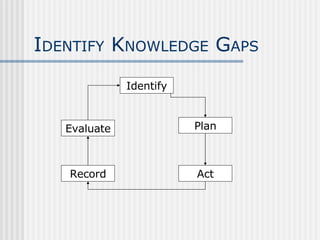
This document provides guidance on how to effectively manage projects. It discusses identifying knowledge gaps, features of successful projects, organizational structure, stages of a project, and things that can go wrong. The key points are:
1. Successful projects have clear goals agreed upon by stakeholders, sufficient resources, and an organizational structure with the right technical capabilities.
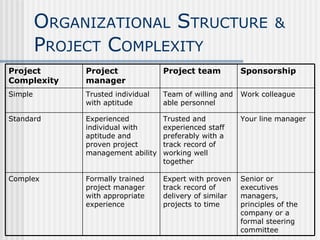
2. There are three main roles in project management - sponsor, project manager, and team members. The project manager is responsible for day-to-day operations while ensuring proper communication, problem-solving, and planning.
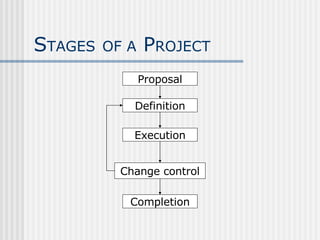
3. Projects go through stages of proposal, definition, execution, change control, and completion. The definition stage establishes objectives, plans, and responsibilities
![H OW TO M ANAGE P ROJECTS E FFECTIVELY Prepared by: Ronak Butala Management Trainee iCubix Infotech Ltd [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/how-to-manage-projects-effectively-119706410439382-2/75/How-To-Manage-Projects-Effectively-1-2048.jpg)