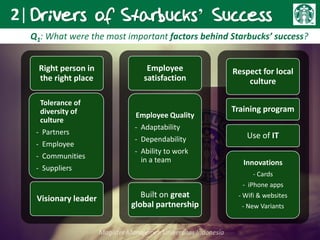
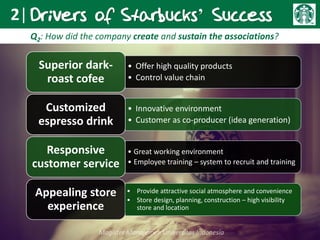
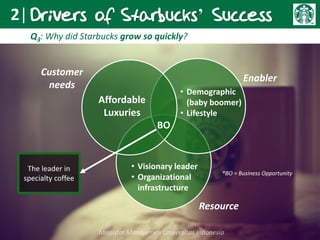
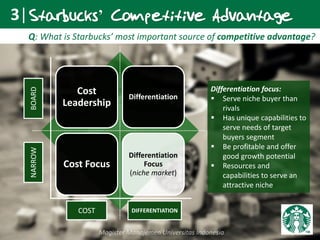
Howard Schultz founded Starbucks in 1987 after purchasing the small Seattle-based coffee chain. Under his leadership, Starbucks grew rapidly by establishing specialty coffee shops across North America and beyond. Key factors in Starbucks' success included Schultz's entrepreneurial vision, a focus on high-quality coffee and customer experience, and strategic expansion. While rapid growth brought management challenges, Starbucks differentiated itself through its coffee expertise and ability to create a welcoming third place environment for customers. To remain competitive, Starbucks must continue innovating its offerings while retaining the qualities that have made its brand successful globally.