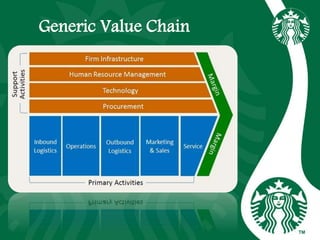
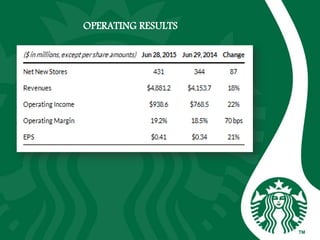
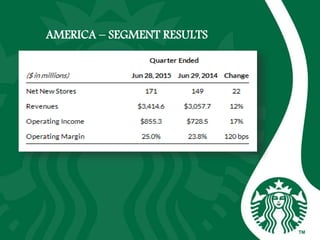
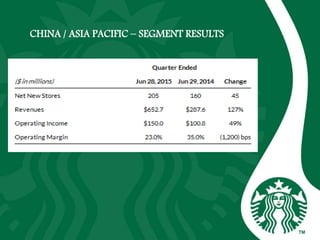
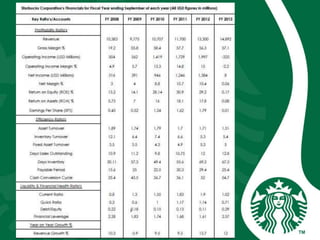
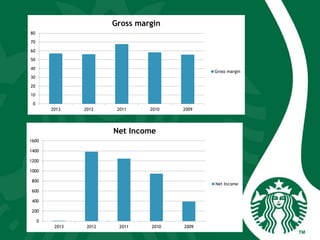
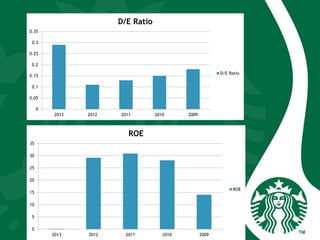
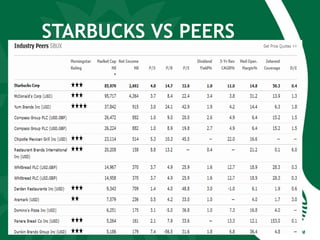
Starbucks was founded in 1971 in Seattle, Washington and initially sold high quality coffee beans and equipment. It has since expanded globally through acquisitions, joint ventures, and licensing agreements. Starbucks now has over 30,000 stores in 80 countries. It entered new markets like Japan, the UK, and China by establishing joint ventures and adapting to local coffee and tea cultures. While global expansion has increased revenues, some markets like France incurred initial losses. Cultural diversity is important to the company and stores aim to respect local traditions.