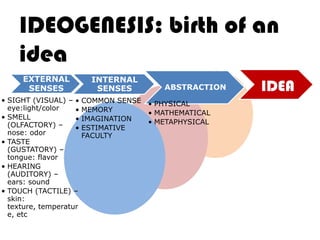
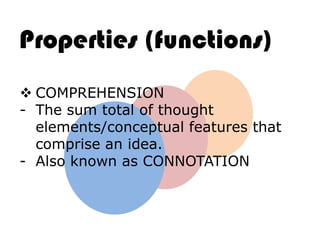
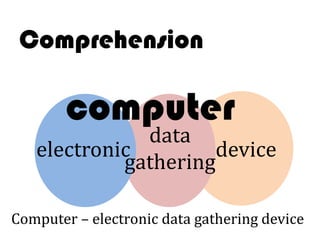
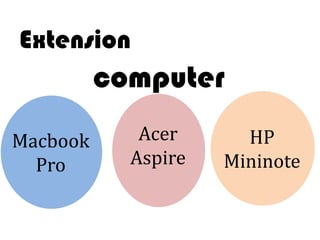
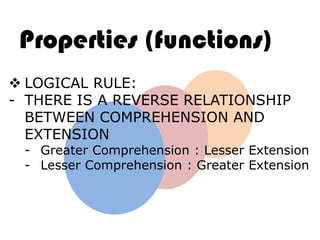
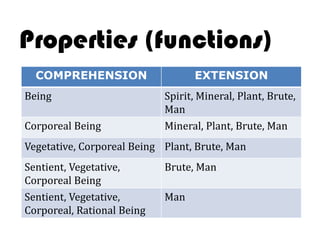
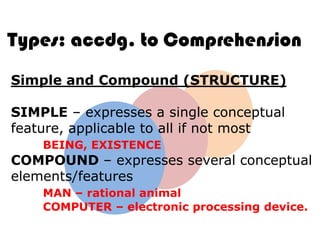
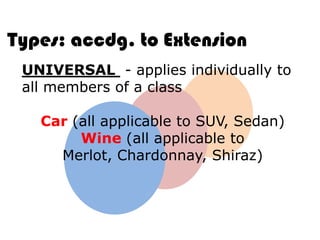
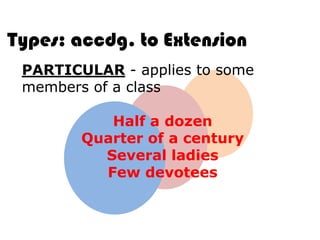
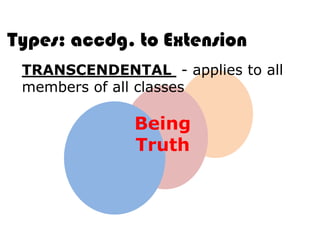
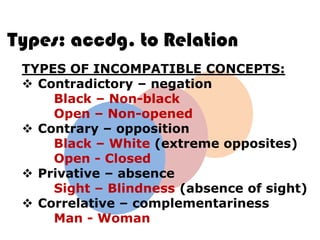
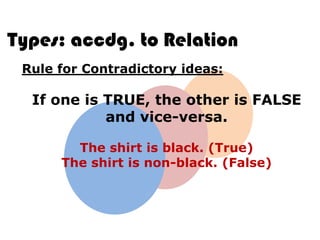
Ideas are the building blocks of knowledge that arise from sensory experiences and mental processes like abstraction. An idea has two main properties: comprehension and extension. Comprehension refers to the conceptual elements that make up the idea's meaning, while extension refers to the range of individual objects the idea applies to. Ideas can be classified according to their structure, subject, relation to other ideas, and scope of application. The types of ideas provide a framework for understanding concepts and their logical relationships.