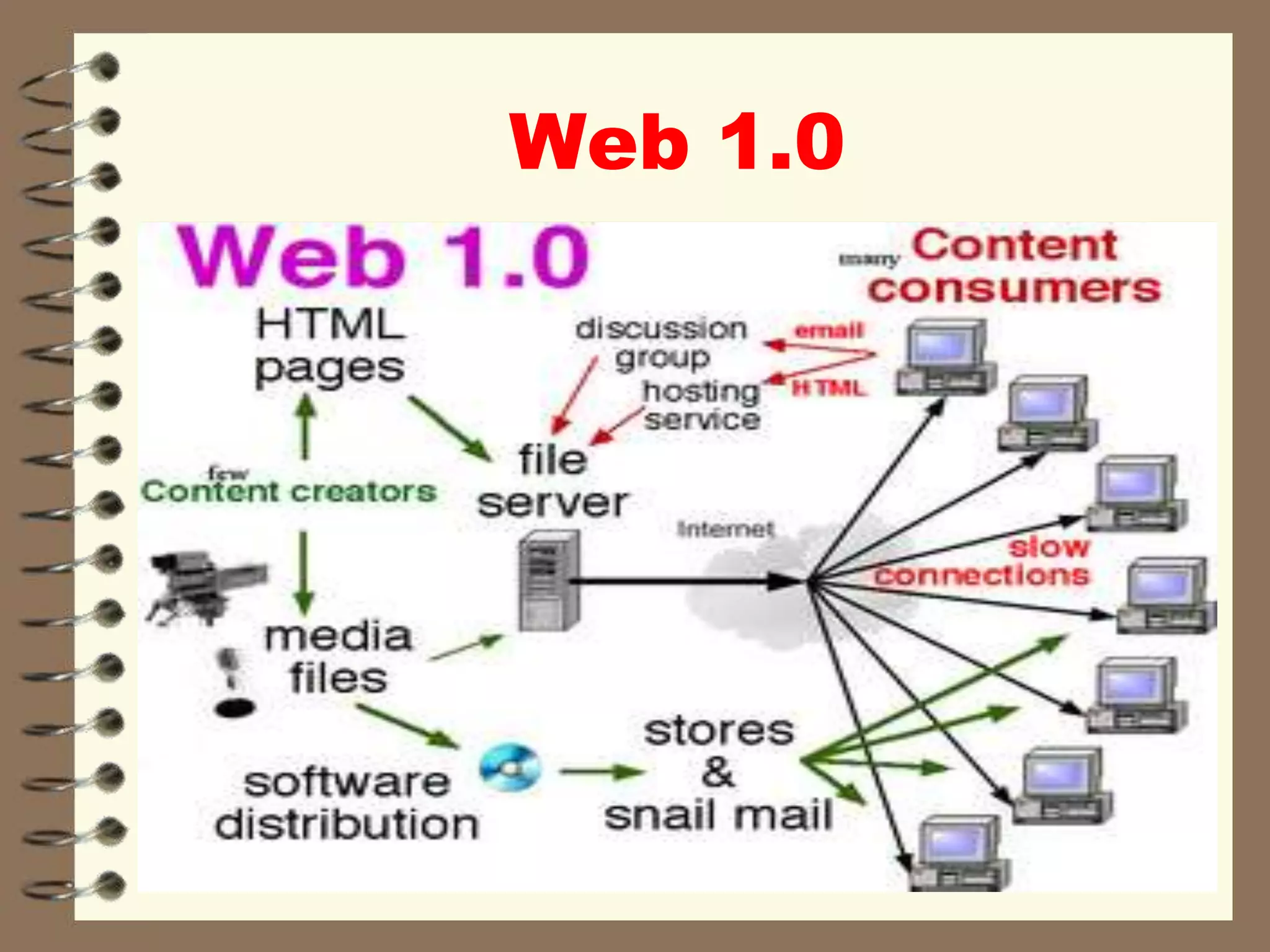
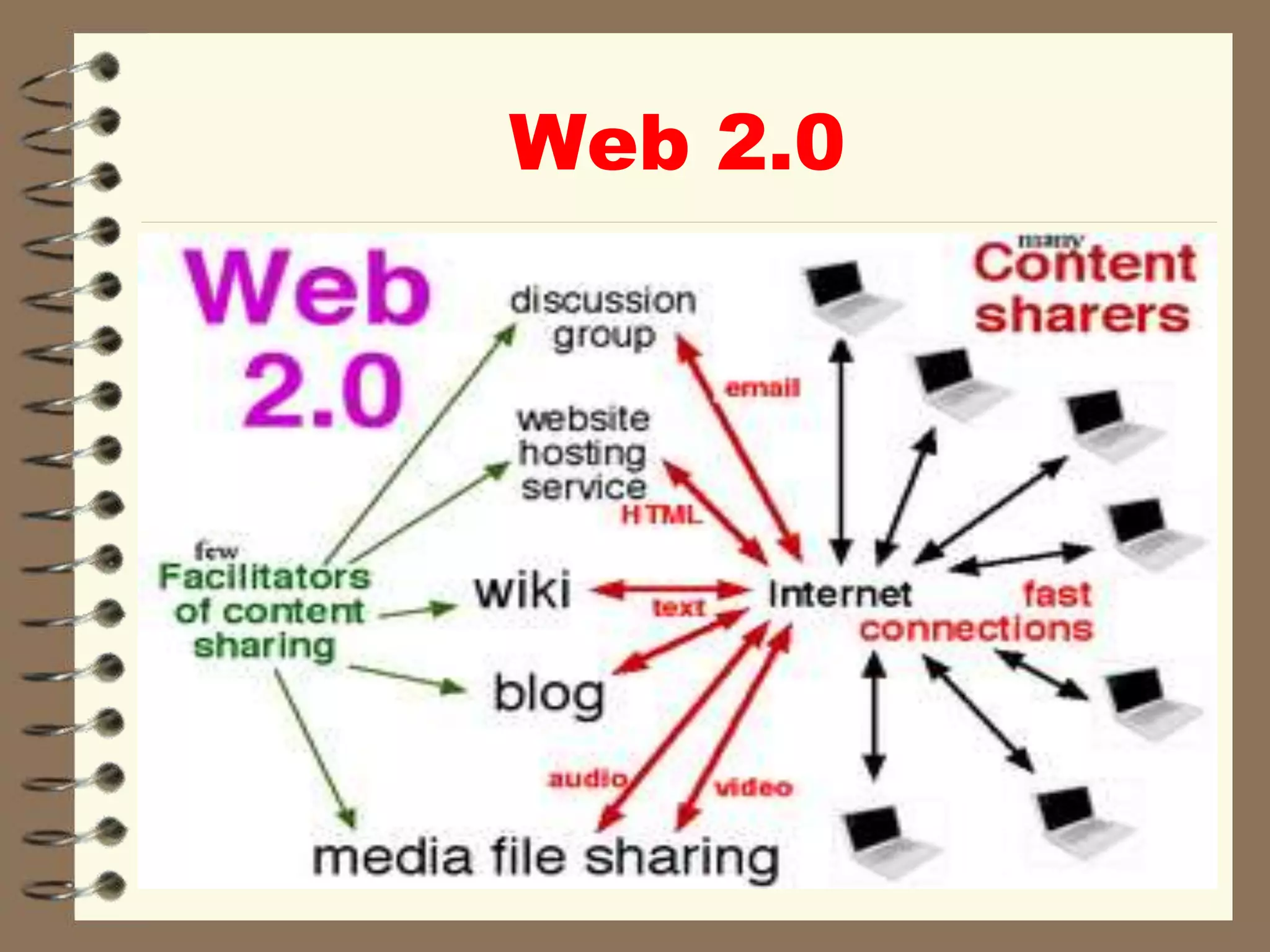
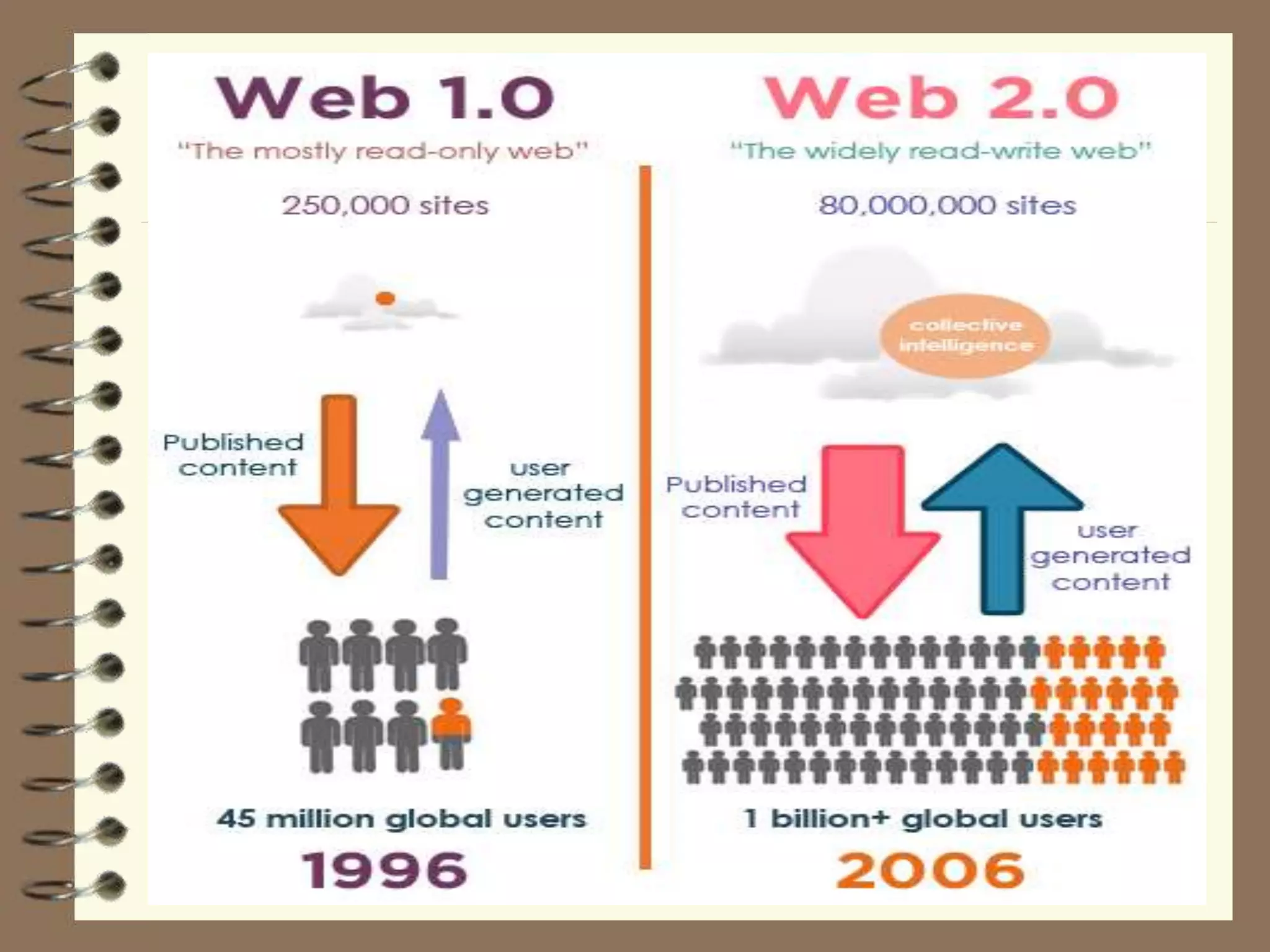
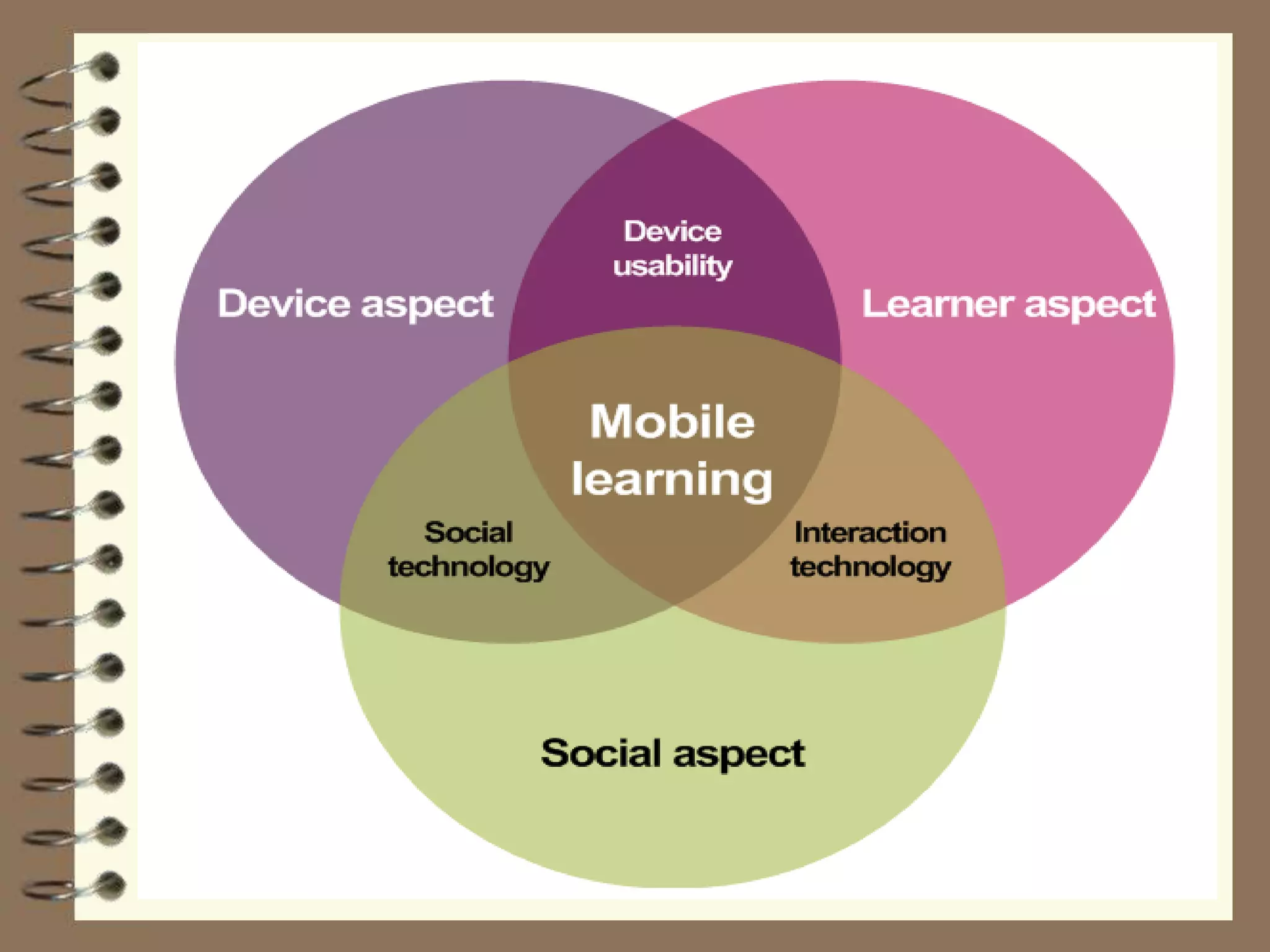
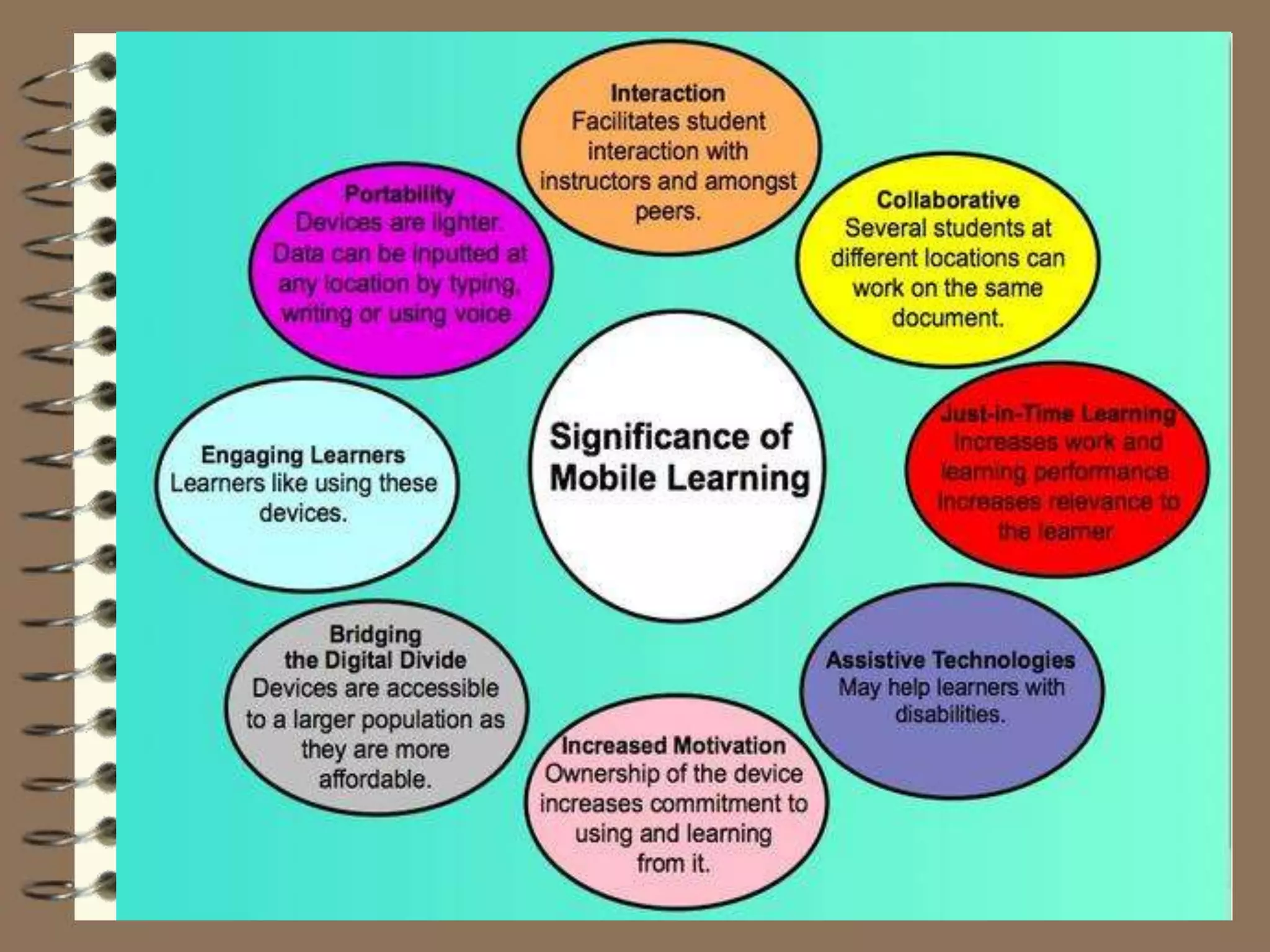
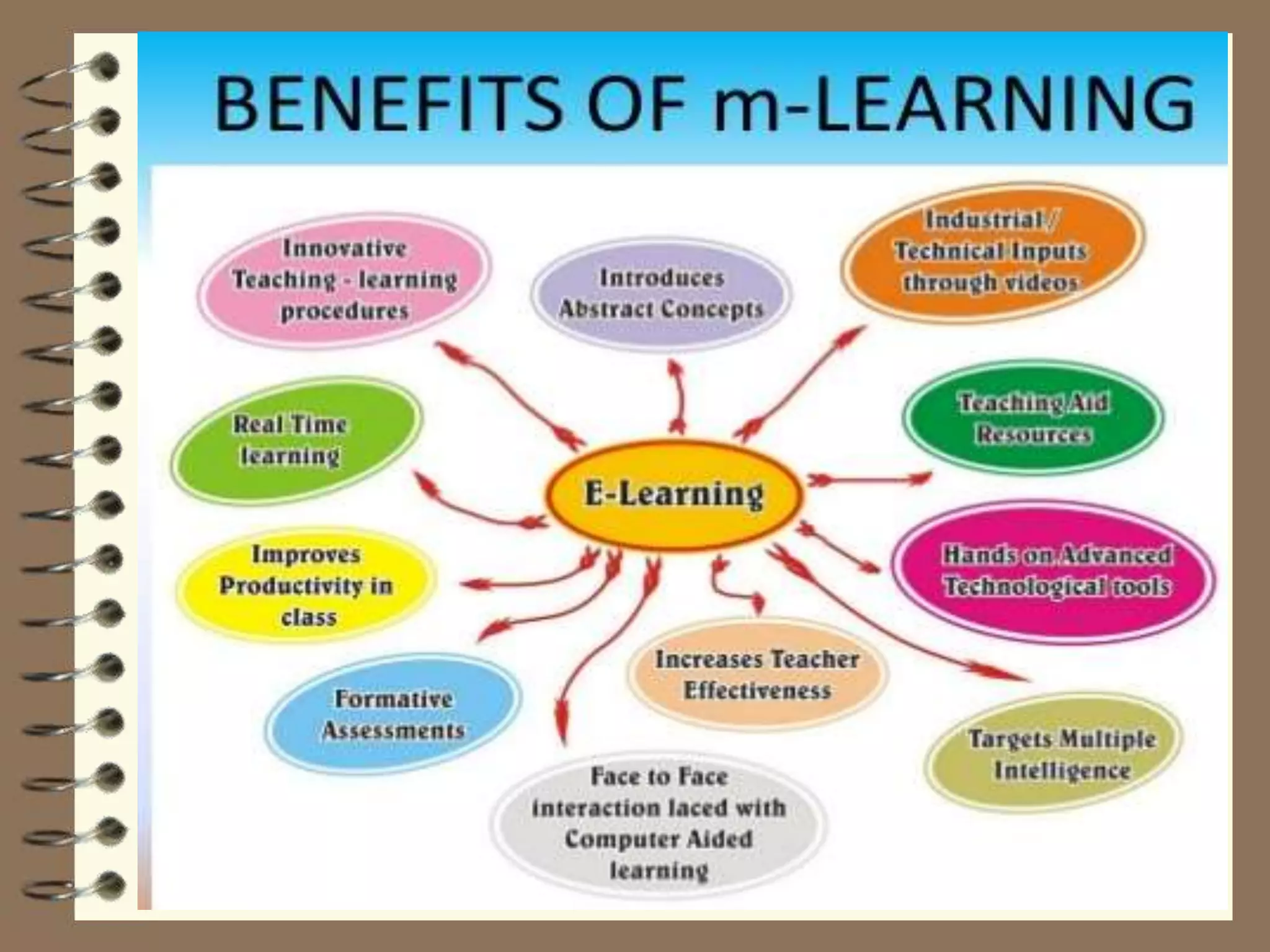
This document discusses Web 2.0 technology and its applications in education. It defines Web 2.0 as websites and applications that allow users to create and share content easily without specialized skills. Some key Web 2.0 applications covered include blogs for sharing opinions, wikis for collaborative writing, podcasts for audio/video files, and social media sites like Facebook and Twitter for networking. Mobile learning (m-learning) using smartphones and tablets is also discussed as a flexible way to access education anywhere.