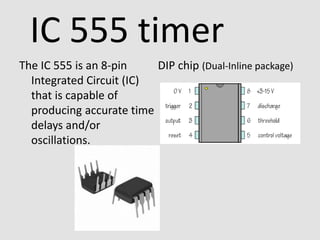
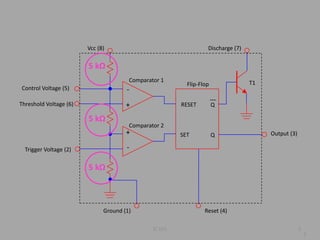
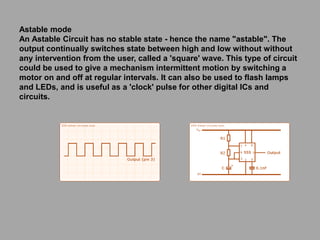
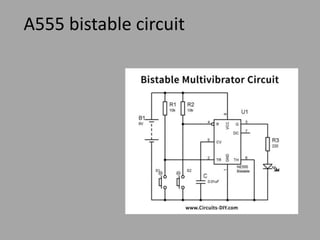
The IC 555 is an 8-pin integrated circuit capable of producing accurate time delays and oscillations. It has three main operating modes - monostable, astable, and bistable - each representing a different type of circuit with a particular output. In astable mode, the output switches continuously between high and low without intervention, producing a square wave. In monostable mode, the output stays low until triggered and then produces one pulse of set length. In bistable mode, the two stable states are high and low, and inputs trigger or reset the state.