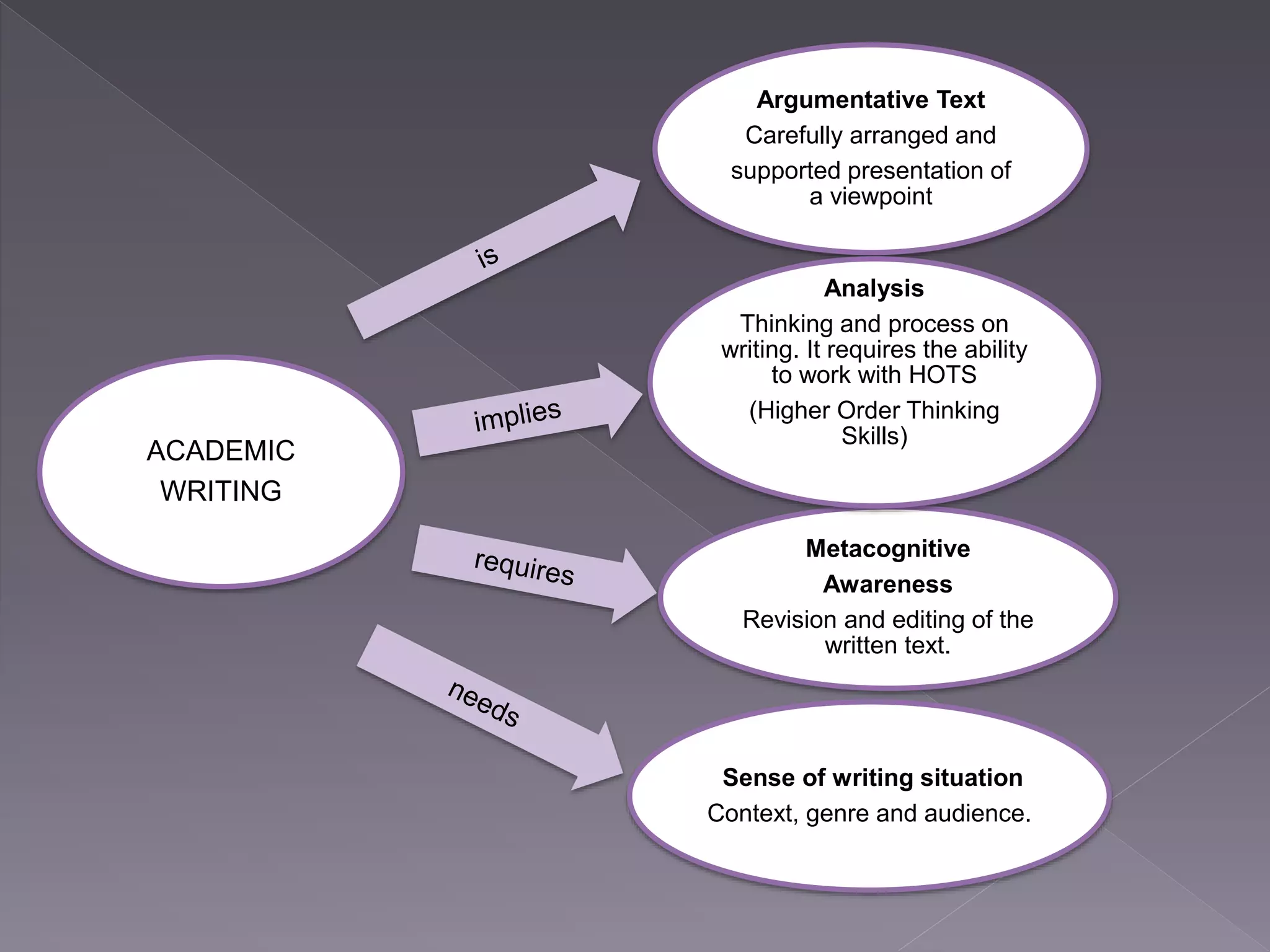
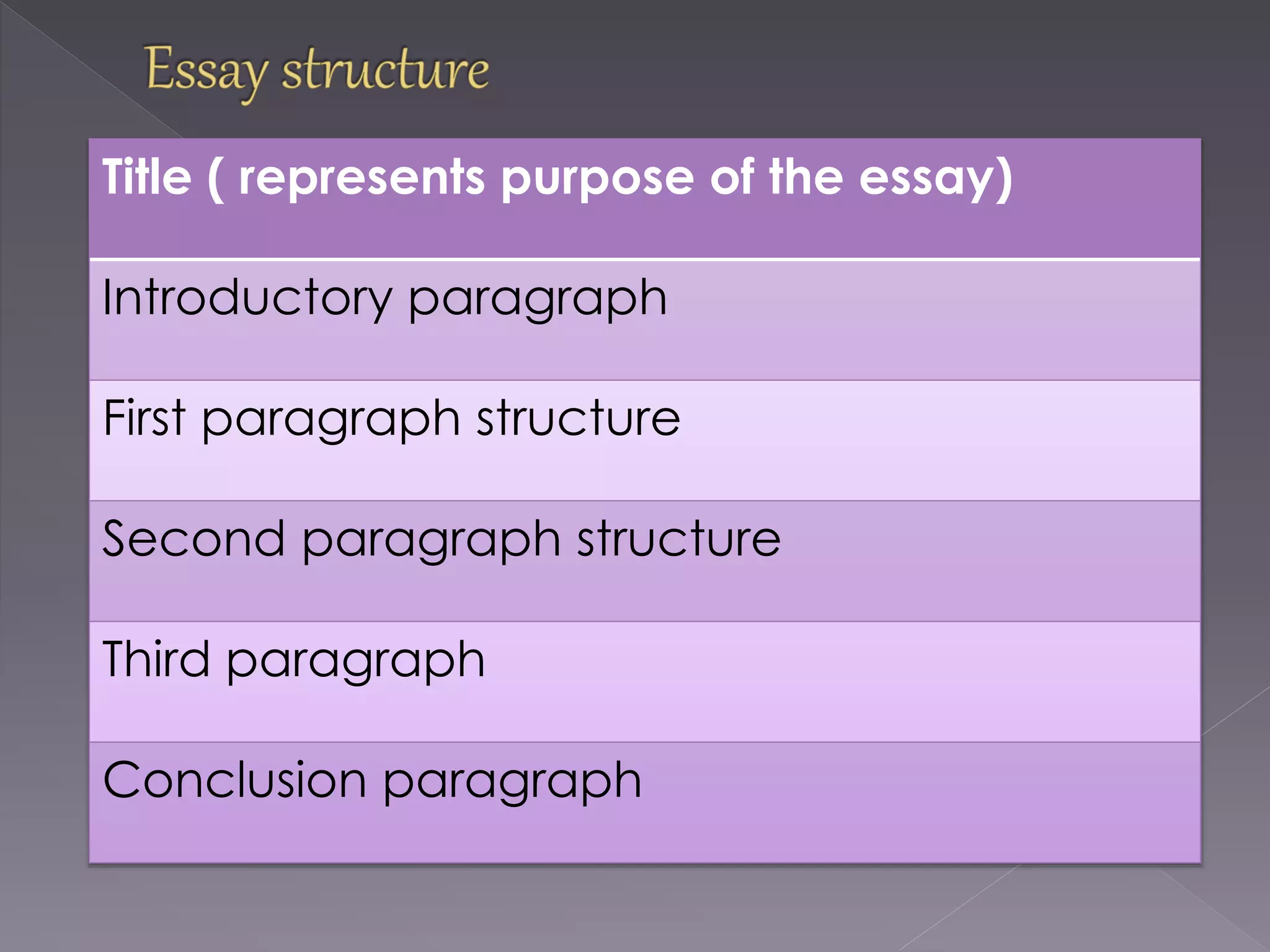
This document provides guidance on academic writing. It discusses the key components of an argumentative text, including presenting a viewpoint with careful arrangement and support. It emphasizes the importance of revision and editing to strengthen analysis and thinking. The document then outlines the structure for an academic essay, including an introductory paragraph with a thesis statement, three body paragraphs with topic sentences and evidence to support the thesis, and a conclusion paragraph. It provides examples of transition words to connect ideas between sentences and paragraphs. Finally, it discusses research, style, and the editing process for academic writing.