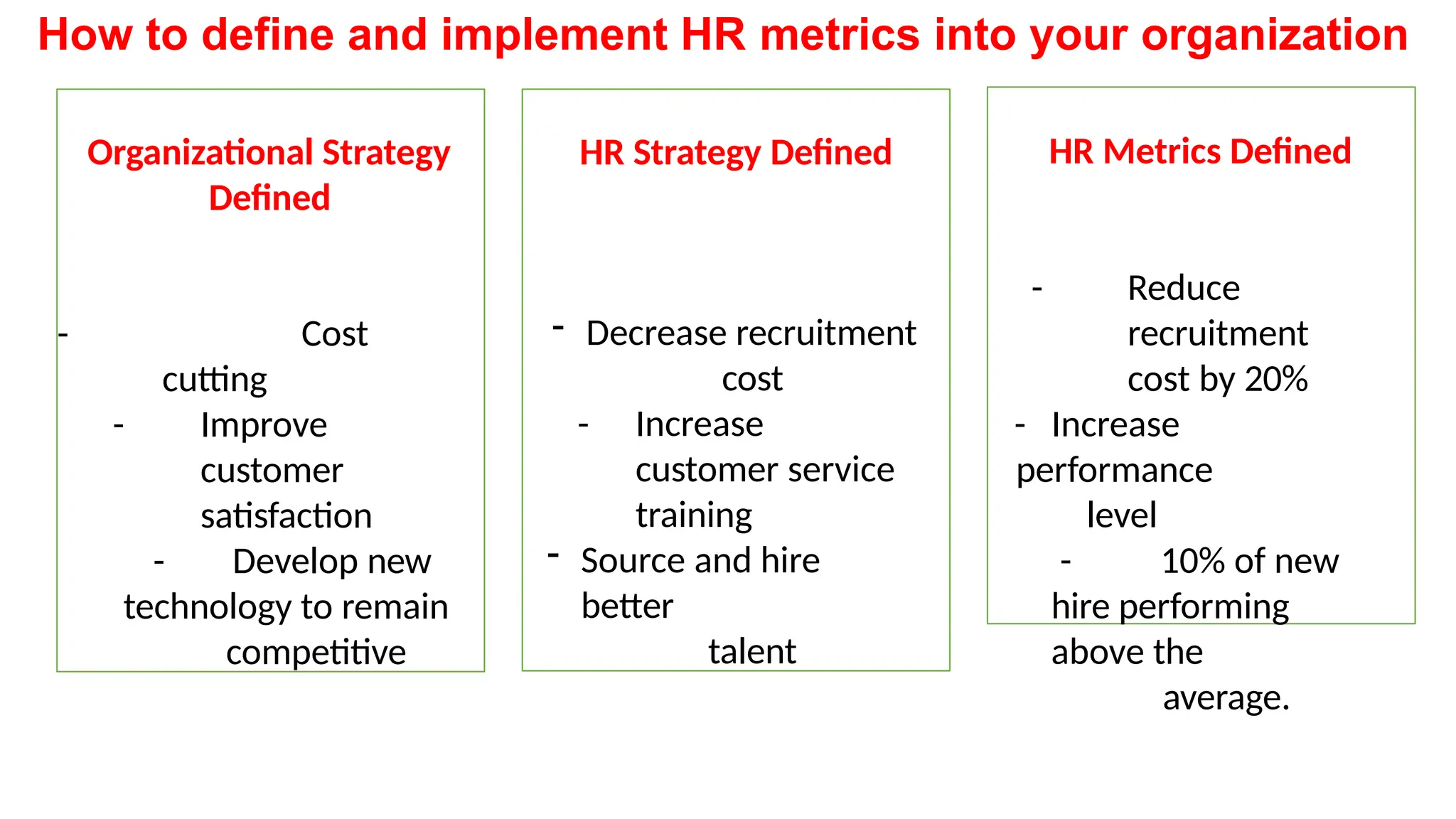
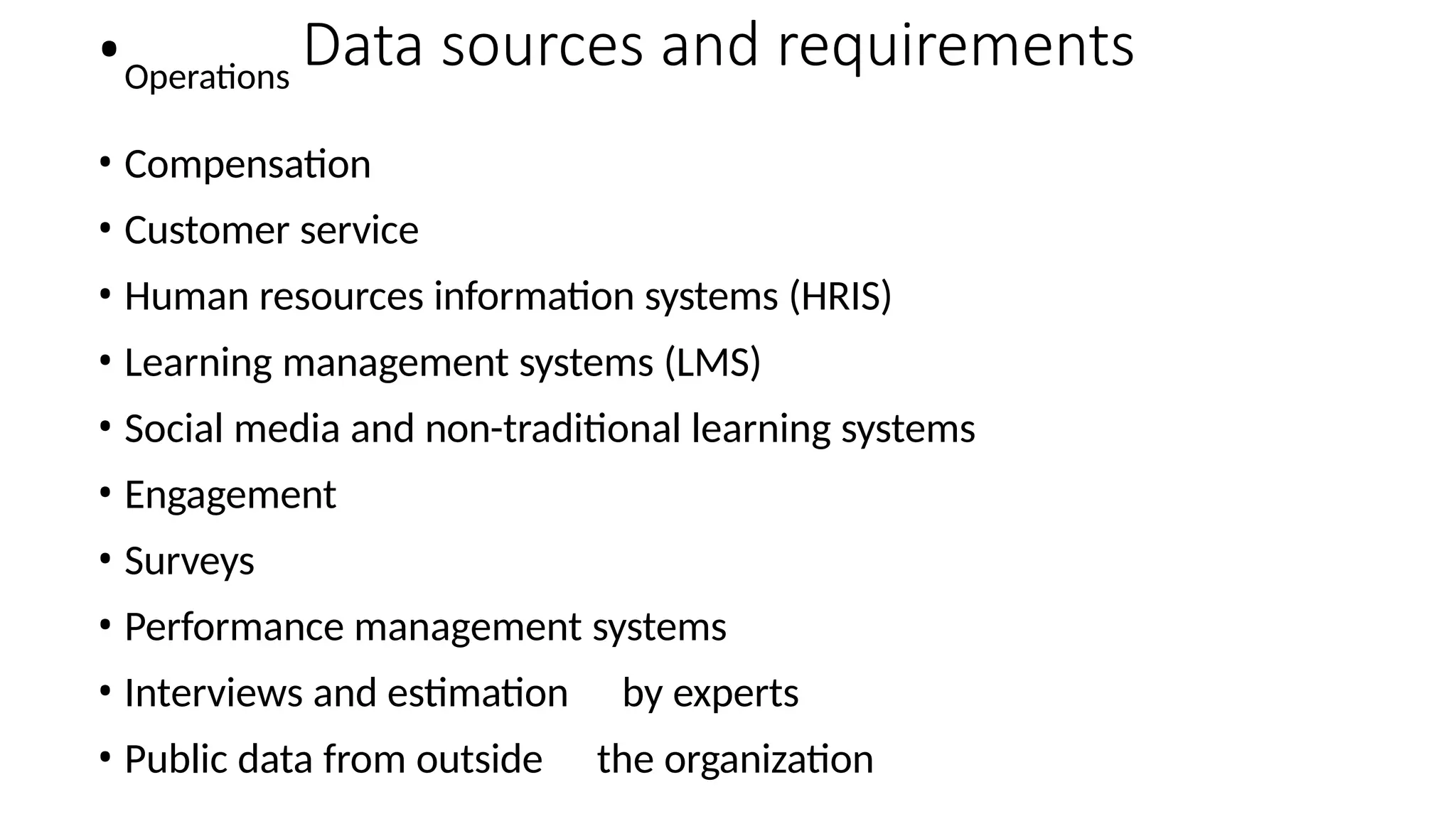
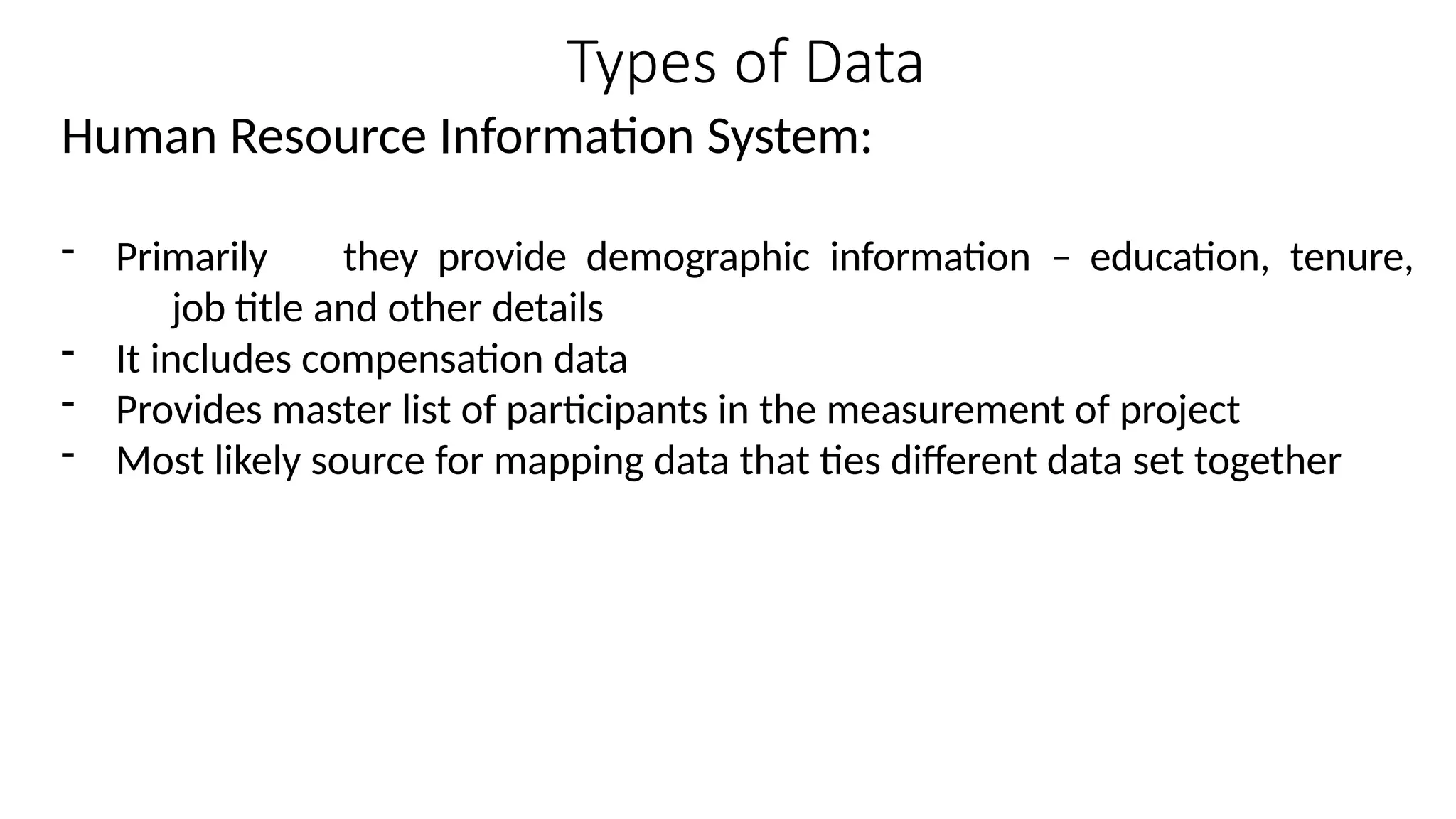
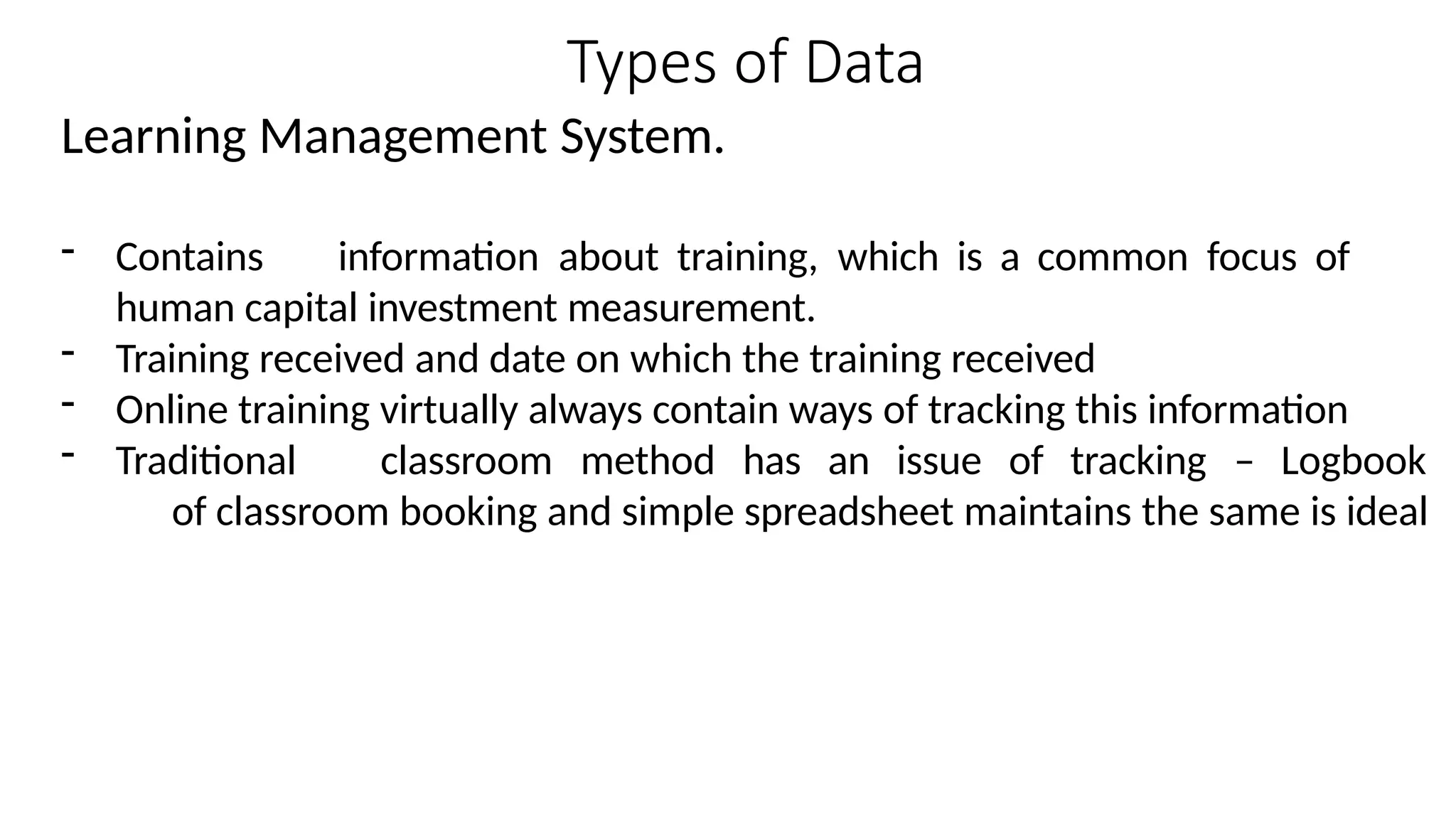
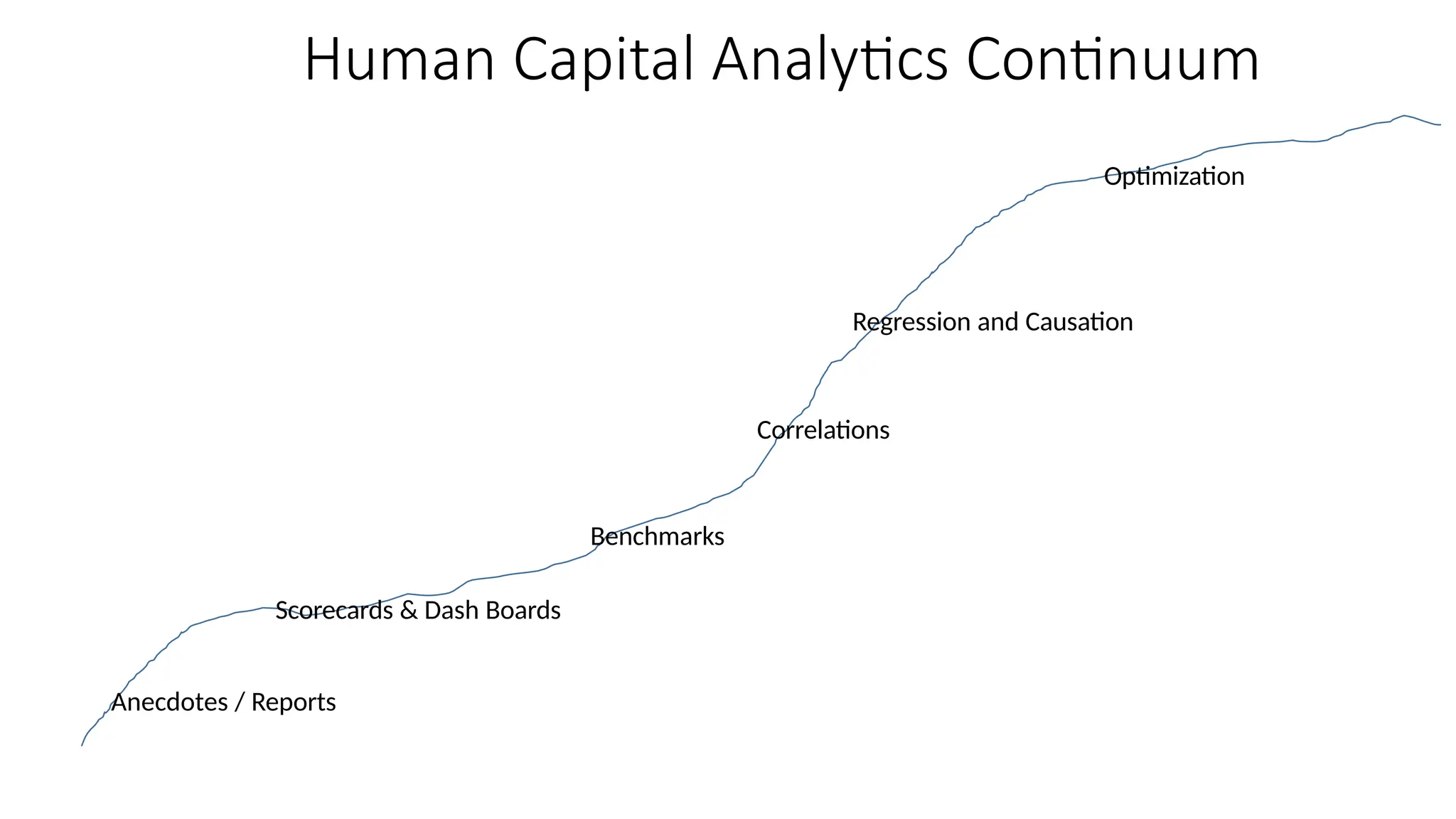
The document discusses the importance of human resource (HR) metrics for measuring the effectiveness of HR initiatives, which include areas like turnover and training. It emphasizes the strategic role of HR in aligning metrics with organizational goals and making data-driven decisions, as well as the various sources and types of data required for these metrics. Additionally, it touches on the ethical considerations in collecting and analyzing HR data to ensure confidentiality and proper use.