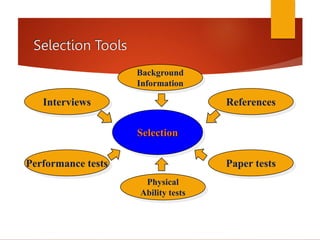
Human resource management involves planning, recruiting, selecting, training, and rewarding employees to help organizations meet their goals. The key functions of HRM include recruitment and selection of candidates, training and developing employees, conducting performance reviews, determining pay and benefits, and managing labor relations. HRM aims to satisfy both organizational and individual needs through activities that attract, retain, and ensure high performance from qualified staff.