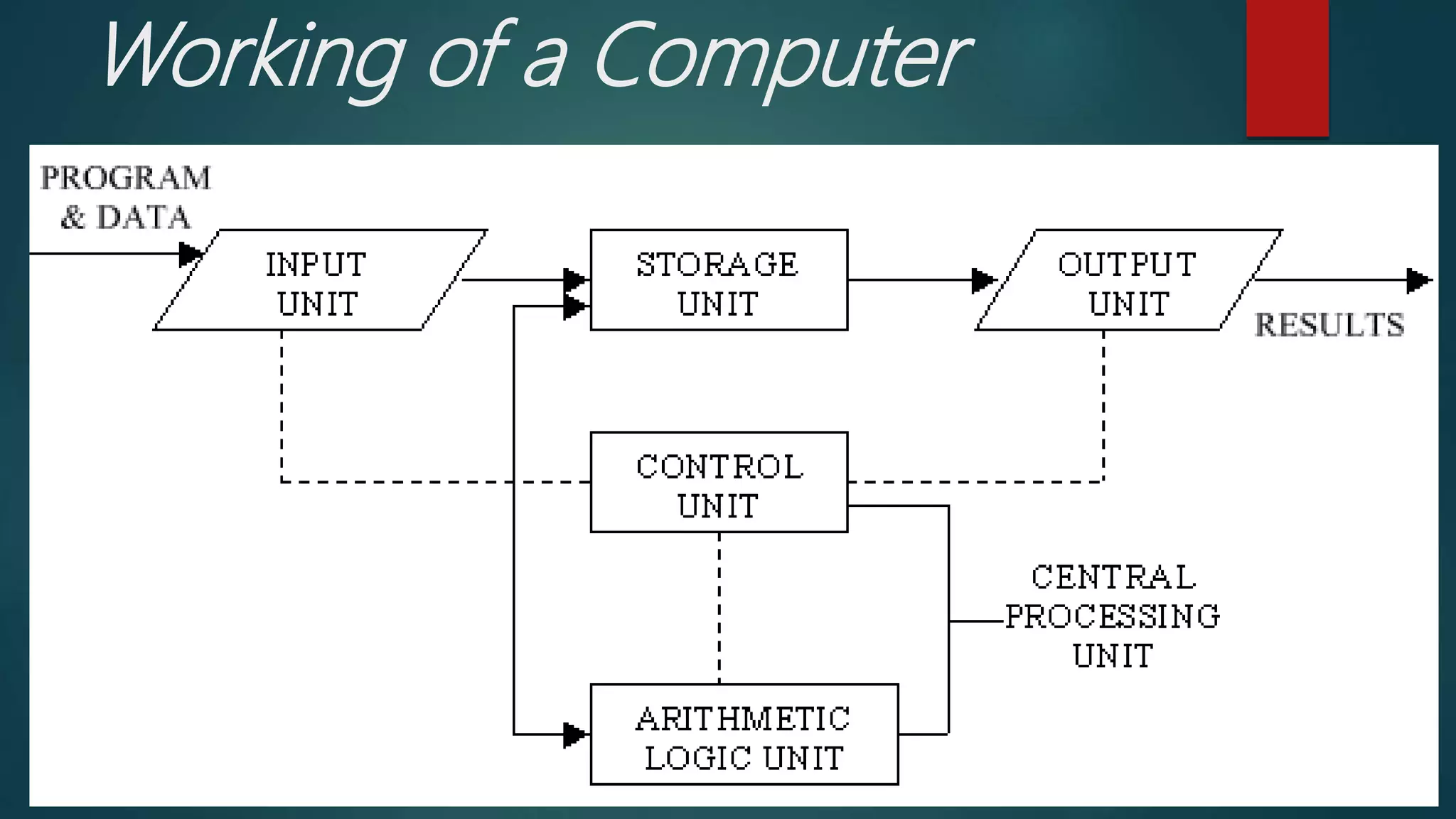
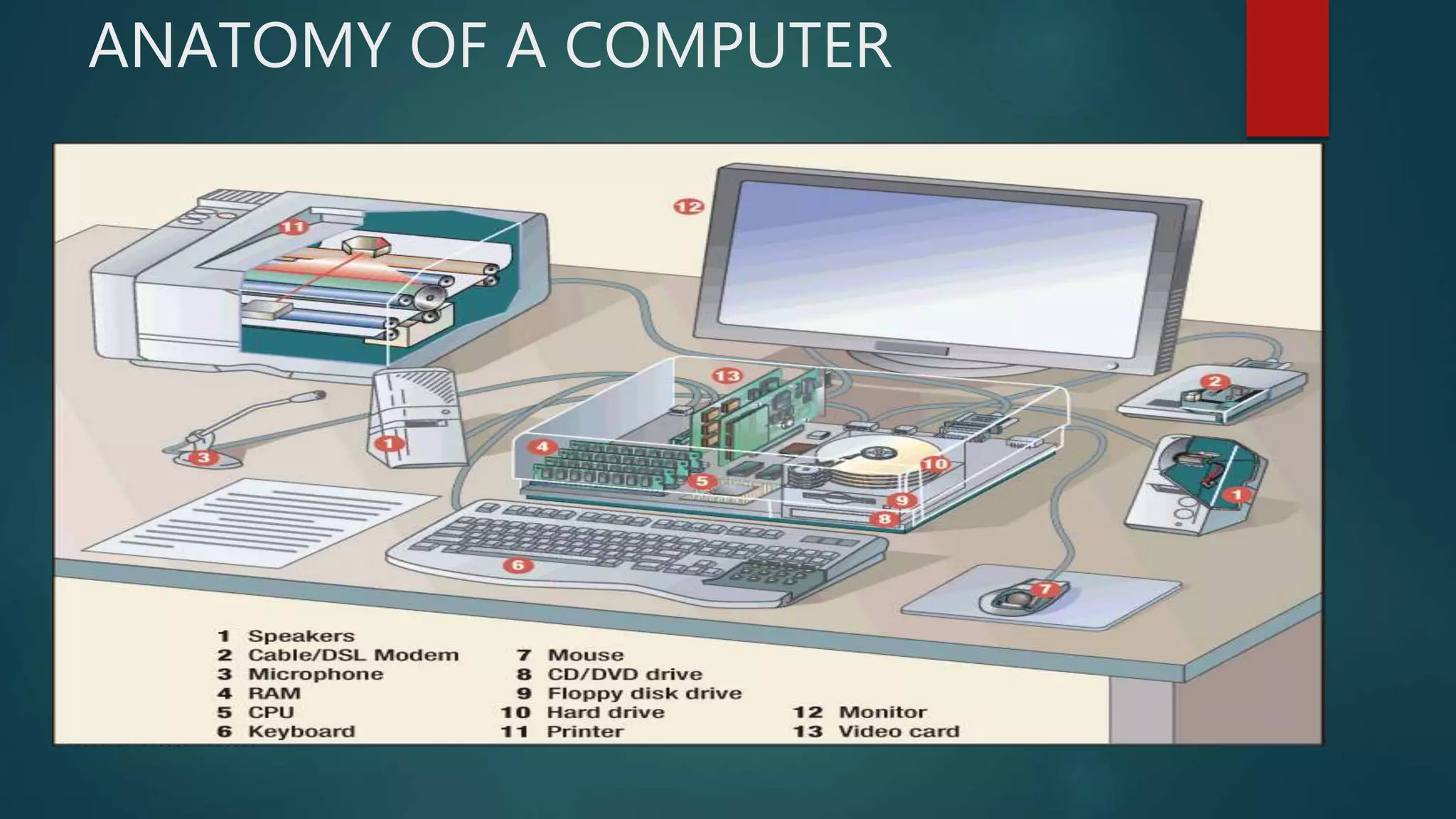
This document discusses information and communication technology (ICT) in learning. It defines ICT and describes the various tools of ICT including informative, situating, constructive, and communicative tools. It explores the uses of ICT in pedagogy, collaboration, assessment, and the learning process. The document also discusses integrating ICT into the classroom and assessment, as well as computer assisted learning and its modes and planning.