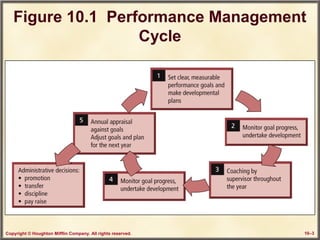
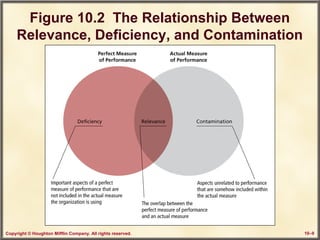
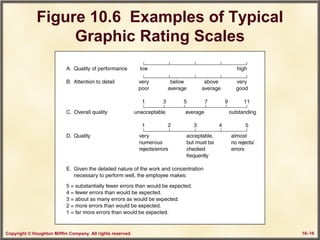
This chapter discusses performance assessment and management in organizations. It covers the strategic importance of linking assessment to organizational goals and values. Performance assessment serves developmental functions like goal setting and career planning, as well as administrative functions like determining compensation. The chapter examines criteria for an effective assessment system, such as validity, reliability and freedom from bias. It also explores methods of appraising performance both objectively and subjectively, as well as strategies for improving the assessment process.