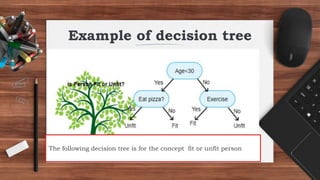
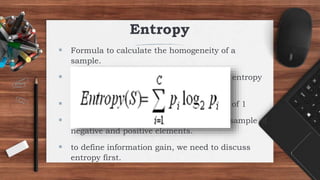
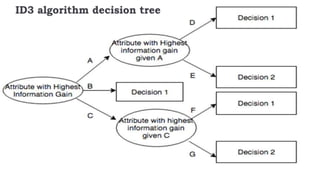
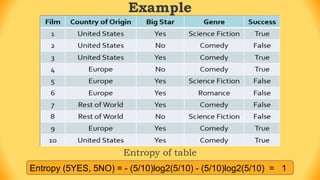
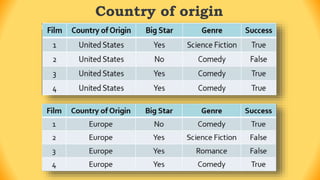
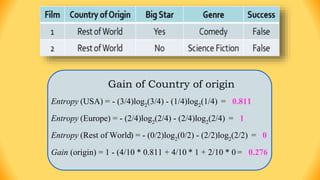
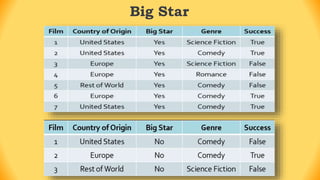
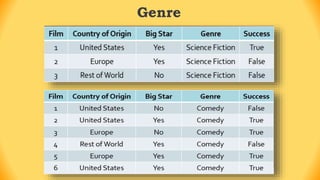
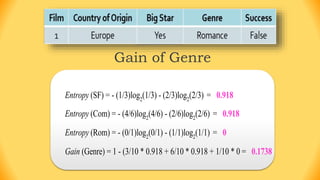
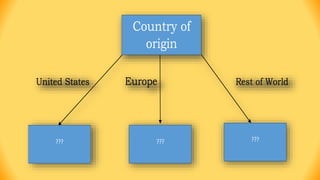
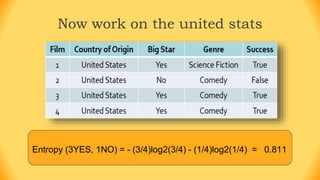
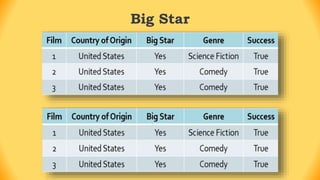
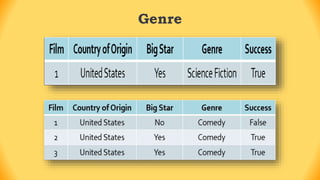
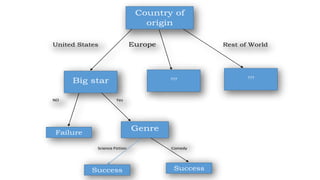
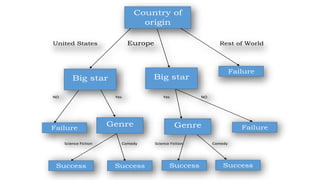
The ID3 algorithm is a decision tree learning algorithm developed by Ross Quinlan. It builds classification models in the form of a decision tree from a set of labeled training data. The algorithm works by selecting the attribute that is most useful for classifying the training examples at each step, starting with the root node. It then splits the examples into smaller subsets based on the value of that attribute. This process continues recursively on each derived subset until the subsets are pure or until stopping criteria are met. The resulting decision tree can then be used to classify new or unknown data instances.