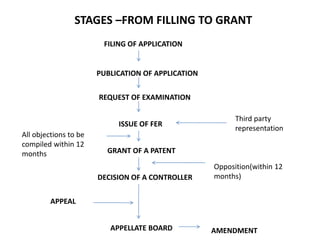
This document provides an overview of the Indian patent system. It defines what a patent is, describes the different types of patents, and outlines the patent application and examination process. Key points include that patents in India are governed by the Patents Act of 1970 and provide 20 years of exclusivity, and that applications undergo formality examination, publication, request for examination, issuance of an examination report, opportunities for opposition, and potential grant of a patent. The rights of patent holders and processes for infringement, licensing, and renewal are also summarized.