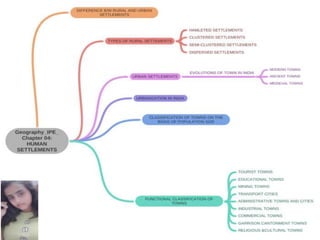
The document discusses human settlements, defining them as areas inhabited by people, ranging from small hamlets to large metropolitan cities. It classifies settlements into rural and urban categories, highlighting differences in population size, standard of living, and primary vs. secondary/tertiary occupations. Various types of rural settlements are described, including clustered, semi-clustered, dispersed, and hamleted settlements, along with factors influencing their formation and characteristics.