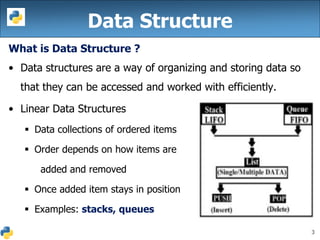
This document discusses linear data structures like stacks and queues. It defines them as ordered data collections where items are added and removed from specific ends. Stacks follow LIFO while queues follow FIFO. The key operations for stacks are push and pop, while queues use enqueue and dequeue. Python implementations are shown using lists. Functions are created to add, remove, and display items for both stacks and queues.





![7
Stack
Applications Using Stacks
• Stacks are prominently used in applications such as:
Recursive Programming
Reversing words
Expression Conversion
• In-fix to Post-fix
Backtracking
Undo mechanisms in word editors
Check if delimiters are matched
• Matching of opening and closing symbols: {,},[,],(,)
• Check: {{a}[b]{[{c}](d(e)f)}((g))} and ({[a}b(c)])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-pythondatastructure-2-200430145813/85/9-python-data-structure-2-7-320.jpg)


![10
Stack
Implementing Stack using List in Python
• To use lists as stacks, that is a data structures (LIFO).
An item can be added to a list by using the append() method.
The last item can be removed from the list by using the pop()
method without passing any index to it.
• Example
>>> stack = ['a','b','c','d']
>>> stack.append('e')
>>> stack.append('f')
>>> stack
Output: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']
>>> stack.pop()
Output: 'f'
>>> stack
Output: ['a, 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-pythondatastructure-2-200430145813/85/9-python-data-structure-2-10-320.jpg)

![12
Stack
#main program starts from here
x=[]
choice=0
while (choice!=4):
print("********Stack Menu***********")
print("1. push(INSERT)")
print("2. pop(DELETE)")
print("3. Display ")
print("4. Exit")
choice = int(input("Enter your choice :"))
if(choice==1):
value = int(input("Enter value "))
push(x,value)
if(choice==2):
pop(x)
if(choice==3):
display(x)
if(choice==4):
print("You selected to close this program")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-pythondatastructure-2-200430145813/85/9-python-data-structure-2-12-320.jpg)





![18
Queue
Implementing Queue in Python
• Usage of list, again presented in Python documentation is to use lists as
queues, that is a first in - first out (FIFO).
• Example
>>> queue = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
>>> queue.append('e')
>>> queue.append('f')
>>> queue
Output: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']
>>> queue.pop(0)
Output: 'a'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-pythondatastructure-2-200430145813/85/9-python-data-structure-2-18-320.jpg)
![19
Queue
Implementing Queue using List in Python
def add_element(Queue,x): #function to add element at the end of list
Queue.append(x)
def delete_element(Queue): #function to remove last element from list
n = len(Queue)
if(n<=0):
print("Queue empty....Deletion not possible")
else:
del(Queue[0])
def display(Queue): #function to display Queue entry
if len(Queue)<=0:
print("Queue empty...........Nothing to display")
for i in Queue:
print(i,end=" ")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-pythondatastructure-2-200430145813/85/9-python-data-structure-2-19-320.jpg)
![20
Queue
#main program starts from here
x=[]
choice=0
while (choice!=4):
print(" ********Queue menu***********")
print("1. Add Element ")
print("2. Delete Element")
print("3. Display ")
print("4. Exit")
choice = int(input("Enter your choice : "))
if(choice==1):
value = int(input("Enter value : "))
add_element(x,value)
if(choice==2):
delete_element(x)
if(choice==3):
display(x)
if(choice==4):
print("You selected to close this program")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-pythondatastructure-2-200430145813/85/9-python-data-structure-2-20-320.jpg)
