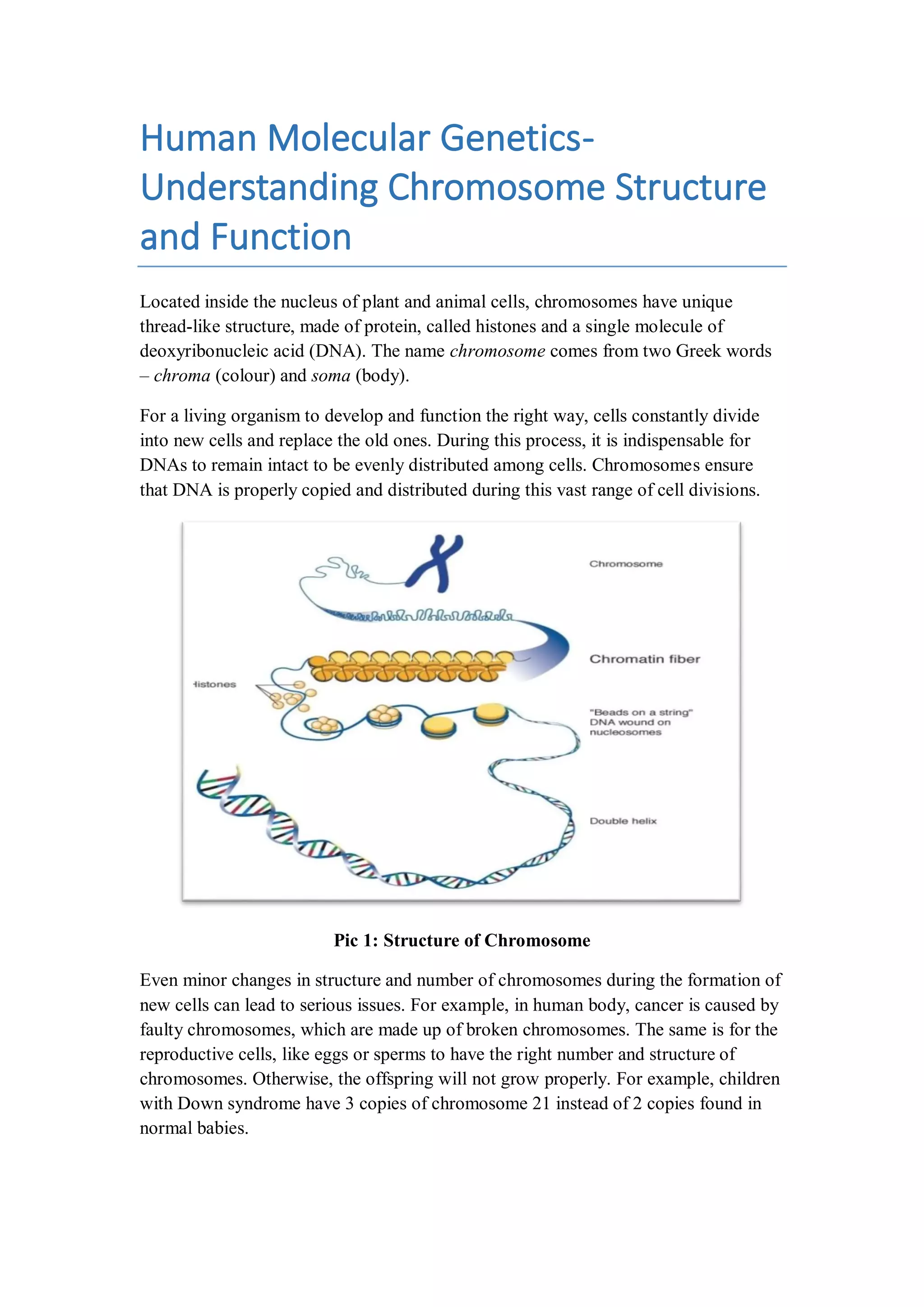
Chromosomes, found in the nucleus of plant and animal cells, are composed of histones and DNA, ensuring proper copying and distribution during cell division. Changes in chromosome structure or number can lead to serious conditions, such as cancer or genetic disorders like Down syndrome. Human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes, inherited from both parents, and advancements in genetics have significantly enhanced our understanding of these structures since the 1990s.