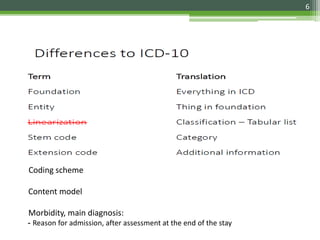
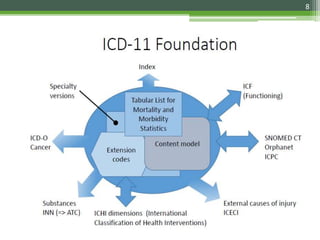
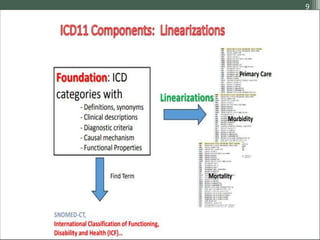
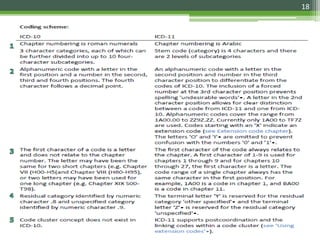
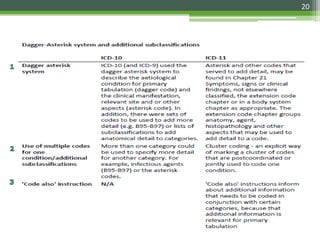
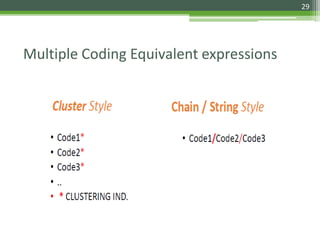
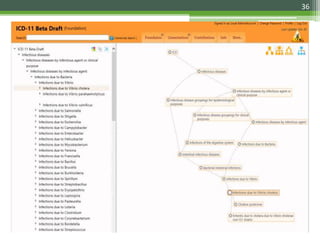
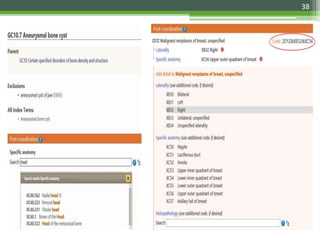
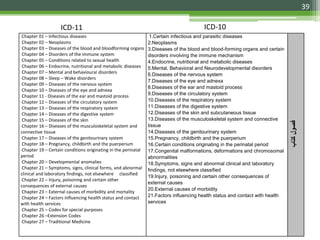
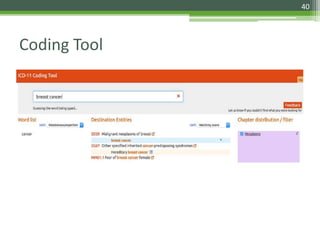
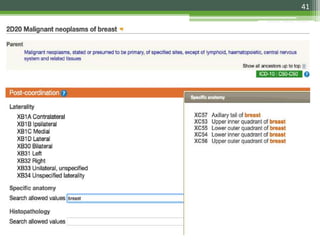
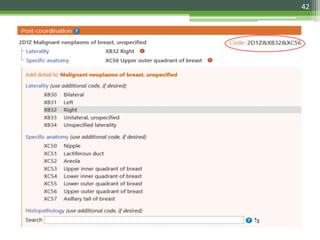
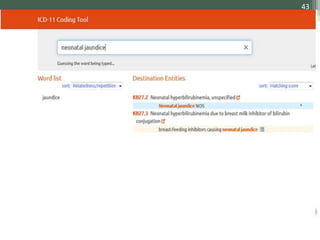
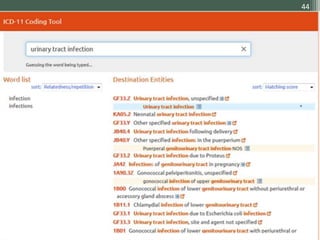
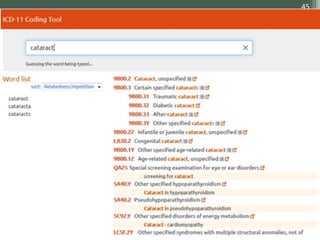
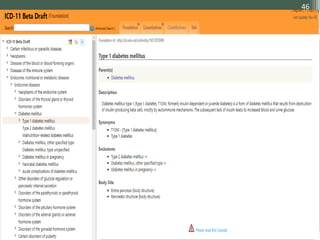
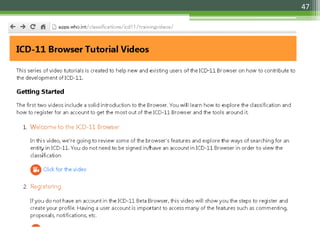
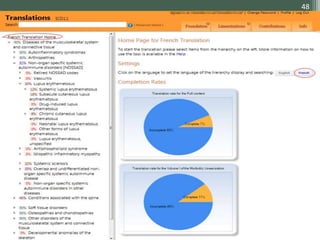
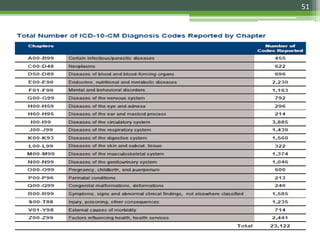
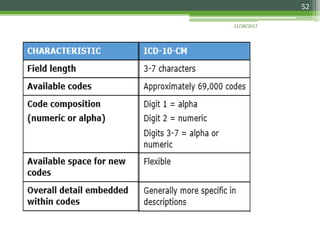
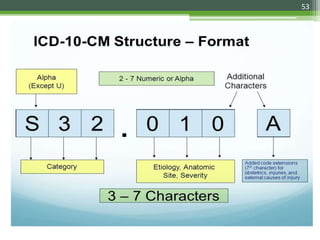
The document details the International Classification of Disease, Eleventh Revision (ICD-11), created by the World Health Organization for documenting medical diagnoses, reflecting modern terminology and accommodating electronic health record environments. It outlines improvements over the previous ICD-10, including updated definitions, a new coding scheme, and the introduction of new chapters and concepts related to various health conditions. The document also highlights the structure, usability, and benefits of ICD-11 in healthcare settings.