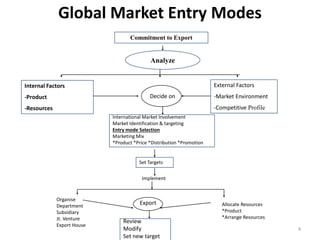
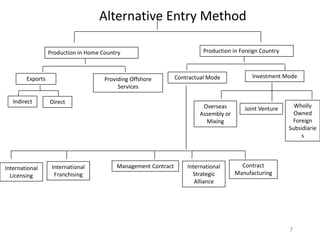
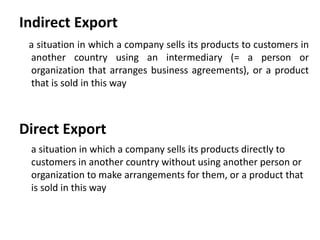
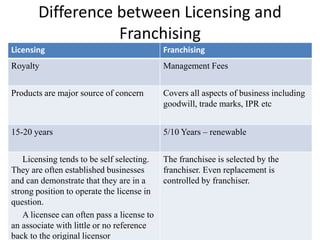
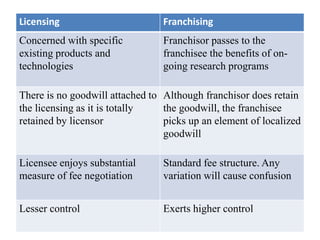
This document discusses various methods for companies to enter foreign markets. It describes options ranging from low-risk contractual arrangements like indirect exports, licensing, and contract manufacturing to higher-risk/control options like joint ventures and wholly owned foreign subsidiaries. For each option, it provides details on characteristics, requirements, and examples. The key factors that companies should analyze in choosing a market entry strategy are the level of control, financial commitment, and risk associated with each alternative.