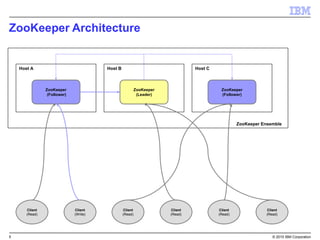
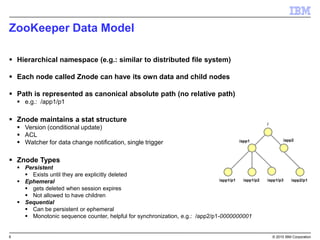
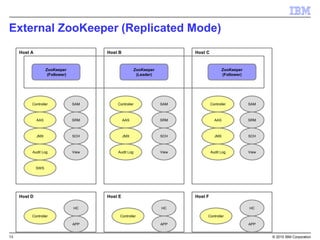
The document provides an overview of Apache Zookeeper as a distributed coordination service, detailing its architecture, data model, and consistency guarantees. It distinguishes between embedded and external Zookeeper and outlines best practices for deployment and management in production environments. Important disclaimers regarding the reliability of the information and potential future product plans are also included.