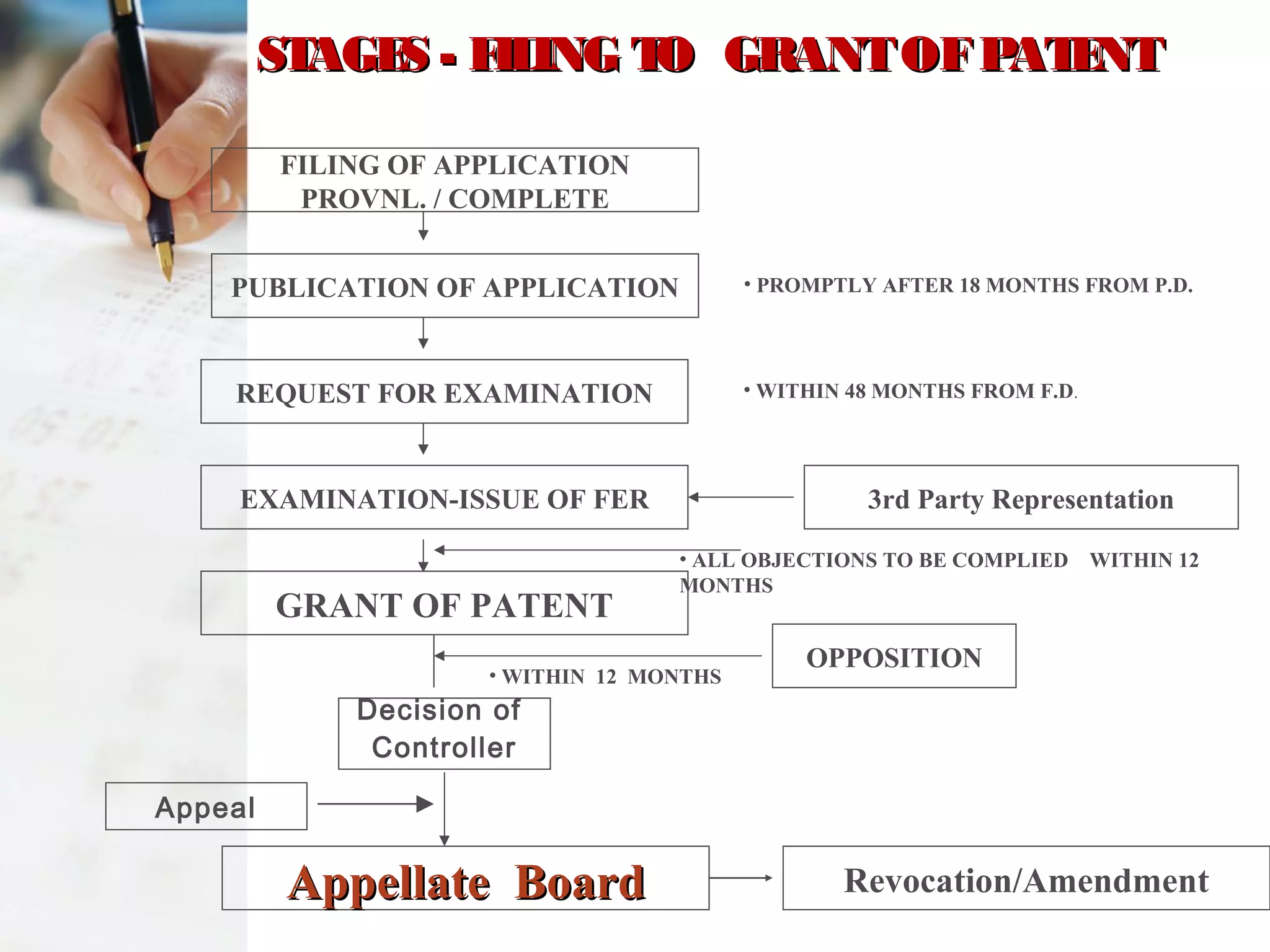
The document discusses the Indian Patent Act of 1970. It provides an overview of the history and types of patents granted under the Act, including ordinary patents, patents of addition, and patents of convention. It describes the patent application process, including formalities checks, publication, requests for examination, opposition proceedings, renewal fees, and rights of a patentee. The key stages from filing a patent application to grant of a patent are outlined.








































![Renewal Fee
• To bepaid within 3+6 monthsfrom dateof
recording in theregister [sec 142 (4) ]
• No feefor 1st
and 2nd
year
• Renewal fee, on yearly basis, isrequired to bepaid
for 3rd
to 20th
for keeping thepatent in force
• Delay upto six monthsfrom duedatepermissibleon
payment of feefor extension of time
• Patent lapsesif renewal feeisnot paid within the
prescribed period](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indianpatentactppt-170809072808/75/Indian-patent-act-ppt-42-2048.jpg)

