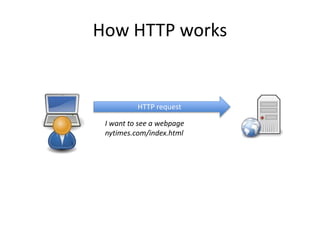
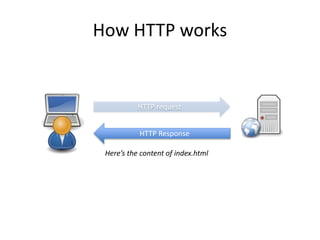
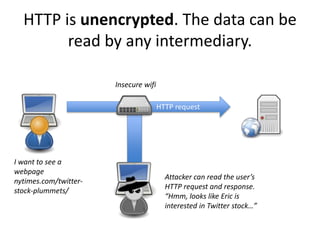
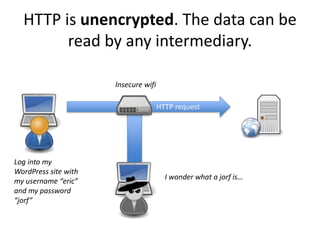
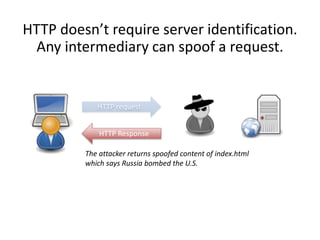
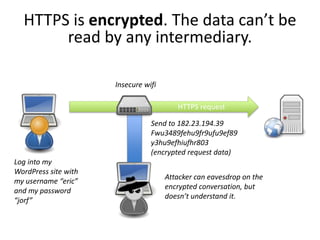
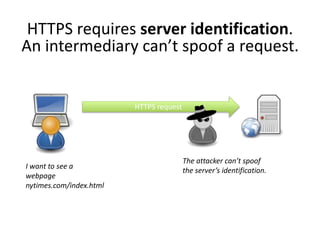
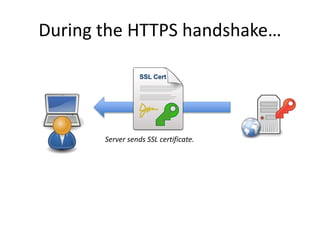
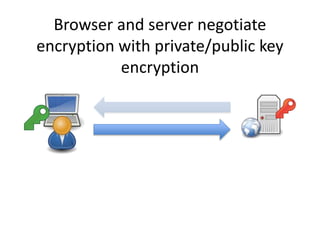
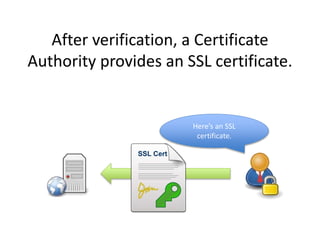
HTTPS provides encryption for HTTP requests and responses to protect data from intermediaries. It encrypts all data except the destination address and uses server certificates and encryption between the browser and server to authenticate identity and enable secure communication. While HTTPS does not prevent brute force attacks, it protects against eavesdropping, content spoofing, and helps websites rank higher on search engines. Certificate Authorities verify server identities and issue signed certificates that browsers recognize to establish encrypted connections.