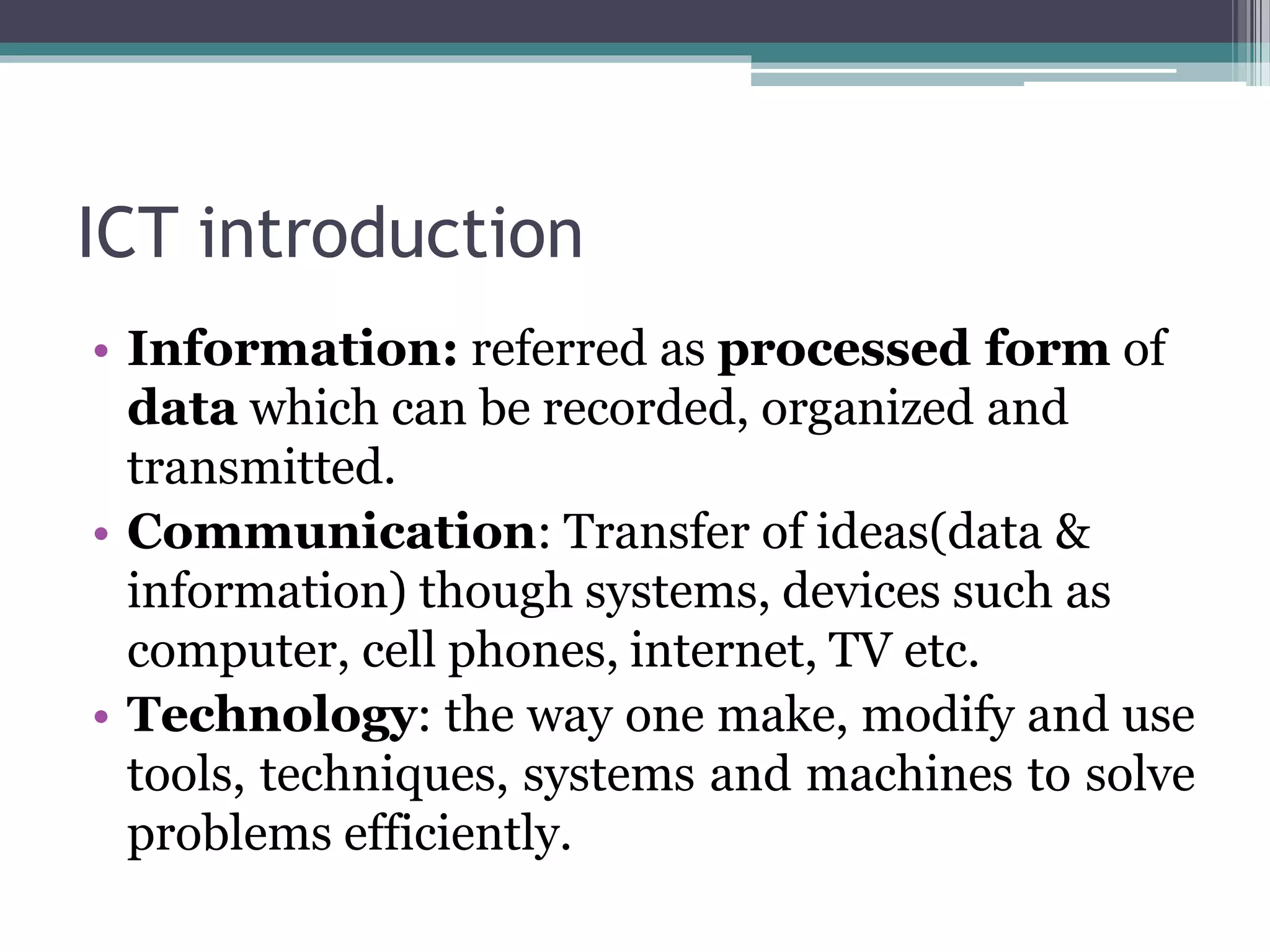
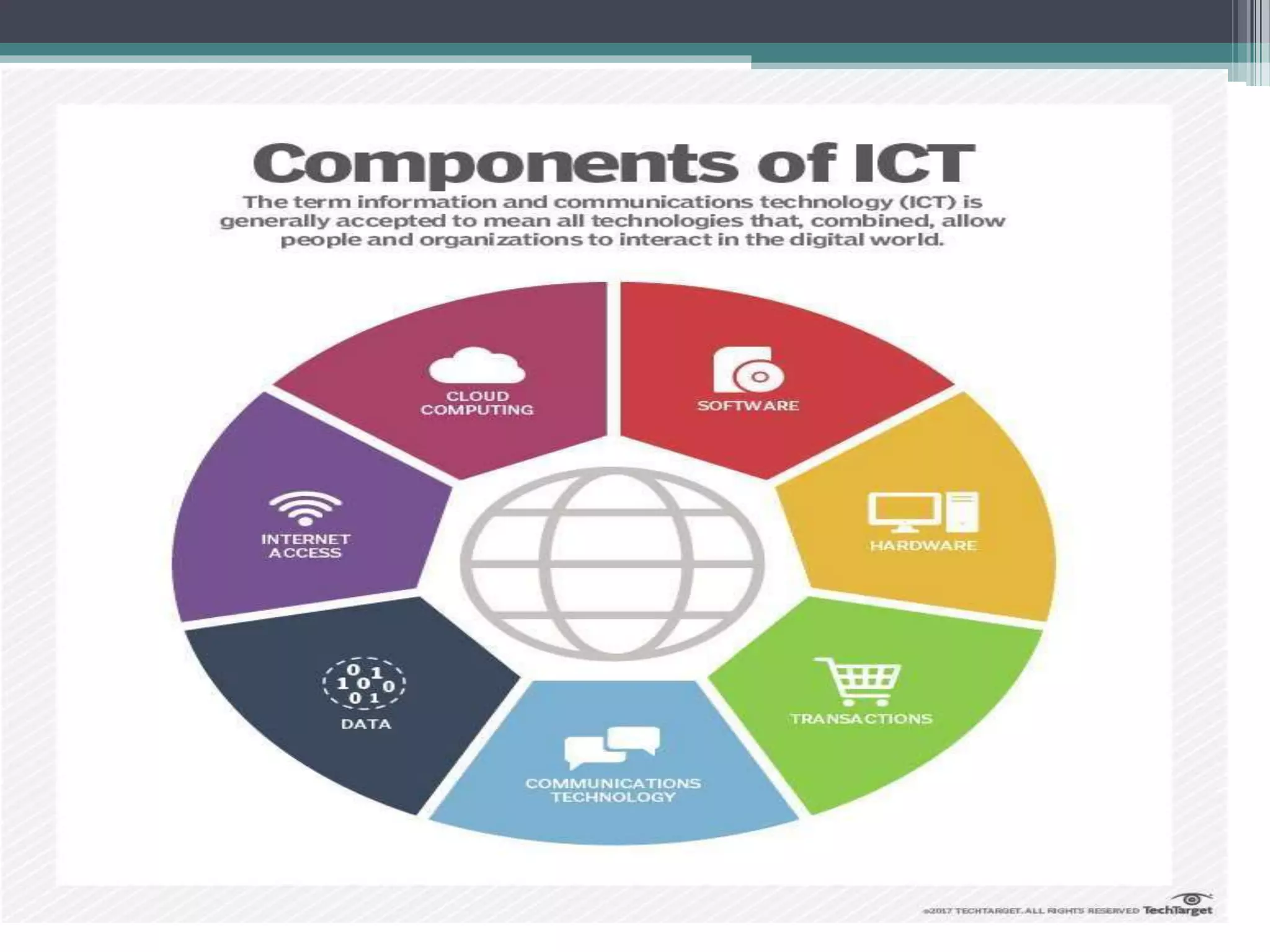
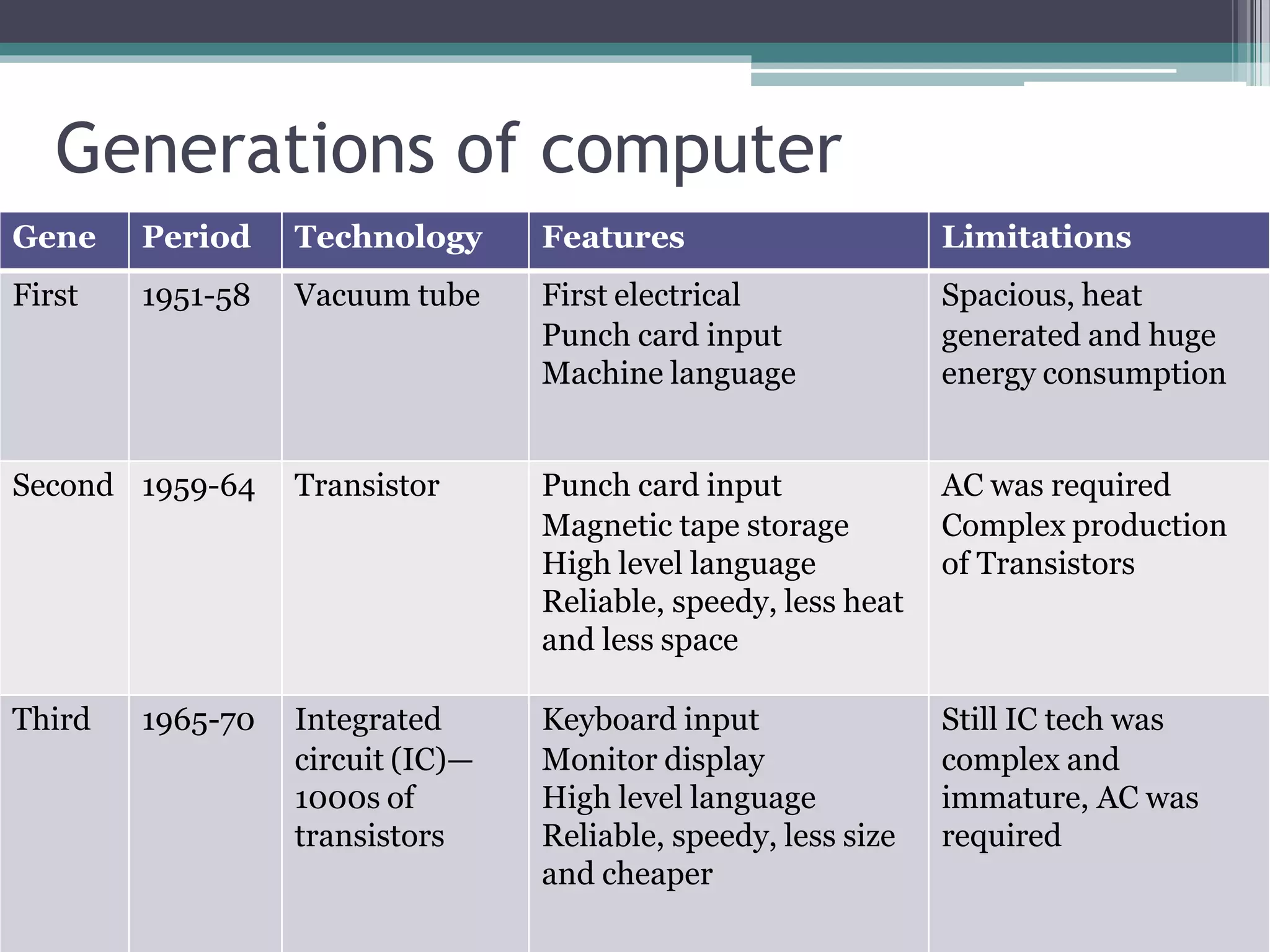
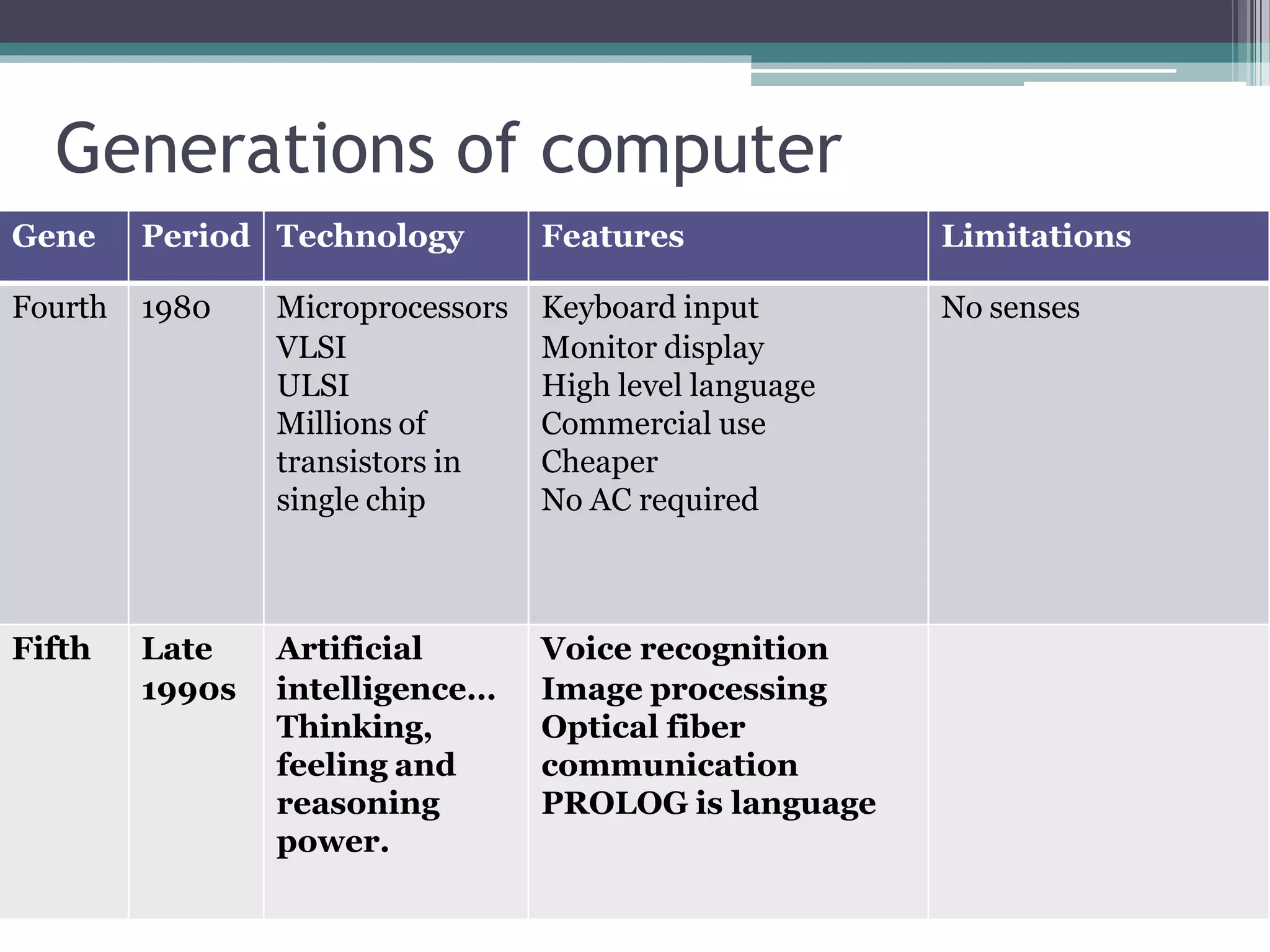
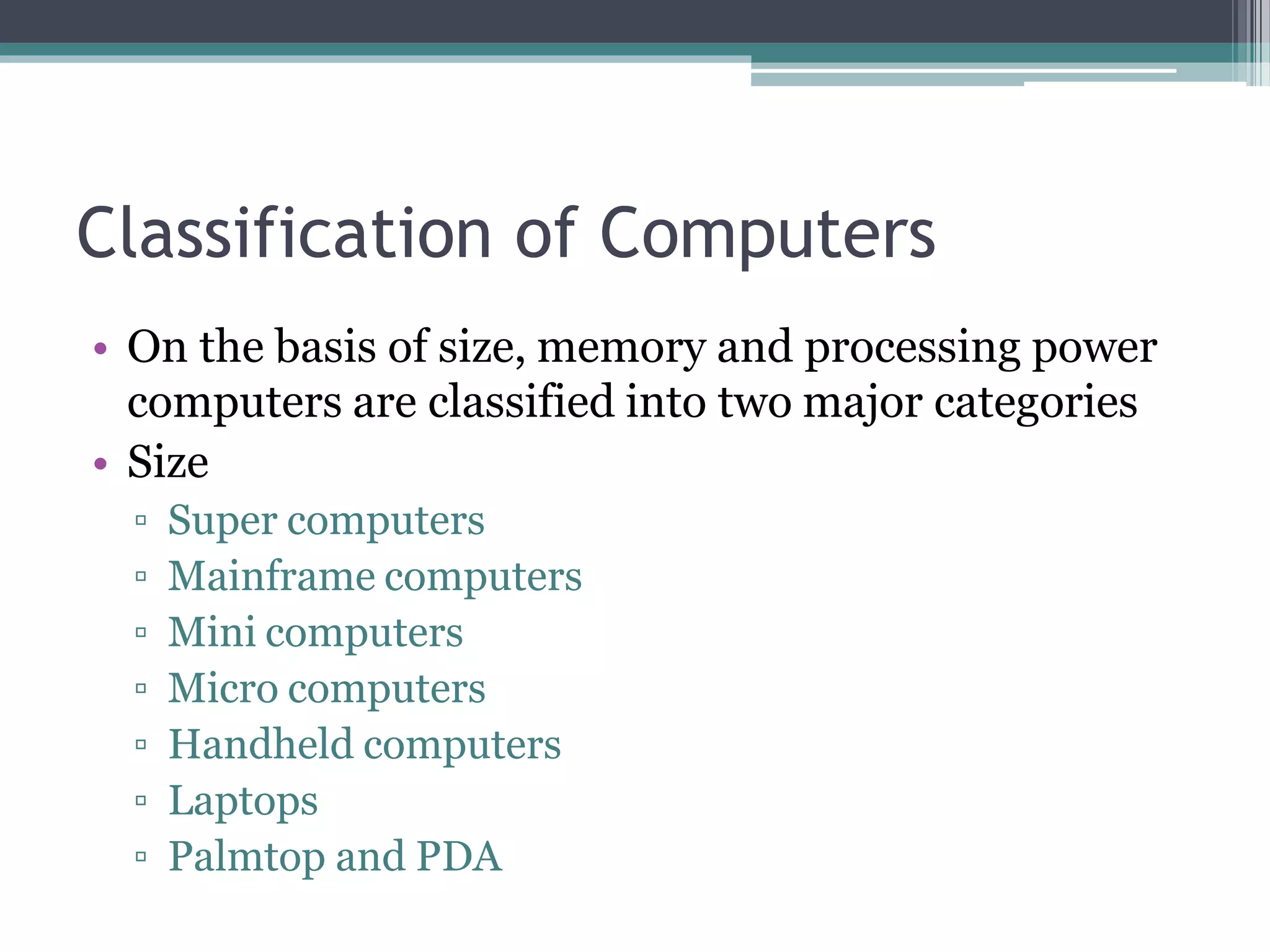
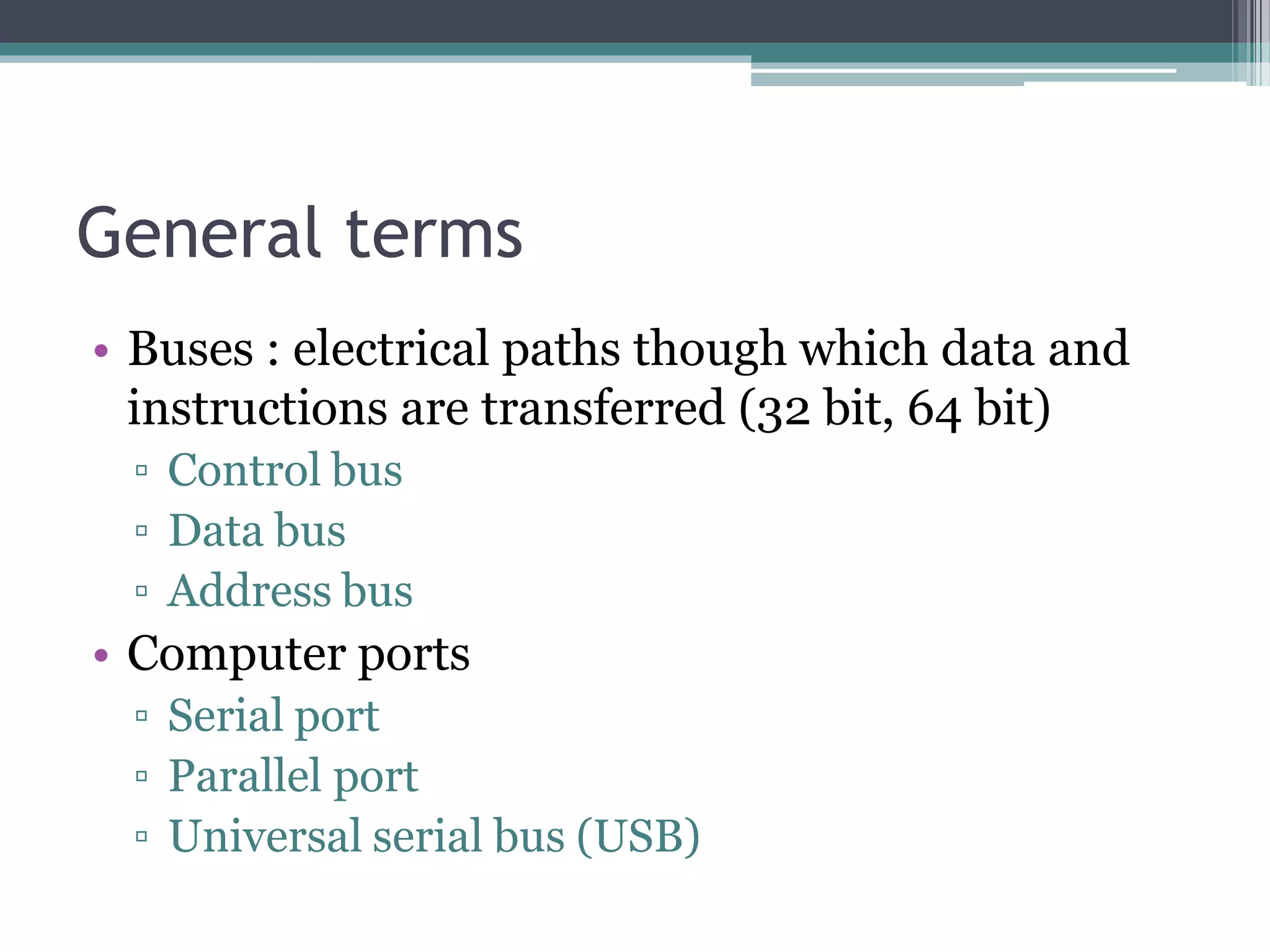
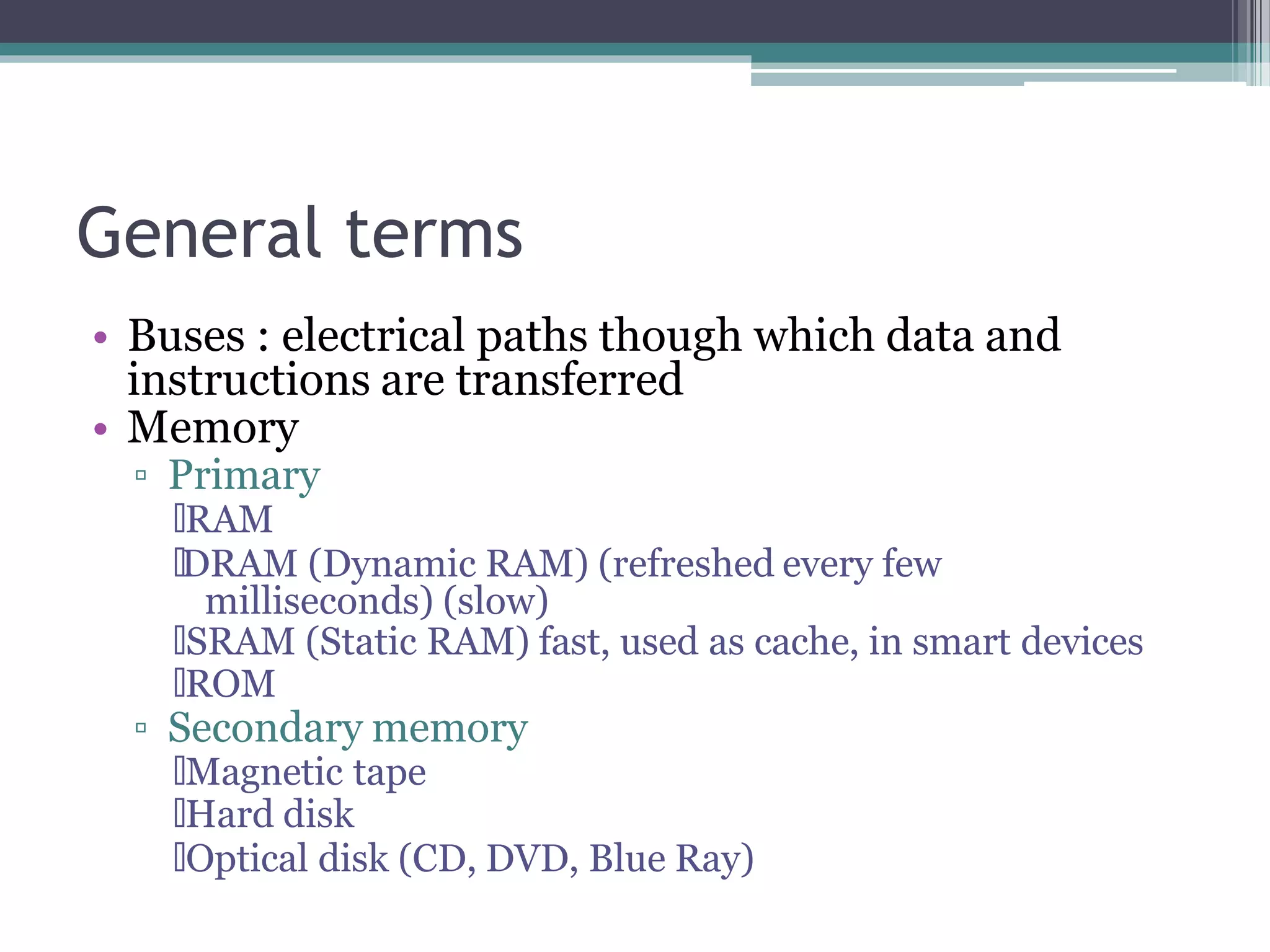
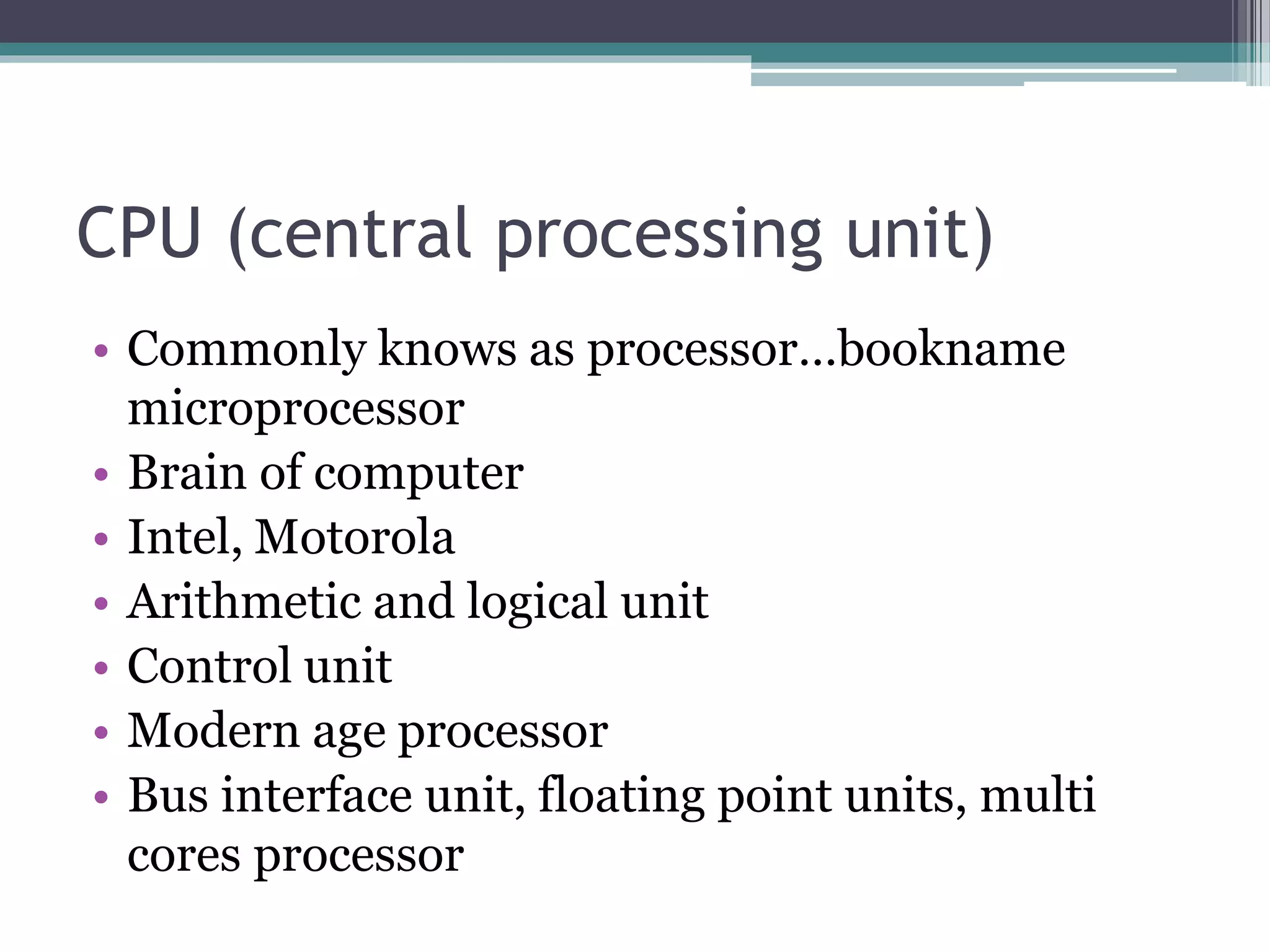
This document provides an introduction to basics of information and communication technology (ICT). It discusses that ICT includes communication devices like cell phones and computers that allow transfer of information. ICT is continuously evolving and comprises manufacturing of equipment, software development, and a variety of services. Major mediums of ICT application include the internet, computers, and cell phones which enable activities like online education, e-commerce, social media, and mobile apps. The document also outlines the benefits of using ICT in teaching and learning, providing examples of how tools like YouTube and Skype can enhance the education experience.