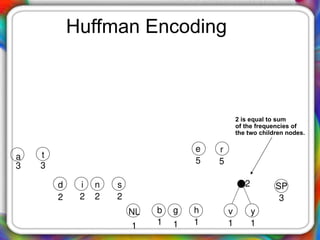
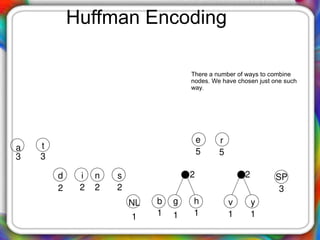
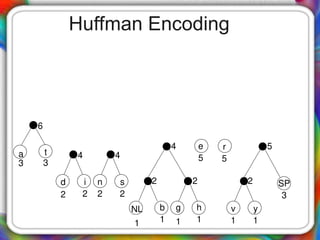
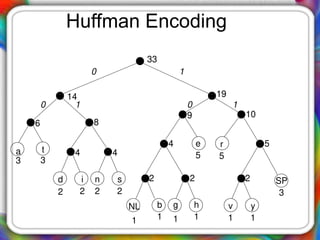
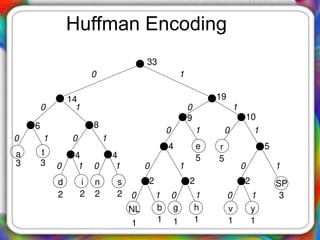
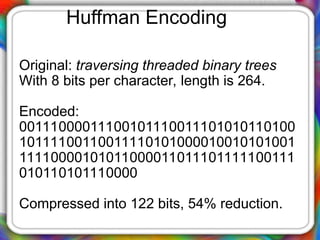
The document discusses Huffman encoding, a data compression method that utilizes binary trees to assign variable-length codes to characters based on their frequency of occurrence. It highlights the effectiveness of Huffman encoding by demonstrating a compression example with the phrase 'traversing threaded binary trees', reducing its size significantly from 264 bits to 122 bits. The process of creating the Huffman tree involves combining nodes of the lowest frequencies until only a root remains, ultimately leading to the assignment of unique binary codes for each character.