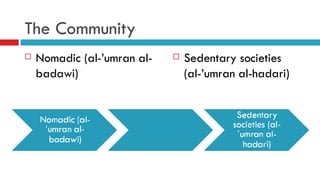
Ibn Khaldun was an influential 14th century Muslim scholar, historian and sociologist. He is considered a forerunner of modern sociology, historiography and economics for his theories on social conflict, the rise and fall of civilizations, and other social sciences. In his magnum opus, Muqaddimah, he developed theories around the concepts of asabiyyah (social cohesion) and umran (civilization) to explain the rise and fall of dynasties and empires. The Muqaddimah covered topics like sedentary and nomadic cultures, social organization, politics, economics and other intellectual sciences in a philosophical and sociological manner that was ahead of his time.



![Biography Arab Scholar Medieval era Name Ibn Khaldun [Abū Zayd ‘Abdu r-Raḥman bin Muḥammad bin Khaldūn al-Ḥaḍramī] Birth 27 May, 1332/732 AH Death 19 March, 1406/808 AH School / Tradition Ash'ari [It was instrumental in drastically changing the direction of Islamic theology, separating its development radically from that of theology in the Christian world.] Main Interests Sociology, History, Historiography, Demography, Economics, Philosophy of History, Notable Ideas Asabiyah Influences Al-Razi [a fundamental and enduring contributions to the fields of medicine, alchemy, and philosophy, recorded in over 184 books and articles in various fields of science.] Influenced Al-Maqrizi, Social sciences [remarkable in this context for his unusually keen interest in the Ismaili Fatimid dynasty and its role in Egyptian history]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ibnu-khaldun3857/85/Ibnu-Khaldun-4-320.jpg)


![Education & Early Years Family social and political activist received a classical Arabic education, studying the Qur'an and Arabic linguistics, the basis for an understanding of the Qur'an, Hadith [1] and Fiqh [2] mathematics, logic and philosophy lost both his parents to an epidemic of the plague which hit Tunis, when he was 17 years old In a typical Muslim family, follow family tradition is common, that is where he strove for a political career And he life adventure begin, in which he spends time in prison, reaches the highest offices and falls again into exile. [1] Hadith relating to the words and deeds of Prophet Muhammad. [2] Fiqh is an expansion of Islamic law, complemented by the rulings of Islamic jurists to direct the lives of Muslim](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ibnu-khaldun3857/85/Ibnu-Khaldun-7-320.jpg)