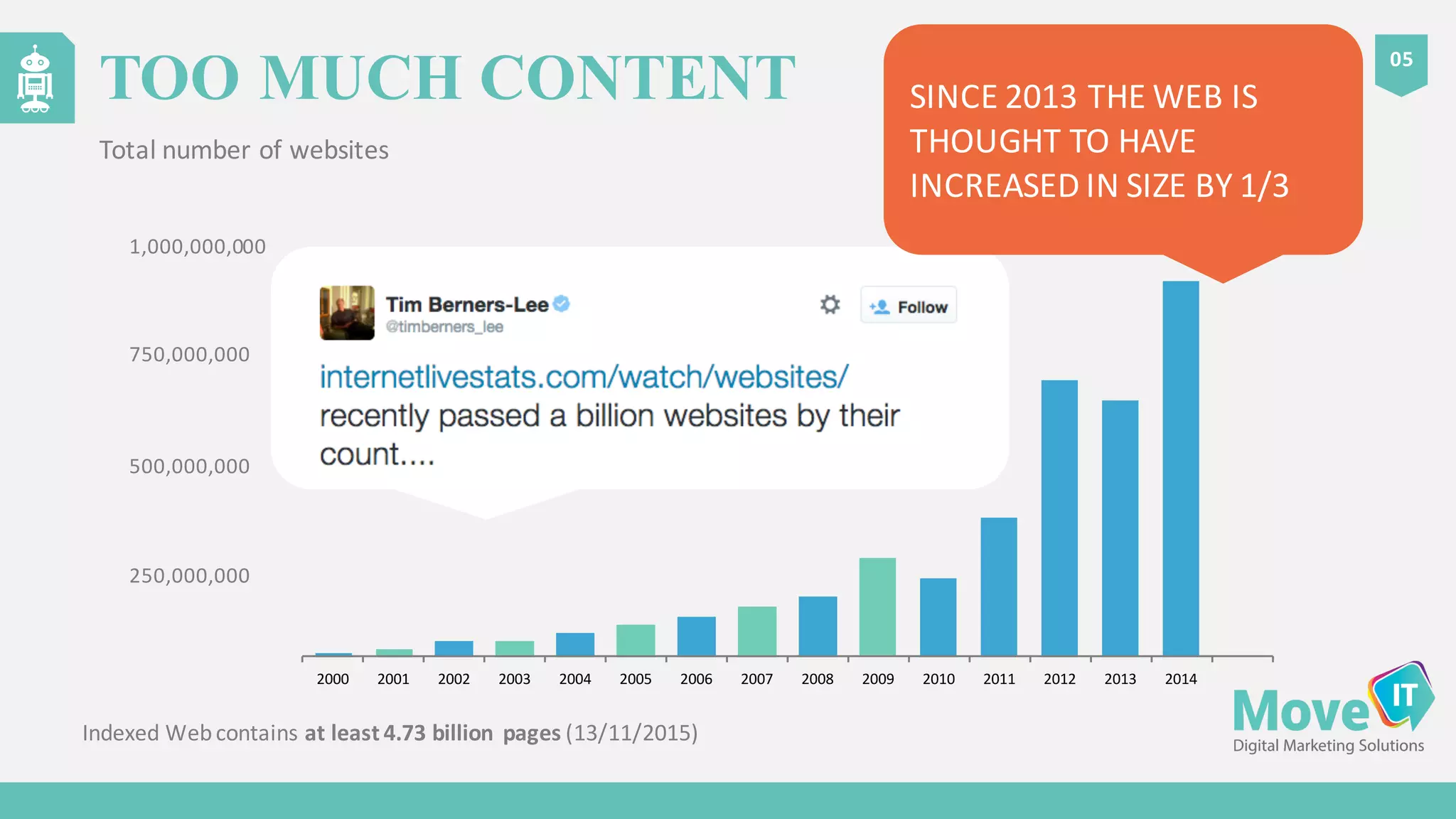
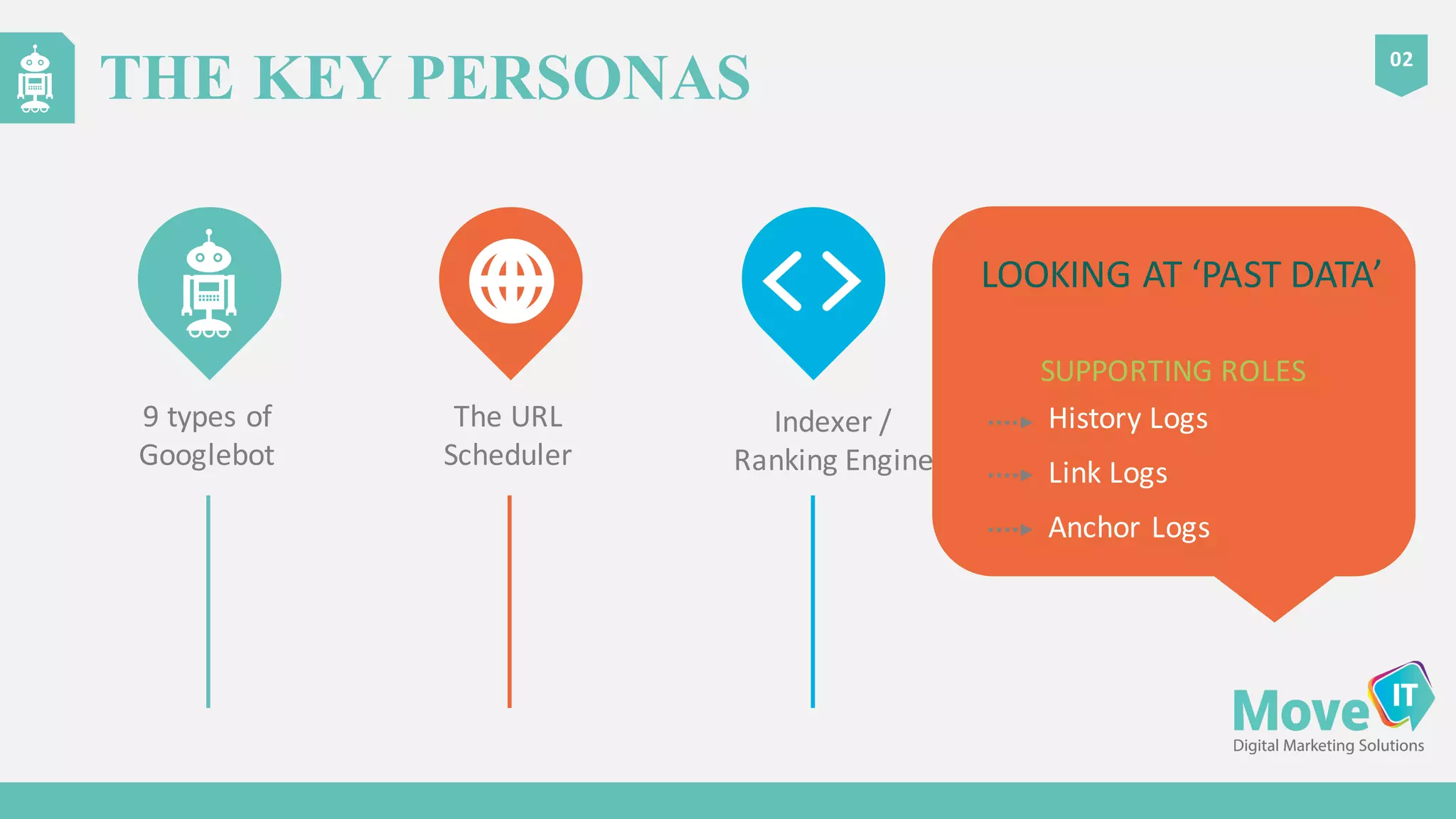
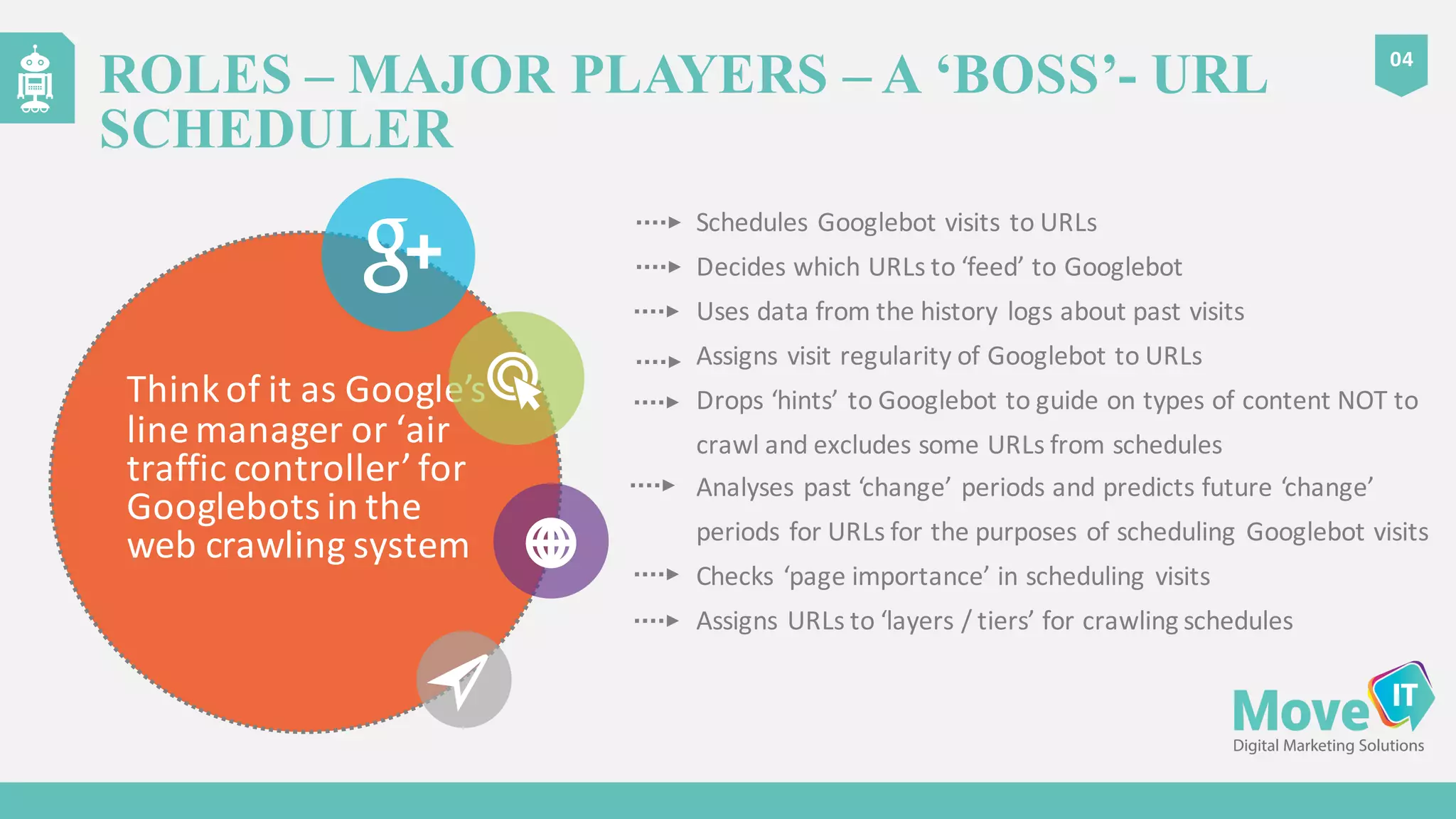
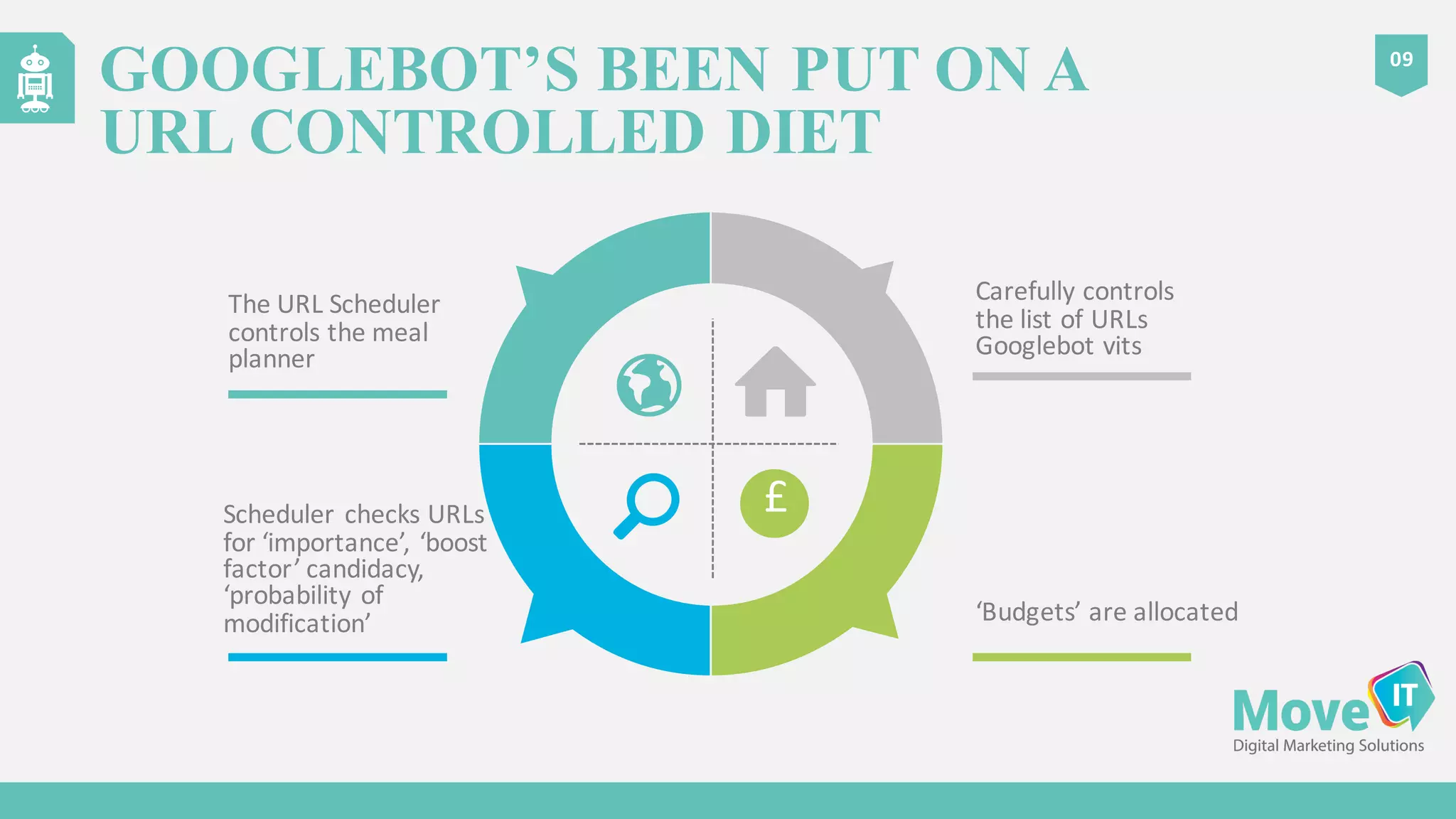
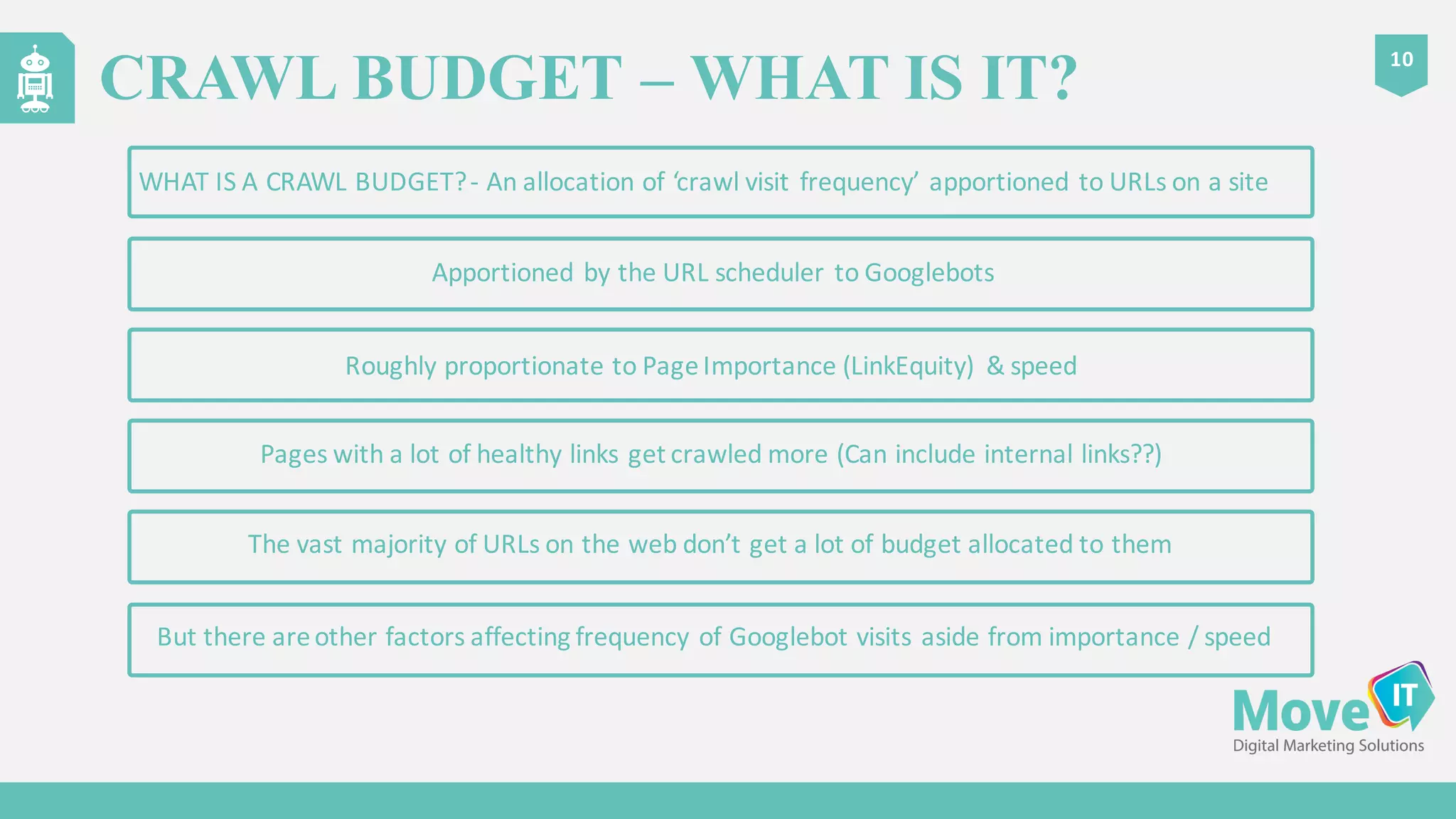
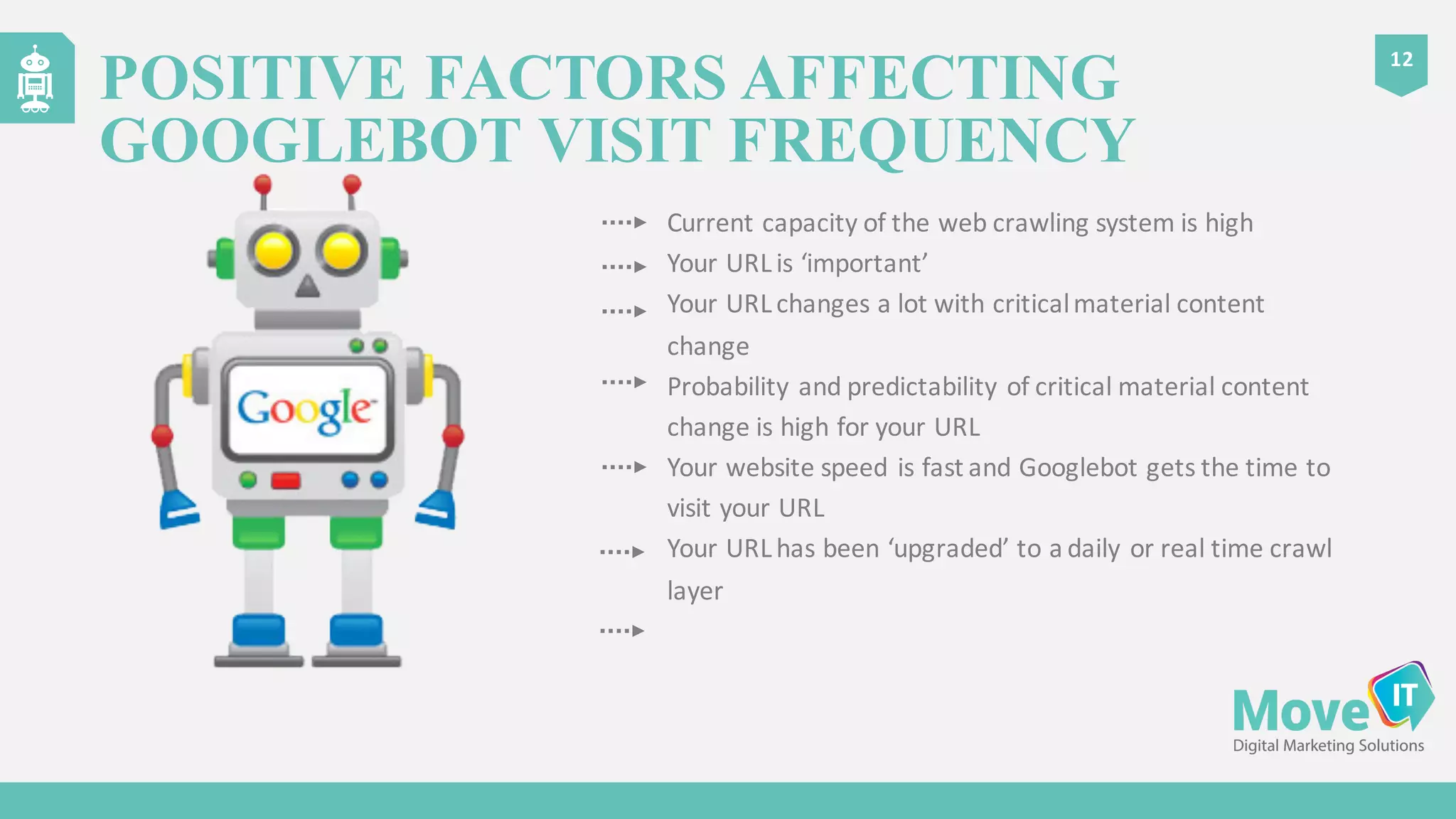
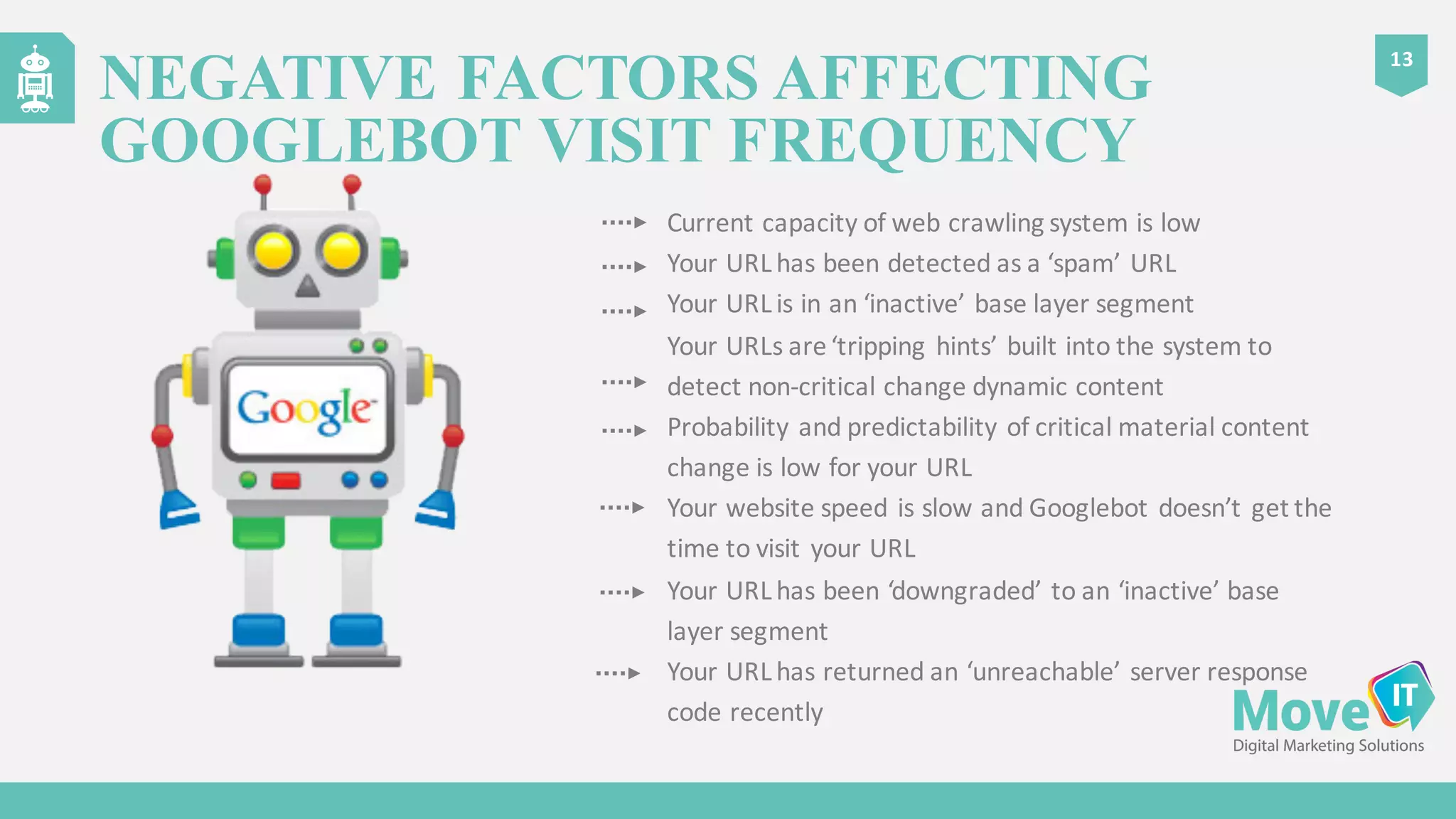
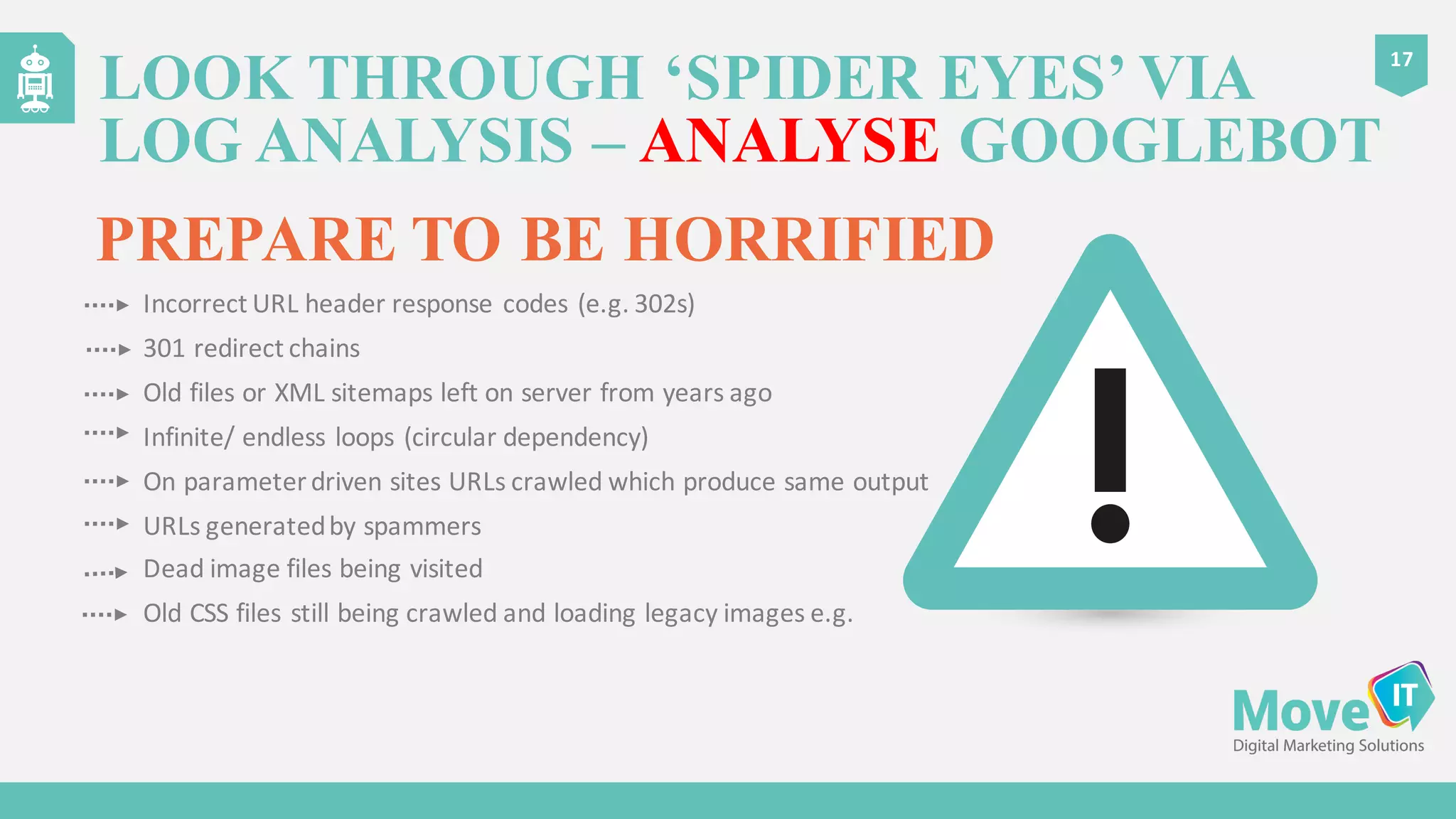
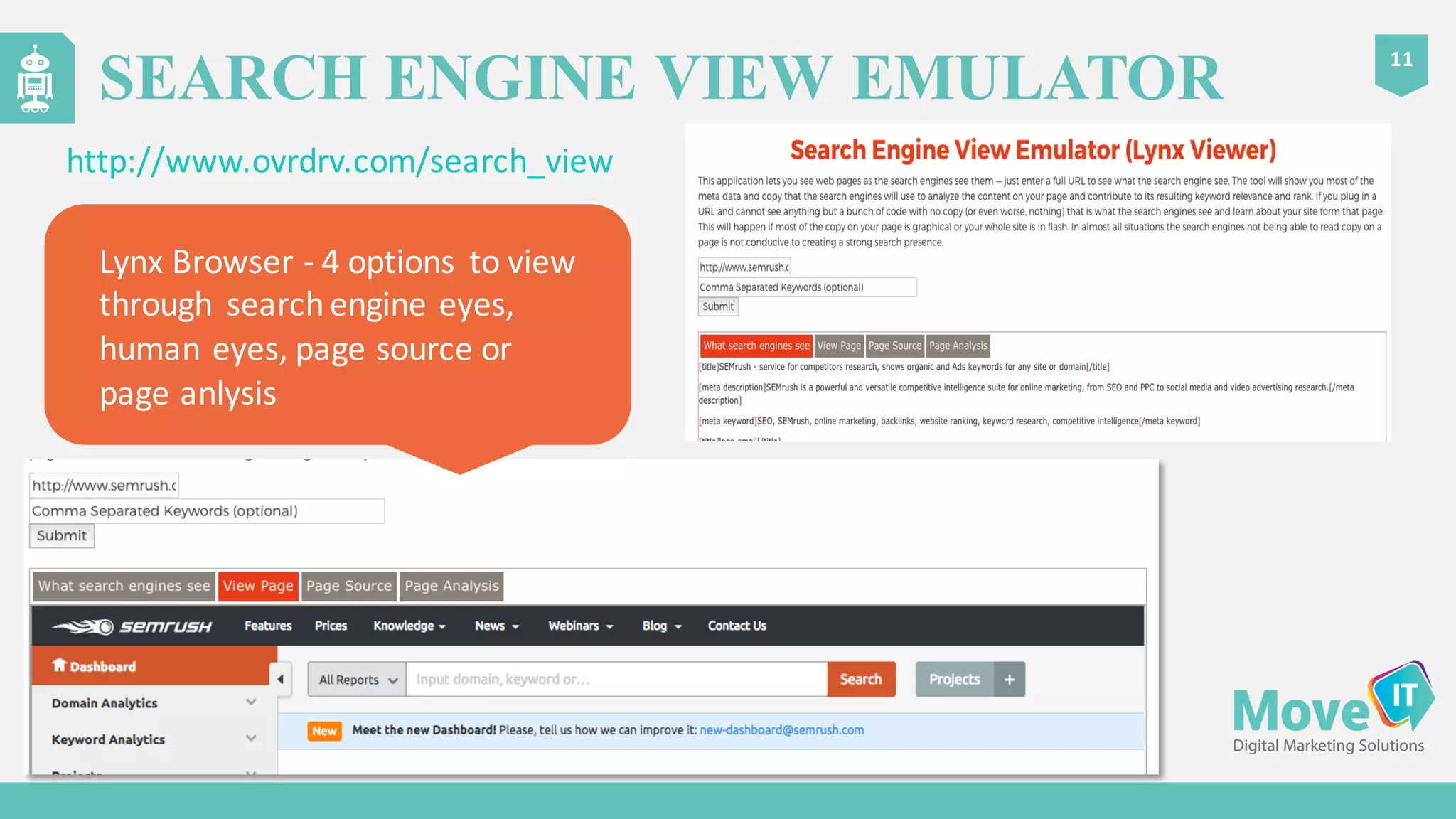
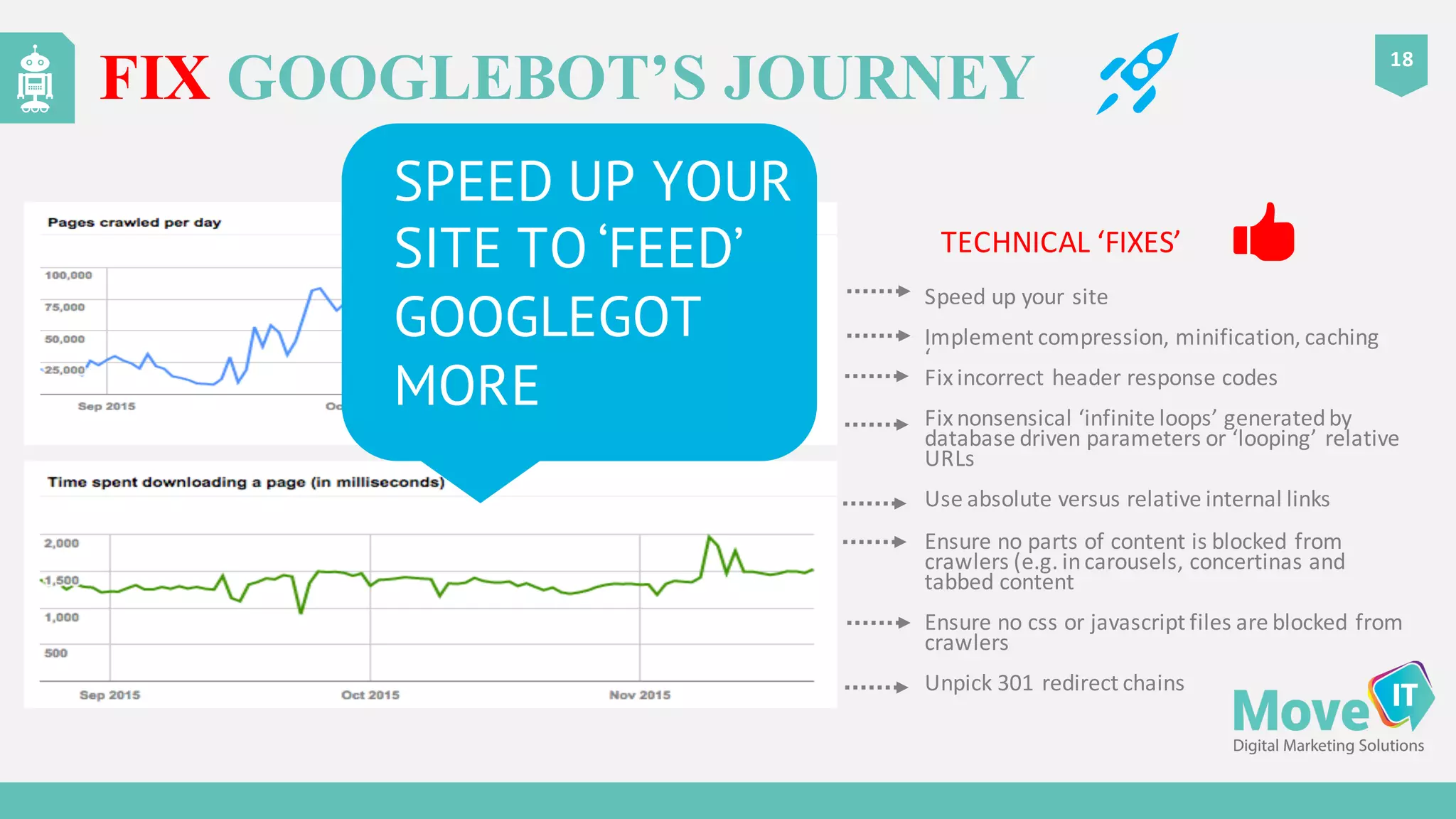
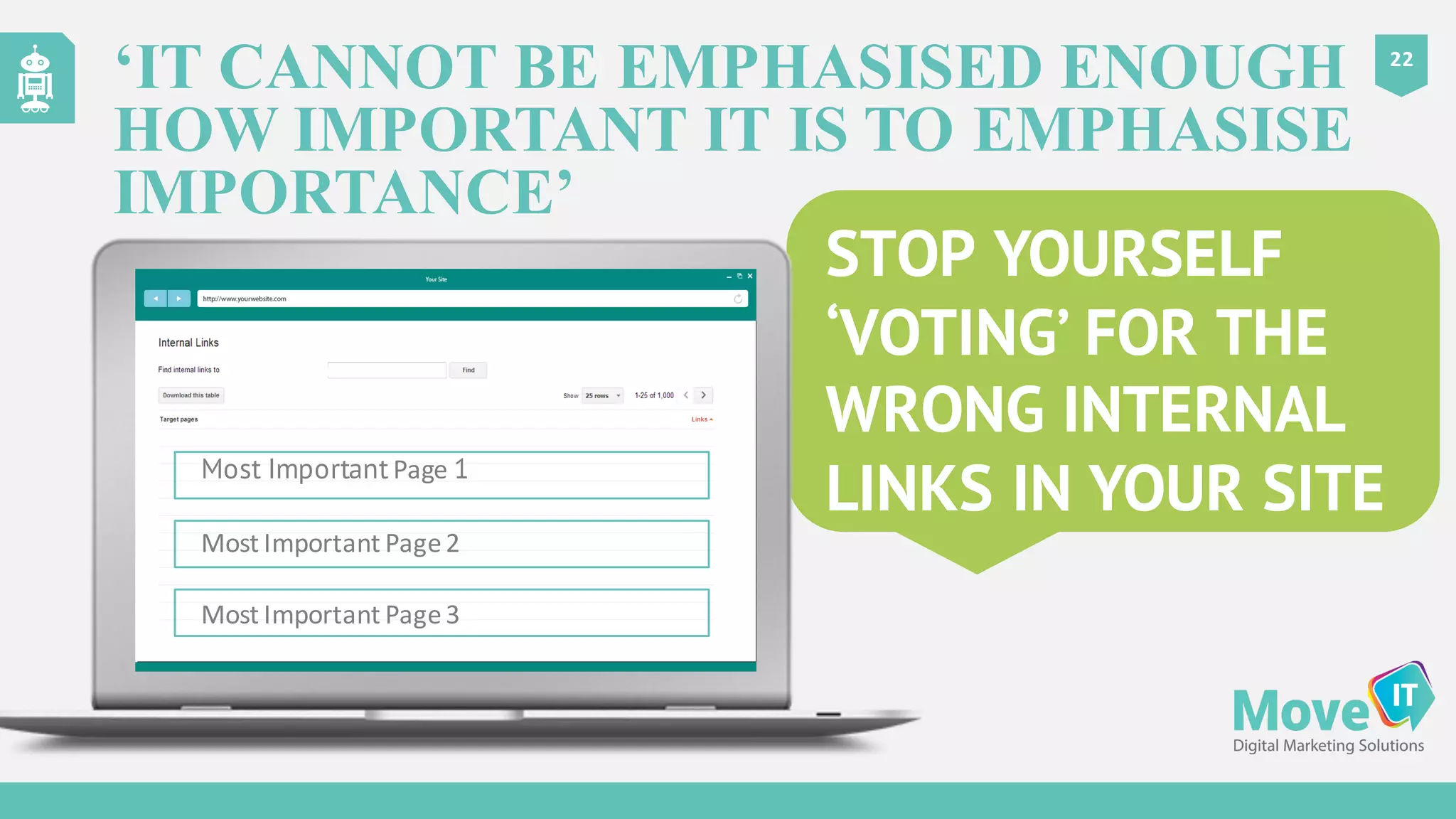
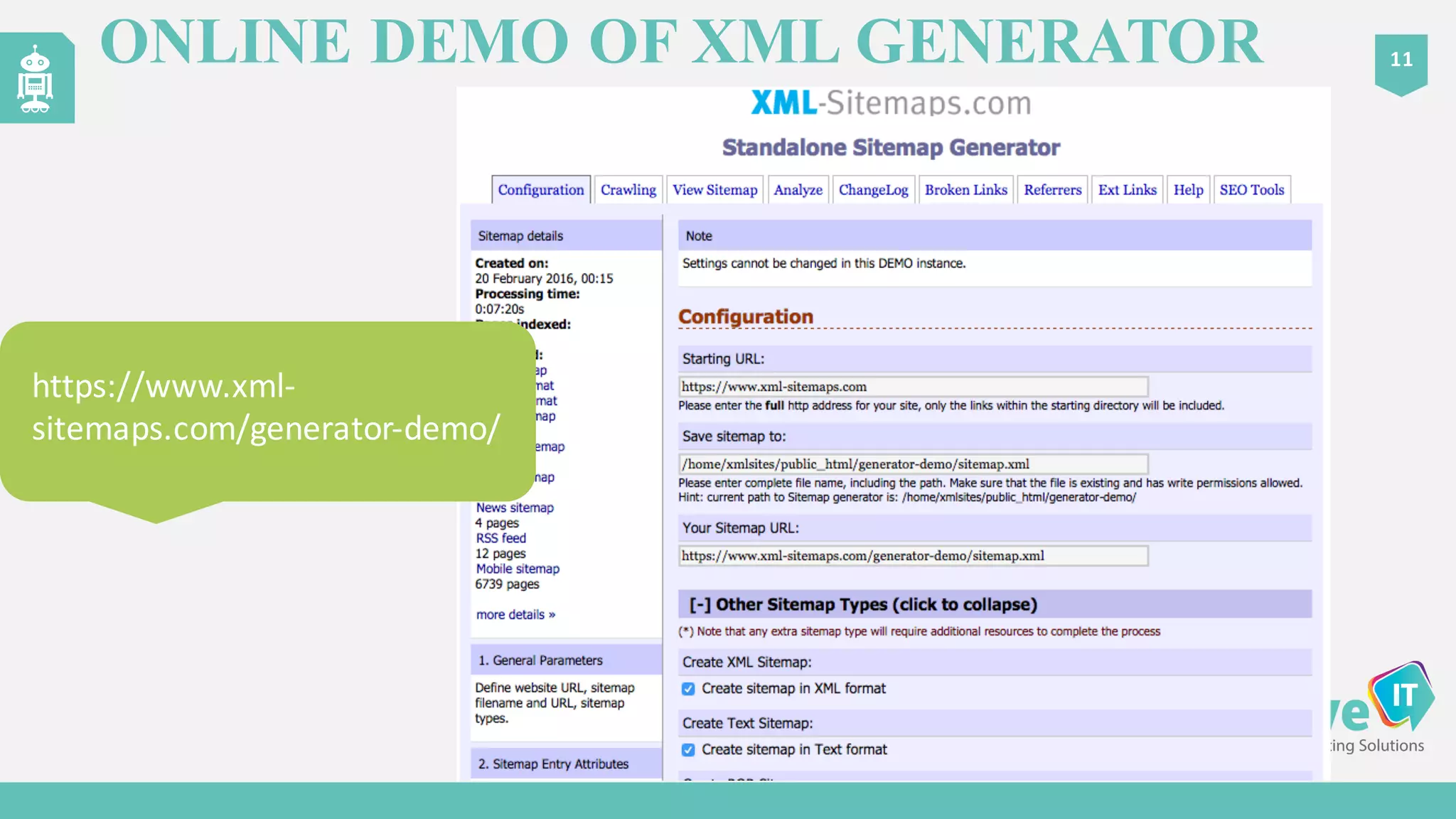
The document discusses the complexities of Google's web crawling process, highlighting the various roles of Googlebot and the URL scheduler in prioritizing and managing the crawling of web pages. It explains factors affecting crawlers' visit frequency, emphasizing the importance of URL significance, site speed, and avoiding unnecessary redirects. Additionally, it provides strategies for optimizing site performance to enhance crawl effectiveness, including the use of XML sitemaps and server log analysis.